Aditya L1 Solar Mission.
Relevance:
- GS Paper – 3, Space Technology.
- Tags: #upsc #competitve-exams #Spacemission #AdityaL1 #solarmission.
Why in the news?
- India’s journey towards the sun began today from the Sathish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota. Aditya L1 to begin its 125-day journey to the sun from today. Aditya in Sanskrit means the Sun. L1 here refers to Lagrange Point 1 of the Sun-Earth system.
- Aditya-L1 is a satellite dedicated to the comprehensive study of the Sun. It has 7 distinct payloads developed, all developed indigenously. Five by ISRO and two by Indian academic institutes in collaboration with ISRO.
What is Aditya-L1 Mission?
- Aditya’sL1 mission is to study the solar winds and the Sun’s atmosphere. It carries seven payloads to observe the photosphere, chromosphere and the outermost layers of the Sun, the Corona.
- This will help understand the problems of coronal heating, Coronal mass ejection, pre-flare and flare activities, dynamics of weather and the study of the propagation of particles and fields in the interplanetary medium.
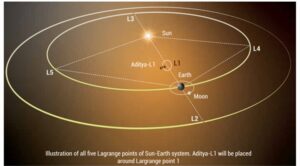
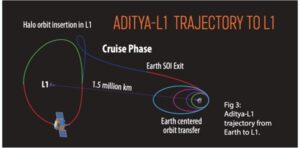
- Aditya-L1 will be placed 1.5-million-km from Earth in a halo orbit around the L1 point, which provides a greater advantages of observing the solar activities and its effect on space weather in real time.
- PSLV C 57 carrying Aditya L1 is the XL variant with longer strap on motors carrying higher fuel quantity.
- In a period of four months, Aditya L1 will reach the Lagrange 1 point.
The 7 payloads include
- Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC).
- Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS).
- Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT).
- Advanced Tri-axial High Resolution Digital Magnetometers.
- Aditya Solar wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX).
- High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS).
- Plasma Analyzer Package for Aditya (PAPA).
What is L1?
For common understanding, L1 is a location in space where the gravitational forces of two celestial bodies, such as the Sun and Earth, are in equilibrium. This allows an object placed there to remain relatively stable with respect to both celestial bodies.
Benefits of Aditya L1 Solar Mission
- The satellite will continue to observe the Sun without any occultation or eclipse due to its positioning in the unique point of L1. This will enable us to comprehend the Sun and how it affects Earth in a better way.
- The information acquired from the mission will help us better understand and predict space weather phenomena that have an impact on the operation of space technology near or on Earth as well as other planets.
- When it comes to the Earth, a magnetic disturbance can occur when the Earth’s magnetic field interacts with the field delivered by the CME.
- Space weather events have the potential to significantly affect our satellites, communication networks, and power grids.
- We can better safeguard ourselves from these occurrences by comprehending the Sun.
What are the Other Missions to the Sun?
- NASA’s Parker Solar Probe: Aims to trace how energy and heat move through the Sun’s corona and to study the source of the solar wind’s acceleration.
- It is part of NASA’s ‘Living With a Star’ program that explores different aspects of the Sun-Earth system.
- The earlier Helios 2 solar probe, a joint venture between NASA and space agency of erstwhile West Germany, went within 43 million km of the Sun’s surface in 1976.
- Solar Orbiter- A joint mission between the ESA and NASA to collect data that will help answer a central question of helio-physics like how the Sun creates and controls the constantly changing space environment throughout the solar system.
- Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE), Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS), WIND, Hinode, the Solar Dynamics Observatory, and Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO).
Source: The Times of India, Indian Express, ISRO.