A voice of Global South.
Relevance
- GS Paper 2 Bilateral, Regional and Global Groupings and Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests
- Tags: #BRICSSummit2023 #voiceofglobalsouth #IndianExpresseditorialanalysis #BRICSAgenda
Why in the news?
15th BRICS summit will be held in Johannesburg, South Africa from August 22-24, 2023, will be the first in-person summit since 2019 due to the COVID-19 pandemic .The summit will be hosted by South Africa, theme of the summit is “BRICS and Africa: Partnership for Mutually Accelerated Growth, Sustainable Development, and Inclusive Multilateralism” .
Evolution of BRICS
| YEAR | EVENT |
| 2001 | Jim O’Neill of Goldman Sachs coins the term “BRIC” to describe Brazil, Russia, India, and China. |
| 2006 | The foreign ministers of Brazil, Russia, India, and China meet on the sidelines of the UN General Assembly and agree to use the acronym “BRIC”. |
| 2009 | The first BRICS summit is held in Yekaterinburg, Russia. |
| 2010 | South Africa joins BRICS. |
| 2011 | BRICS establishes the BRICS Development Bank. |
| 2012 | BRICS establishes the BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement. |
| 2013 | New Development Bank (NDB) is established with initial capital investment of $10 billion from each member country. |
| 2014 | BRICS leaders issue the Ufa Declaration, which calls for a more equitable and inclusive global system. |
| 2015 | BRICS leaders issue the Goa Declaration, which reaffirms their commitment to cooperation and development. |
| 2016 | BRICS leaders issue the Xiamen Declaration, which calls for increased cooperation on trade, investment, and infrastructure. |
| 2017 | BRICS leaders issue the Johannesburg Declaration, which reaffirms their commitment to fighting terrorism and promoting sustainable development. |
| 2018 | BRICS leaders issue the Argentina Declaration, which calls for increased cooperation on digital economy and artificial intelligence. |
| 2019 | BRICS leaders issue the Brasilia Declaration, which reaffirms their commitment to multilateralism and free trade. |
| 2020 | BRICS leaders issue the virtual summit declaration, which calls for increased cooperation in the fight against COVID-19 |
| 2021 | BRICS leaders issue the New Delhi Declaration, which reaffirms their commitment to cooperation and development in the post-COVID-19 era. |
Initial Dismissal
- Pundits initially thought that BRICS was an incompatible group because they didn’t see any common ground between the members.
- They were from different regions, had different political systems, and different economic strengths.
Changing Attitudes
- As the group has grown and matured, attitudes towards it have shifted. There is now growing concern about the BRICS’ collective influence and potential.
Why change in attitude?
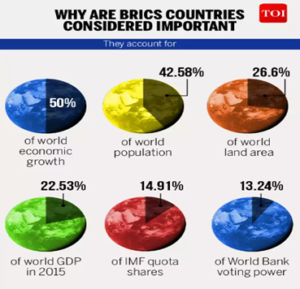
- Firstly à BRICS countries have achieved significant economic growth in recent years. They are now among the largest economies in the world, and their combined GDP is larger than that of the G7 countries.
| Group | Share of Global GDP(PPP) |
| BRICS | 31.67% |
| G7 | 30.31% |
- BRICS countries have been increasingly cooperating on a number of issues, such as trade, investment, and infrastructure. This cooperation has given them a greater voice on the global stage.
- BRICS countries have been critical of the status quo in the global economy. They have called for a more equitable and inclusive system and they have challenged the dominance of the West.
Eagerness in developing world
Multilateral financial institutions (MFIs)
- Are often seen as being subservient to the Western political-economic agenda, which means that they are influenced by the policies and interests of Western countries.
- Caused serious concerns in developing nations, who feel that MFIs are not acting in their best interests.
- They impose harsh conditions on loans to developing countries, which make it difficult for them to repay their Loans
- That they are not transparent about their lending practices.
- That they do not adequately address the needs of the poorest and most vulnerable people in developing countries.
Emergence of New Development Bank (NDB)
- BRICS established the New Development Bank (NDB) in 2014.
- Initial investment of $10 billion from each of the five member countries.
- NDB headquartered in Shanghai, China.
Easy Access and Attention
- Viable Alternative to Western Institutions: provide developing countries with an alternative source of financing.
- The NDB is seen as being more independent and less politicized than Western MFIs, and is therefore more likely to act in the best interests of developing countries.
Prominent Initiatives Supported by NDB in India
The New Development Bank (NDB) has allocated financial support to several significant infrastructure endeavors in India, These include:
- Mumbai Metro rail, the Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut Regional Rapid Transit System, and various Renewable Energy initiatives.
- To date, the NDB has granted approval for 14 key projects within India, amounting to approximately USD 4.2 billion in funding.
- During 2020, India unveiled a loan agreement worth 1 billion USD with the NDB. The aim of this pact is to enhance rural employment opportunities and bolster infrastructure development.
Expanding Participation
- Countries like Bangladesh, UAE, Uruguay, and Egypt acquired smaller stakes in NDB in 2021.
- Shows growing interest in NDB’s approach and offerings.
US dollar’s dominance in the global financial system
- BRICS nations are concerned about the US dollar’s dominance and are looking for ways to reduce their reliance on it.
- Creation of an alternative payment system that would be based on their own currencies.
- BRICS nations are also discussing the possibility of creating a new reserve currency that would replace the US dollar.
Growing interest in joining BRICS
- More countries are showing interest in joining BRICS, including Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt, Algeria, and Argentina.
- South African Foreign Minister Naledi Pandor has received multiple requests to join BRICS.
- This is a sign that BRICS is becoming more important in the global economy.
Major Challenges faced by BRICS Members
Economic Disparities
- Brazil and Russia facing economic downturns, while China and India sustain strong growth.
- South Africa’s economy struggling, marked by high unemployment and inequality.
Political Variations
- Russia’s annexation of Crimea and involvement in conflicts straining relations with fellow BRICS members.
- China’s territorial claims in the South China Sea causing tensions with other members having competing claims.
Western media tries to sow discord between BRICS Members
- US think tank claimed that China and India are at odds over BRICS expansion, Indian government has denied that there are any differences between India and China over BRICS expansion
- South African foreign minister Naledi Pandor alleged that
“Someone… is trying to spoil our summit… creating all sorts of stories”
Institutional Hurdles
- BRICS’ New Development Bank (NDB), established in 2014 for development funding, encountering difficulties in loan disbursement and project selection.
- The Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA), a pool of reserves, yet to be tested.
Coordination Challenges
- Disagreements on NDB and CRA governance, along with differing priorities in trade, investment, and climate change, hinder BRICS’ unified stance.
External Influences
- Emergence of protectionism, nationalism, and populism in advanced economies posing trade, investment, and capital access challenges for BRICS.
Significance of BRICS for India
Geo-Political Strategy
- Amid current geopolitics, India faces challenges in balancing its strategic interests between the U.S. and the Russia-China axis.
- BRICS offers a platform for India to navigate and balance its approach with the Russia-China axis.
Global Economic Transformation
- BRICS nations share a common goal of reforming the global financial and monetary system for a fair and balanced international order.
- Within the G20, BRICS plays a vital role in shaping global economic policies and enhancing financial stability.
Countering Terrorism
- BRICS serves as a platform for India to mobilize collective efforts against terrorism.
Advancing Global Influence
- India actively seeks membership in key global forums like the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) and Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG).
- BRICS provides a means to engage with China and resolve mutual disputes, while also gaining support from other member countries.
BRICS as a Catalyst for Reformed Multilateralism
Global multilateral economic infrastructure needs reform
- BRICS countries have more than 30% share of global GDP, but only 15% say in institutions like IMF.
- This shows that the global multilateral economic infrastructure is unfair and needs reform.
India’s role in BRICS
- India should give preference to making BRICS a catalyst for reformed multilateralism.
- India can also use its position in BRICS to champion the cause of the Global South, which refers to developing countries in Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
- Prime Minister Modi has been supporting the interests of the Global South in global talks.
- As the G-20 chair, PM Modi advocated for the inclusion of the 55- country African Union in the group, reflecting his commitment to advancing Global South concerns.
BRICS Role in Global leadership
- India, South Africa, and Brazil are emerging economies that can play a leading role in representing the Global South.
- BRICS countries can use their collective influence to push for reform of the global multilateral economic infrastructure.
- They can also work together to create new institutions that are more equitable and inclusive.
- Avoiding a New Cold War: The idea that BRICS opposes G-7 could lead to a harmful Global South vs. Global North conflict. This must be prevented.
- They can persuade developed nations to accept the new reality of a Multipolar world and to build more inclusive democratic structures in the multilateral arena.
BRICS’ evolution from a mere economic concept to a platform for emerging economies signifies a transformative shift in global governance. As BRICS aims to be the voice of the Global South, its leaders must embody Jim O’Neill’s vision of representative global economic governance. By prioritizing reformed multilateralism, inclusivity, and cooperation, BRICS can navigate the complex global dynamics while working towards a more balanced and just global order.
Source: Indian Express
Mains Question
Discuss the Evolution, Significance, and Challenges of the BRICS grouping in shaping global geopolitics and economic order. How has India’s participation in BRICS impacted its foreign policy and strategic interests?