BHUTAN’S OPENING MOVE, ITS GELEPHU GAMBIT
Syllabus:
GS 2:
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Focus:
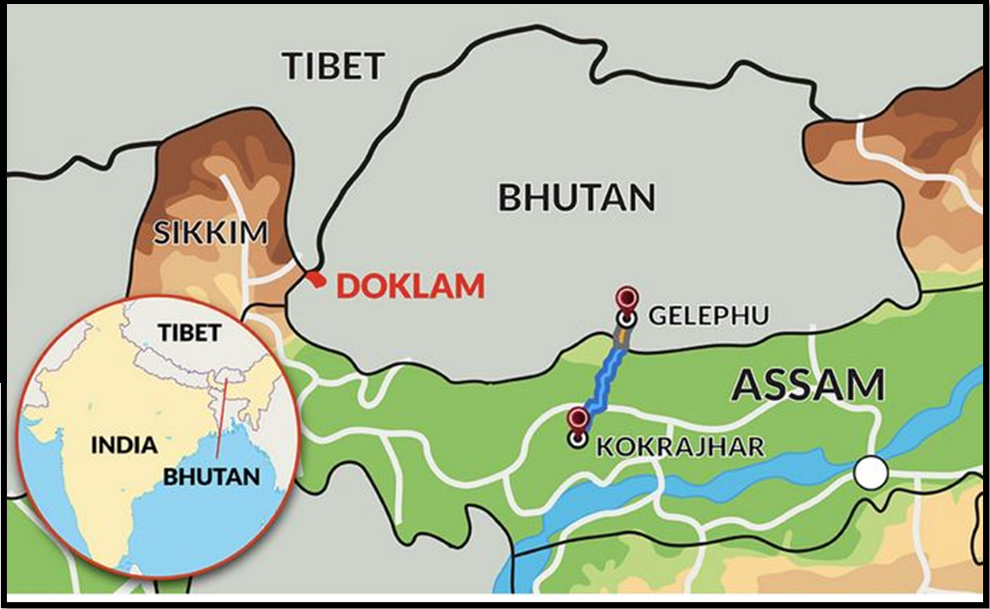
- Bhutan is focusing on creating a regional economic hub in Gelephu, bordering Assam, India.
Source:- Hindu
Overview
- Bhutan is focusing on creating a regional economic hub in Gelephu, bordering Assam, India.
- The initiative, called “Gelephu Mindfulness City” (GMC), aims to spread across 1,000 sq km as a carbon-neutral city with non-polluting industries.
- Gelephu is envisioned to serve as an investment, health, and wellness hub, drawing comparisons to cities like Neom and Nusantara rather than traditional financial centers.
- This project aligns with India’s “Act East” connectivity plans and seeks to enhance regional connectivity.
Challenges and Considerations
- Gelephu’s geography poses natural challenges, including high rainfall and proximity to wildlife corridors.
- Security concerns stem from insurgencies in neighboring areas and reliance on India for trade and transport infrastructure.
- The project necessitates significant support from India, given Bhutan’s limited access and geopolitical considerations.
Bhutan’s Motivations
- Economic diversification beyond hydropower and tourism, with a focus on sustainable development.
- Addressing youth outmigration and geopolitical pressures, particularly from China.
- Expanding Gelephu’s airport to international standards, requiring Indian expertise and investment.
Regional Implications for India
- Strengthening ties with Bhutan amidst concerns over China’s influence in the region.
- India’s investment in infrastructure projects in Bhutan aligns with broader regional connectivity and energy plans.
- Potential to recast regional dynamics, supporting South Asian integration and addressing global geopolitical challenges.
Strategic Importance
- Bhutan acts as a crucial buffer state between India and China, enhancing India’s security.
- India supports Bhutan with defense, infrastructure, and communication aid, ensuring Bhutan’s sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- India contributes to Bhutan’s border infrastructure development, bolstering its defense capabilities.
- During the 2017 Doklam standoff, Bhutan allowed Indian troops to counter Chinese advancements.
India – Bhutan
Economic Importance
- India is Bhutan’s primary trading partner and the main destination for its exports.
- India aids in developing Bhutan’s hydropower sector, a major revenue source for Bhutan.
- Bhutan benefits from Indian financial assistance for its development initiatives.
Cultural Importance
- Both nations share deep Buddhist cultural ties.
- India aids Bhutan in preserving its cultural heritage and is a popular destination for Bhutanese students seeking higher education.
Environmental Importance
- Bhutan’s commitment to carbon neutrality is supported by India through partnerships in renewable energy, forest conservation, and sustainable tourism initiatives.
Potential Impact
- While the GMC faces considerable challenges, it represents a significant opportunity for Bhutan and the region.
- The project aligns with global trends towards sustainable, mindful urban development and could set a precedent for regional cooperation.
- Success would require overcoming natural, security, and geopolitical hurdles, with India playing a pivotal role.
Key Highlights of the Gelephu Smart City Project
- Economic Integration: Aims to create an economic corridor connecting South Asia with Southeast Asia, utilizing India’s northeastern states.
- Environmental and Sustainable Goals: Focuses on environmental standards and sustainability to attract quality investment from internationally screened companies.
- Industry Focus: Includes zero emission industries and leverages Bhutan’s strengths in tourism and wellness, alongside infrastructure companies.
- Special Administrative Region: Will operate under unique laws to enhance international investment opportunities.
- Regional Impact: Seen as a pivotal transformation point for both Bhutan and the broader South Asian region.
- India-Bhutan Railway Line: The Government of India commits to constructing the first railway line to Gelephu, enhancing connectivity.
- Expanded Access: The railway will link to roadways and trading points in Assam and West Bengal, opening pathways to Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia, and Singapore.
| Bhutan
General Information
Rivers
Government
|
Source:
The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
“Assess the strategic significance of Bhutan’s Gelephu initiative for India and the broader South Asian region. Discuss the potential challenges and opportunities it presents, considering geopolitical, economic, and environmental factors.”