Biotransformation Technology
Context: A UK-based startup, based at Imperial College in London, claims to have developed a technology that could alter the state of plastics and make them biodegradable. The company calls the process “biotransformation”. It claims the technology would digest the plastic packaging waste naturally with the help of microbes and biodegrade the waste without leaving behind any microplastics.
What is Biotransformation technology?
- Biotransformation technology is a novel approach to ensure plastics that escape refuse streams are processed efficiently and broken down.
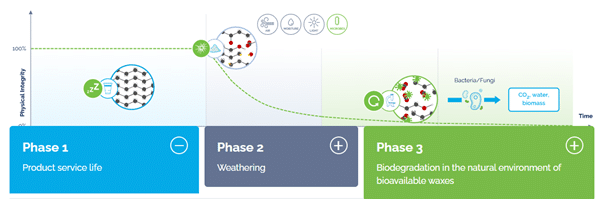
- Plastics made using this technology are given a pre-programmed time during which the manufactured material looks and feels like conventional plastics without compromising on quality.
- This biotransformation technology is the world’s first that ensures polyolefins fully biodegrade in an open environment causing no micro plastics.
Stages of Biotransformation
- Once the product expires and is exposed to the external environment, it self-destructs and biotransforms into bioavailable wax.
- This wax is then consumed by microorganisms, converting waste into water, CO2, and biomass.
Need of Technology
- India is generating 3.5 billion kgs of plastic waste annually and that the per capita plastic waste generation has also doubled in the past five years.
- In 2019, plastic packaging waste from e-commerce firms was estimated at over a billion kilograms worldwide.
- A joint research project by the Department of Management Studies, IIT Delhi, and Sea Movement noted that Amazon generated nearly 210 million kgs (465 million pounds) of plastic from packaging waste in 2019.
- They also estimated that up to 10 million kgs (22.44 million pounds) of Amazon’s plastic packaging ended up in the world’s freshwater and marine ecosystems as pollution in the same year.
- However, Amazon India has now eliminated the single-use plastics across its fulfilment centers. Flipkart has also done the same in 2021 across its supply chain.
Where can this technology be used?
- Food packaging and health care industries are the two prime sectors that could use this technology to reduce waste.
- The increase in cost is relatively small compared to conventional plastic that does not contain” this technology.
Is this being used in India?
- Some well-known Indian firms in food and packaging industries deploy such technologies.
- Within healthcare and pharma industries, this technology provides biodegradable solutions for non-woven hygiene products like diapers, sanitary napkins, facial pads, etc.
Other steps
- The Indian government has launched multiple initiatives to move the country towards sustainability.
- They introduced a plastic waste management gazette to help tackle the ever-growing plastic pollution caused by single-use plastics.
- Last year, the Indian government imposed a ban on single-use plastics to bring a stop to its use in the country.
- The National Dashboard on Elimination of Single Use Plastic and Plastic Waste Management brings all stakeholders together to track the progress made in eliminating single-use plastic and effectively managing such waste.
- An Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) portal helps in improving accountability, traceability, and facilitating ease of compliance reporting in relation to EPR obligations of the producers, importers and brand-owners.
- India has also developed a mobile app to report single use plastics grievances to check sale, usage or manufacturing of single use plastics in their area.
What are the alternatives to reducing plastic waste?
- A switch to jute or paper-based packaging could potentially cut down plastic waste.
- This could also build sustainability within the paper industry, and save on the import bill on ethylene solutions.
- The wooden packaging is yet another alternative, but that will make the packaging bulkier and increase cost.
- The Government of Tamil Nadu, in Chennai, organised National Expo and Conference of Startups to raise awareness on alternatives to single-use plastics. The alternatives showcased were made using coir, bagasse, rice and wheat bran, plant and agricultural residue, banana and areca leaves, jute and cloth.
| Practice Question
1. What is Biotransformation Technology? How can it help in plastics waste reduction? |