ANALYZING INCOME INEQUALITY IN INDIA
Why in the News?
- India witnesses a significant 15% fall in income inequality over the last decade, according to the State Bank of India (SBI).
- The analysis primarily relies on taxpayer data, potentially excluding a majority of income-earners outside the tax net.
Source : TH
Outcomes of Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS):
- Nearly 80% earn below ₹2.5 lakh annually, challenging overall income assessment.
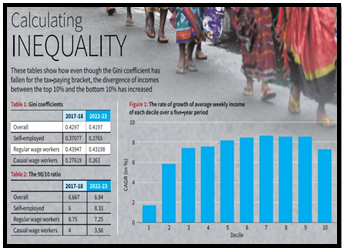
- Gini coefficient drops from 0.4297 in 2017-18 to 0.4197 in 2022-23, signalling reduced inequality.
- Despite the overall decline, a visible income polarization emerges, notably among self-employed workers.
- Top 10% of self-employed individuals experience significant income growth, intensifying polarization.
About Periodic Labour Force Survey :
- The NSO, under MoSPI, conducts the PLFS survey to gauge India’s employment and unemployment landscape.
- Launched in April 2017, the survey focuses on estimating key indicators like Worker Population Ratio, Labour Force Participation Rate, and Unemployment Rate.
- PLFS provides timely insights into the employment scenario, particularly in urban areas.
| Key Terms
Gini coefficient The Gini coefficient is a statistical measure representing the degree of income or wealth inequality within a population, ranging from 0 (perfect equality) to 1 (perfect inequality). |

 Source : TH
Source : TH

