Adhir Ranjan Chowdhury has a wish list for Parliament’s Winter Session: Prime Minister should listen to the Opposition
Mains GS Paper II: Parliament-Structure, organization, functioning and conduct of business etc.
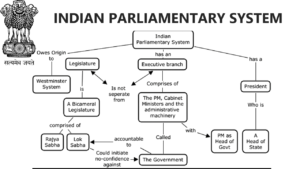
Parliament:
- The most significant representation of Indian democracy is the parliament.
- To call the House and MPs to attend to legislative and other work, utilise the following procedures:
- debates, discussions, committee exemptions, and other mechanisms
- Through their elected representatives, the people can participate in decision-making and keep the government accountable thanks to the parliament.
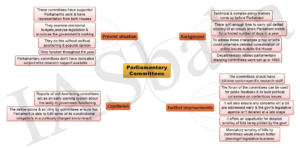
Parliamentary Committee:
- A Parliamentary Committee is a body of MPs that is chosen, appointed, or proposed by the Speaker or Chair of the House.
- The Speaker serves as the committee’s chairman, and it reports its findings to him or to the House.
- The idea of a parliamentary committee originally appeared in the British Parliament.
- They base their legal position on Articles 105 and 118.
- The privileges of MPs are covered by Article 105.
- Article 118 gives the Parliament the authority to create regulations governing its operations.
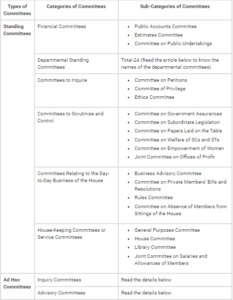
Two types of Parliamentary Committees:
- Standing Committees
- Ad Hoc Committees
The Standing Committees:
- They are permanent (constituted every year or periodically) and work on a continuous basis.
- Example: Financial Committees, Departmental Standing Committees, Committees to Enquire etc
Ad Hoc Committees:
- They are transient and vanish once the duty they were given is finished.
- The primary Ad hoc Committees are the Select and Joint Committees on Bills.
Current Parliamentary issues:
- There are currently a lot fewer bills that are sent to committees.
- About 27% of bills in this government’s first term (2014–19) were referred to committees.
- Less than 10% of the bills introduced in the 17th Lok Sabha have been referred to committees (compared to 71 percent in the 15th Lok Sabha).
- less opportunities for opposition speakers to address the public.
Current economic problems in the country:
- The World Bank (in October 2022) estimated: India will grow at 5(six point five)percent in the current fiscal year (FY 22-23)
- which is a downward revision by one percentage point since June.
- Inflation soaring above the 6 percent target
- Interest rates are rising
- Macroeconomic policies are becoming restrictive
- Rupee is plunging to all-time lows against the US dollar.
- According to the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE): India’s unemployment rate was at 3(eight point three)percent in August 2022.
Other issues:
- ED, CBI or Election Commission: They are facing ideological subversion and destruction.
- According to the most recent UN Universal Periodic Review (UPR) report, India’s human rights situation has significantly deteriorated since 2017.
- Adivasi and Dalit communities, which have historically been marginalised, are not given fair justice or protection.
- India ranks last among 180 nations on the Environment Performance Index (EPI).
- emissions of greenhouse gases are quickly rising as the air quality is deteriorating.
- The 10 most polluted cities in the world are all located in India, according to the 2021 World Air Quality Report.
Way Forward
- Discuss the current challenges: It is high time for Parliament to discuss the advancing challenge and for the government to open the floor for the same.
- UPR mechanism:According to the Indian government, being the largest democracy in the world, “India firmly supports the UPR as a crucial tool.”
- The highest standards of human rights are upheld by India..
- Amrit Mahotsav: It cannot be celebrated by disrespecting Parliament, curtailing the independence of institutions, suffocating free expression, restricting the space to the political leaders,
- Allow committees to be formed: The majority of these committees are controlled by the government, and the majority vote is always used to reach a resolution, so governments and the opposition party shouldn’t be frightened of them.
- Fostering the trust of parliamentarians: The utility and relevance of the committee system are of utmost importance to both the ruling party and the opposition parties.
QUESTION FOR MAINS
- To what extent, in your view, the Parliament is able to ensure accountability of the executive in India?(UPSC 2021) (200 WORDS, 10 MARKS)