BUDGET PUSH FOR INFRASTRUCTURE
Why in the News?
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman’s Budget for 2024-25 allocates ₹11.8 lakh crore for capital expenditure, comprising 3.3% of GDP, aimed at boosting state spending on infrastructure.
- States will receive ₹1.5 lakh crore as long-term interest-free loans for infrastructure development.
Source:FortuneIndia
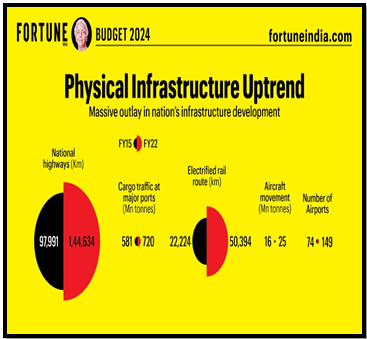
Sectors in Focus
- Transport: The transport sector’s allocation forms the bulk of infrastructure expenditure at 11.29%, with the Ministry of Roads, Transport, and Highways receiving ₹2.7 lakh crore.
- Railways: The outlay continues to be over 3%, with a record allocation of over ₹2.55 lakh crore, focusing on projects like automatic train protection systems.
- Power: Marginal improvement in allocations.
- Aviation and Shipping: The Ministry of Civil Aviation saw a 21% decline in allocation, while the shipping sector’s budget stagnated.
Challenges and Private Sector Reluctance
- Roads: Despite the expansion of the national highway network, profitability of new agreements remains untested, with a need to shift focus from asset creation to maintenance and safety.
- Railways: Challenges include skewed freight movement, delay in infrastructure provision, and need for efficient freight vehicle operations.
- Shipping and Airports: The need for a plan to develop underutilized ports and the privatization of additional airports are crucial.
- Private Investment: Market risks and project delays impact returns, leading to reluctance in private sector investments.
Government Schemes for Infrastructure Development in India
Associated Article: |