Advanced Glycation End Products Linked to Rising Diabetes Rates
Why in the news?
A recent clinical trial highlights the role of AGEs in India’s diabetes surge, urging dietary changes to lower AGE intake and reduce inflammation and insulin resistance.
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) Overview:
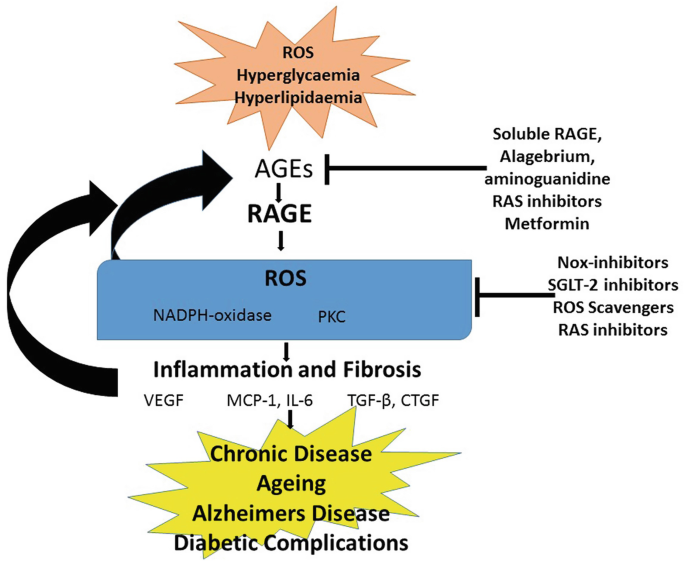
- Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) are harmful molecules formed when sugars react with fats or proteins.
- These compounds result from high-temperature cooking methods like frying, roasting, and grilling, and are also produced naturally in the body.
- A diet rich in AGEs, particularly from processed and fast foods, contributes to diabetes, especially in India.
Why AGEs Are Harmful:
- At high concentrations, AGEs damage cells and tissues by interacting with receptors on blood vessels and organs.
- AGEs can impact protein function, alter hormones and free radicals, and modify the extracellular matrix.
- This leads to chronic inflammatory diseases, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular issues, osteoporosis, and arthritis.
- Hyperglycemia, common in diabetes, accelerates AGE production and causes blood vessel damage.
Study Recommendations:
- A low-AGE diet is beneficial for overweight and obese individuals.
- Such a diet includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy, cooked by boiling or steaming.
- The study showed improved insulin sensitivity and reduced inflammation with a low-AGE diet.
- Insulin sensitivity refers to how efficiently cells respond to insulin for glucose uptake.
What are Lipids?
- Lipids are fatty or waxy chemical compounds in your body.
- They don’t dissolve in water and help with various body functions.
Examples of Lipids:
- Cholesterol: Assists in fat absorption, vitamin intake, and hormone production.
- HDL (High-Density Lipoproteins): Known as “good” cholesterol, removes cholesterol from arteries.
- LDL (Low-Density Lipoproteins): “Bad” cholesterol, can stick to artery walls and cause blockages.
- VLDL (Very Low-Density Lipoproteins): Transports triglycerides from the liver to cells.
Functions of Lipids:
- Triglycerides: Store and transport energy.
- Steroid Hormones: Send cellular messages.
- Bile Salts: Aid fat digestion.
- Phospholipids and Cholesterol: Form cell membranes.
Importance of Insulin Sensitivity
- Definition: Insulin sensitivity refers to how effectively cells respond to insulin for glucose uptake from blood.
- Health Benefits: A low-AGE diet improves insulin sensitivity, helping reduce diabetes risk and inflammation, supporting overall metabolic health.
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times