ASSESSING LGBTQIA+ COMMUNITIES’ RIGHTS AT THE END OF PRIDE MONTH
Syllabus:
GS 1: Salient features of Indian Society. And Social Empowerment
GS 2: Welfare Schemes for Vulnerable Sections of the population
Focus:
- The Supreme Court of India’s recent rejection of same-sex unions has brought the focus back to the legal struggles and societal challenges faced by LGBTQIA+ communities, highlighting the need for continued advocacy and reforms to achieve true equality and acceptance.
Legal Status and Recognition
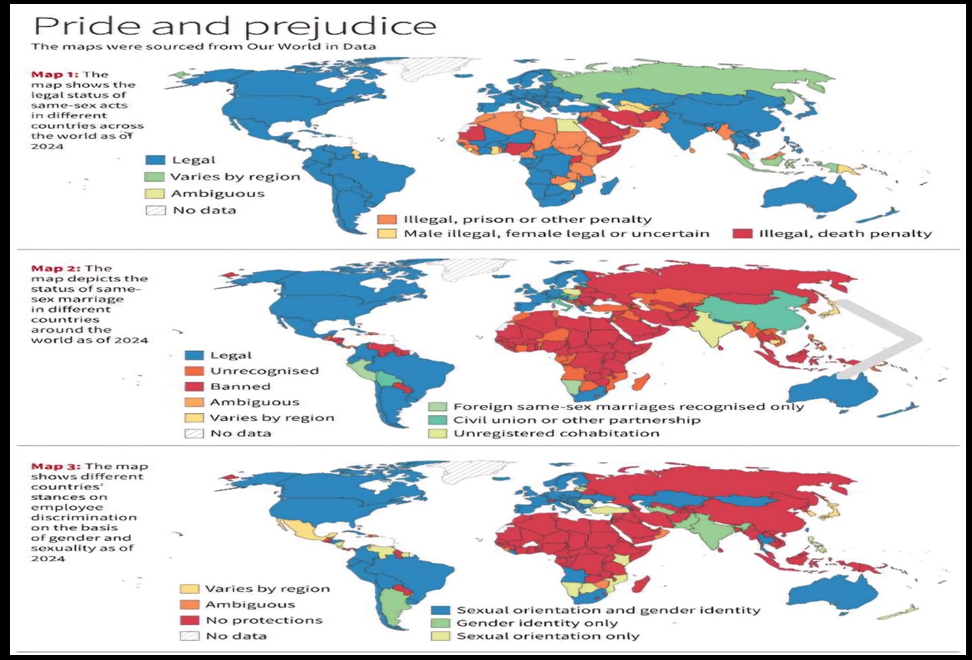
- Post-Section 377: While India decriminalized homosexuality in 2018, legal recognition of same-sex unions remains unaddressed.
- Global Comparison: Globally, 59 countries criminalize queer expressions, with severe penalties like imprisonment or death in some.
- Marriage Rights: Despite global variations, 37 countries fully recognize same-sex marriage, whereas India acknowledges no legal framework.
- Ambiguous Recognition: India leaves the status of LGBTQIA+ communities ambiguous, with some provisions for civil unions but no legal marriage recognition.
- Legal Discrimination: Discrimination persists despite legal decriminalization, affecting access to legal protections and societal inclusion.
Employment and Legal Protections
- Transgender Rights: The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019, addresses discrimination but lacks specific protections based on sexual orientation.
- Legal Aid: India offers legal aid based on gender identity but lacks similar provisions for discrimination based on sexual orientation.
- Global Standards: Legal protections for queer employees vary globally, with 27 countries offering specific protections based on sexual orientation.
- Employee Discrimination: In India, discrimination based on gender identity is prohibited, but protections for sexual orientation are not guaranteed.
- Parental Recognition: LGBTQIA+ individuals in India face barriers in co-parenting rights, contrasting with global norms where 39 countries allow same-sex adoption.
Challenges and Struggles
- Continued Struggles: Despite legal milestones, LGBTQIA+ communities in India fight for constitutional rights, societal acceptance, and workplace equality.
- Family and Social Acceptance: Many queer individuals in India confront challenges in gaining familial acceptance and societal recognition.
- Workplace Equality: Achieving growth and equality in professional environments remains a significant challenge for LGBTQIA+ individuals.
- Legal Recognition: Lack of legal frameworks for registering sexuality hinders LGBTQIA+ communities’ rights and protections.
- Inclusive Society: India’s LGBTQIA+ communities strive for broader inclusion and justice in everyday interactions and legal frameworks.
Socio-Cultural Challenges and Community Support
- Social Stigma and Discrimination: Addressing societal stigma and discrimination faced by LGBTQIA+ individuals in various aspects of life.
- Family Acceptance Programs: Programs and initiatives aimed at fostering acceptance and support within families of LGBTQIA+ individuals.
- Community Outreach: Outreach programs to build solidarity within the LGBTQIA+ community and provide support networks for marginalized individuals.
- Educational Initiatives: Promoting inclusive education and awareness in schools and colleges to combat prejudice and promote acceptance.
- Cultural Sensitization: Initiatives to sensitize cultural and religious communities about LGBTQIA+ issues and foster dialogue towards acceptance and inclusion
Legal Reforms and Advocacy Efforts
- Campaigns for Legal Recognition: Ongoing campaigns and legal challenges aimed at achieving legal recognition of same-sex marriages and civil unions in India.
- Policy Advocacy: Advocacy efforts directed towards policymakers to amend existing laws and introduce new legislation to protect LGBTQIA+ rights.
- Judicial Interventions: Strategic litigation and court interventions to secure legal protections against discrimination based on sexual orientation.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educational campaigns to raise public awareness about the importance of legal reforms for LGBTQIA+ equality.
- International Engagement: Engaging with international human rights bodies and organizations to leverage global support for legal reforms in India.
History of Recognition of LGBTQIA+ in India
|
Way Forward
- Legal Reforms: Advocate for comprehensive legal recognition of same-sex marriages and civil unions in India.
- Policy Implementation: Ensure the effective implementation of existing anti-discrimination laws, particularly for sexual orientation.
- Educational Programs: Integrate LGBTQIA+ issues into school curriculums to foster early acceptance and understanding.
- Public Awareness: Launch nationwide campaigns to combat stigma and raise awareness about LGBTQIA+ rights and issues.
- Judicial Support: Encourage judicial activism to protect and expand the rights of LGBTQIA+ individuals.
- Family Counseling: Provide resources and counseling to families to support acceptance of LGBTQIA+ members.
- Healthcare Access: Improve access to healthcare services tailored to the specific needs of LGBTQIA+ individuals.
- Community Networks: Strengthen community support networks to provide safe spaces and resources for LGBTQIA+ individuals.
Conclusion:
While decriminalization marked progress, achieving full equality for LGBTQIA+ individuals in India requires comprehensive legal reforms, societal acceptance, and robust support systems to combat discrimination and promote inclusivity.
Source: The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the impact of the decriminalization of Section 377 on the LGBTQIA+ communities in India. What further legal and social measures are needed to ensure equality and inclusivity for these communities?
Associated Articles: