ADITYA L1
Why in the News?
- Aditya L1, ISRO’s mission to study Sun, set to be placed in final orbit.
Source: Ajj tak
About Aditya L1
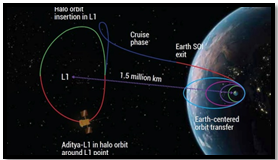
- Aditya-L1 represents India’s inaugural space-based observatory-class solar mission, aimed at studying the Sun from a considerable distance of 1.5 million kilometers. It is anticipated to take about 125 days to reach the L1 point.
- Aditya-L1 follows ISRO’s AstroSat (2015) as the second mission in its astronomy observatory-class.
- The mission’s travel duration is notably shorter than India’s previous Mars orbiter mission, Mangalyaan.
- The spacecraft’s intended orbit is a halo orbit situated around the Lagrangian point 1 (L1) within the Sun-Earth system.
Lagrange Points
Source: NASA
- Lagrange Points are specific locations in space where the gravitational forces of two substantial celestial bodies, like the Sun and Earth, counterbalance each other.
- These points allow small objects, such as spacecraft, to maintain their orbits with minimal fuel consumption.
- There exist five Lagrange Points, each characterized by unique attributes, facilitating stable orbits for smaller masses.
In the Sun-Earth system, L1 is particularly significant for solar observations. Placing a satellite in a halo orbit around L1 offers continuous unobstructed views of the Sun, avoiding eclipses or occultation.

 Source: Ajj tak
Source: Ajj tak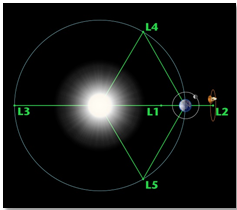 Source: NASA
Source: NASA

