ADITYA-L1 MISSION: STUDYING THE SUN FROM L1 HALO ORBIT
Why in the News?
- After the successful launch of Aditya L1 , it was successfully placed at L1 Halo Orbit.
Source: NASA
About L1 Point Significance:
Solar Observation Focus:
- Aditya-L1 mission aims to study the Sun extensively, observing its atmosphere, corona, and solar eruptions.
- The goal includes monitoring Solar Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) influencing space weather.
Continuous View and Early Alerts:
- Positioned 1.5 million km from Earth towards the Sun, Aditya-L1 ensures an uninterrupted line of sight for continuous solar observations.
- L1’s strategic location allows early warnings of solar eruptions, enabling proactive measures against potential disruptions to space technologies.
Lagrangian Point L1 Stability:
- L1 is a Lagrangian point where gravitational forces from Earth and the Sun balance, allowing relative stationarity.
- Aditya-L1, though in an orbit around L1, ensures stability for consistent and precise solar observations.
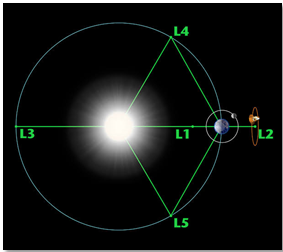
| About Lagrange Points
Definition: According to NASA , Lagrange Points represent locations in space where objects, once positioned, exhibit a tendency to remain stationary. These points occur when the gravitational forces exerted by two significant masses precisely balance the centripetal force necessary for a smaller object to co-move with them. · Five positions in space where gravitational forces of two large bodies, like Earth and Sun, create stable points. · Denoted as L1 to L5. · L1 commonly used for solar observatories like Aditya L1. · L2 used for space telescopes and observatories. · L3, L4, and L5, less commonly used, form equilateral triangles with the large bodies, providing stable regions for satellite placement. |

 Source: NASA
Source: NASA 

