BRACE FOR STRONGER INFLATION AND CENTRAL BANK RISKS
Syllabus:
GS 3:
- Effects of Liberalization on the Economy, Changes in Industrial Policy and their Effects on Industrial Growth
- Growth, Development and Employment.
Focus:
The evolving landscape of global economics and technological advancements, particularly in AI and automation, has spurred discussions on their impact on inflation and central bank policies. These factors highlight the need for adaptive strategies to navigate future economic challenges effectively.
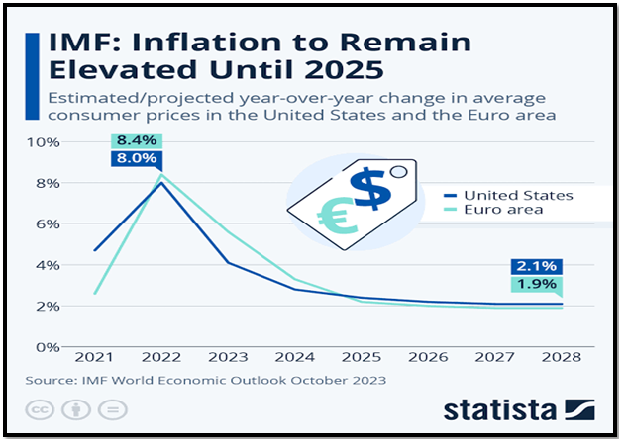
Source: Statista
Current Economic and Political Landscape:
- Changing Political Landscape: Significant political shifts globally, driven by factors like societal aging, climate change, and technological advancements, are likely to influence policy directions.
- Pressure on Central Banks: Central banks will face mounting pressures from various quarters, including demands for increased fiscal spending and rising debt levels across many countries.
- Impact of Fiscal Policy: Radical political agendas often prioritize expansive fiscal policies, necessitating substantial increases in government spending across sectors like military, education, and climate-related initiatives.
- Debt Sustainability Concerns: Real interest rates are expected to revert to historical norms, potentially straining government budgets with higher debt service costs.
- Central Bank Dilemma: Balancing fiscal expansion with monetary policy tightening poses challenges for central banks already managing high debt levels and economic uncertainty.
- Risk of Fiscal Dominance: There is a growing concern that fiscal priorities and debt levels may overshadow traditional monetary policy autonomy, a phenomenon known as ‘fiscal dominance.’
Demographic Trends and Economic Impacts
- Labour Force Dynamics: With aging populations and shrinking working-age demographics, economies may experience slower growth and increased spending on elder care, potentially driving inflation.
- Immigration and Labor Supply: While some argue aging populations could see increased savings and potential immigration benefits, resistance to immigration in many countries may limit these benefits.
- Inflationary Pressures: Demographic shifts and labor shortages could lead to wage inflation, further impacting overall inflationary trends in economies.
- Trade Protectionism: Global trends towards protectionism, exemplified by policies like tariffs, are likely to increase the costs of foreign goods, potentially fueling inflationary pressures.
- Impact on Import Prices: Sudden tariff implementations could lead to immediate inflation spikes, complicating central banks’ efforts to stabilize inflation through monetary policy.
- Long-term Effects of Protectionism: Gradual adjustments in import prices and reduced consumer demand could mitigate inflationary impacts over time, depending on how protectionist policies unfold.
Global Economic Interdependence
- Trade Network Impacts: Complex global supply chains and trade agreements influence pricing dynamics, affecting inflation rates in interconnected economies.
- Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rate variations impact import costs and export competitiveness, influencing inflation trends globally.
- Policy Coordination: Coordinated monetary policies among major economies can stabilize global inflation expectations and financial markets.
- Commodity Price Influence: Volatility in commodity prices, such as oil and metals, impacts inflation rates worldwide due to their essential role in production and consumption.
- Post-Pandemic Recovery: Divergent economic recovery paths post-pandemic affect global inflation dynamics, requiring tailored policy responses from central banks and policymakers.
- Regional Economic Integration: Collaborative efforts in regional economic blocs promote stability and resilience against global economic shocks, influencing inflation management strategies.
| Measures to Control Inflation in India
1. Monetary Policy Measures: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) uses tools like repo rate, reverse repo rate, and cash reserve ratio (CRR) to regulate money supply and credit availability, thereby influencing inflation. 2. Fiscal Policy Adjustments: Government adjusts fiscal measures such as taxation, subsidies, and public spending to manage aggregate demand and curb inflationary pressures. 3. Buffer Stock Operations: Government maintains buffer stocks of essential commodities like food grains to stabilize prices through procurement and release operations. 4. Price Stabilization Fund: Establishing funds to intervene in markets during price spikes, particularly for perishable goods and essential commodities. 5. Supply-side Interventions: Enhancing agricultural productivity, storage infrastructure, and logistics to reduce supply constraints and mitigate price volatility. 6. Monetary Policy Committee (MPC): Formed under the RBI Act to set inflation targets and implement policies aimed at achieving price stability. 7. Public Distribution System (PDS): Subsidized distribution of essential commodities through fair price shops to ensure availability at affordable prices for vulnerable sections of society. 8. Regulatory Measures: Monitoring and regulating markets to prevent hoarding, speculative activities, and cartelization that can artificially inflate prices. |
Challenges of Deglobalization and Green Transition
- Monopoly Profits and Inflation: Reduced competition from deglobalization may increase monopoly profits, prompting central banks to consider inflationary measures to counterbalance economic inequalities.
- Union Power Dynamics: Conversely, increased union power in a deglobalized scenario could mitigate inflationary pressures by advocating for fairer wealth distribution.
- Green Regulation Costs: Green regulations imposing higher costs on traditional energy sources could escalate production expenses, potentially translating into higher consumer prices.
- Central Banks’ Green Agenda: Central banks focused on green initiatives may tolerate higher inflation temporarily to facilitate the transition towards renewable energy and sustainable practices.
- Technological Advances and Productivity: Despite inflationary concerns, advancements in technologies like AI could enhance productivity, easing inflationary pressures in the long term.
- Risk to Central Bank Independence: Political shifts towards radical policies, such as anti-immigration measures or unrestrained spending, could compromise central bank independence, historically linked with inflationary consequences.
Way Forward:
- Balanced Policy Approach: Governments must adopt a balanced approach, promoting fiscal prudence while ensuring monetary policy autonomy to mitigate inflationary pressures.
- Investment in Future Skills: Prioritize investment in education and skills development to meet the demands of technological advancements and enhance productivity.
- Green Transition Support: Central banks should support the transition to a green economy by incentivizing renewable energy investments and sustainable practices.
- Labor Market Reforms: Implement flexible labor market reforms to address demographic shifts and mitigate wage inflation while supporting workforce participation.
- International Cooperation: Foster international collaboration to manage global trade tensions and ensure stable supply chains, reducing dependency on protectionist measures.
- Technological Integration: Embrace AI and digital technologies to enhance productivity, lower production costs, and ease inflationary pressures over the long term.
- Transparent Policy Communication: Central banks and governments should communicate transparently about policy decisions to enhance market confidence and predictability.
- Long-term Planning: Develop and implement long-term economic strategies that prioritize stability, sustainability, and inclusive growth to navigate future uncertainties effectively.
Conclusion
In navigating these complexities, policymakers must balance embracing technological progress with ensuring inclusive economic growth and stability. Collaborative global efforts and proactive policy measures will be crucial in managing inflationary risks while harnessing the potential of advanced technologies for sustainable development.
Source:The Mint
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the impact of technological advancements such as AI and automation on global inflation trends. What strategies should governments adopt to manage inflation effectively while promoting economic growth and inclusivity?
Associated Article:
https://universalinstitutions.com/economic-growth-and-development/