A TIME-HONOURED CONNECT: BRIDGING THE GULF BETWEEN INDIA AND OMAN
Syllabus :
- GS2: Bilateral, Regional and Global Groupings and Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in the News?
- Sultan Haitham bin Tarik of Oman is on a state visit to India, marking his first visit since assuming office in 2020.
- Indian Prime Minister’s landmark visit to Oman in 2018 solidified crucial agreements in trade, defence, and security, enhancing diplomatic ties.
Source: Hindi Arise
Historical and Cultural Ties:
- Ancient Maritime Connection: For centuries, India and Oman have enjoyed a thriving maritime trade, with ships carrying spices, textiles, and precious metals across the Arabian Sea.
- Shared Cultural Heritage: Cultural influences have flowed freely between the two regions, evident in similarities in language, music, and culinary traditions.
- Warm Relations with the Ruling Family: Sultan Qaboos, who ruled Oman for nearly 50 years, fostered close ties with India, welcoming Indian businesses and professionals to contribute to the country’s development.
- Vibrant Indian Community: Over 700,000 Indians reside in Oman, playing a vital role in the country’s economy and social fabric.
Areas of Strategic Partnership:
- Pillar of India’s West Asia Policy: Oman serves as a crucial pillar of India’s strategic engagement in the West Asia region.
- Twin Pillars – Mutual Trust and Shared Interests: The India-Oman strategic partnership, established in 2008, rests on the bedrock of mutual trust and shared interests in regional stability, security, and economic prosperity.
- Defence and Security Cooperation: Defence and security collaboration are fundamental aspects of the partnership.
- A 2005 MoU paved the way for joint exercises involving all three wings of India’s defence forces, marking Oman as the first Gulf country to engage in such collaborations.
- Maritime security cooperation is evident through India’s naval presence in the Gulf of Oman, dedicated to anti-piracy operations.
- Trade and Economic Collaboration:
- Bilateral trade surged to $12.388 billion in FY2022-23, showcasing the substantial economic ties between India and Oman.
- Over 6,000 joint ventures, coupled with an investment exceeding $7.5 billion, exemplify the depth of economic collaboration beyond numerical trade indicators.
- Energy Security and Rupay Debit Card Launch:
- Oman holds strategic importance in India’s energy security, emerging as the second-largest market for Oman’s crude oil exports, following China.
- The introduction of the Rupay debit card in Oman in October 2022, aligning with India’s digital public infrastructure initiative, strengthens the economic bond between the two nations.
- Indian Diaspora :
- In Oman, there are approximately 620,000 Indians, with around 480,000 employed as workers or professionals. Some Indian families have resided in Oman for over 150 to 200 years.
- Duqm Port Agreement:
- A historic MoU on Duqm Port, signed during Indian Prime Minister’s visit, stands as a landmark achievement in the partnership.
- Duqm’s strategic proximity to the Chabahar port in Iran aligns with India’s maritime security roadmap, including developments in Seychelles and Mauritius.
- This agreement provides crucial basing facilities and logistical support for Indian naval operations, solidifying the depth of security ties.
- ‘Operation Sankalp’ during the 2019 Persian Gulf crisis showcased the Indian Navy’s commitment to ensuring safe passage for Indian-flagged ships, particularly near Oman.
Emerging Areas of Cooperation:
- Space Exploration: The signing of an MoU on space cooperation during the PM’s visit to Oman in 2018 paves the way for joint endeavours in space technology and exploration.
- Rare Earth Metals: Potential collaboration in exploring and extracting rare earth metals, critical for modern electronics, could further strengthen the partnership.
- Connectivity Projects: The proposed India-Middle-East-Europe Connectivity Corridor (MEEC) and undersea gas pipeline project from Oman to India offer exciting avenues for enhanced economic integration.
- Undersea gas pipeline: SAGE’s proposal for a 1,400 km pipeline from Oman to India.
Source: ET
Programme of Cooperation (POC) :
- The POC for Cooperation in Science and Technology (2022–2025) was established, building on a 1996 agreement between India and Oman.
- The collaboration focuses on sustainability and scientific resource utilization.
- Implementation Authorities: The Department of Science & Technology, Government of India, and the Office of Science, Knowledge & Technology Transfer, Government of Oman, will oversee POC implementation.
- Joint Scientific Projects: Both nations will initiate joint scientific projects based on mutual interests, collaboratively developed by Indian and Omani institutions.
- Exchange of Experts: Encouragement for the exchange of scientists, researchers, experts, and specialists to implement selected joint projects is a key aspect.
- Technology Development Objective: The primary goal is to develop applicable technology for mutual benefit.
- Key Areas of Cooperation (2022–2025):
- Medicinal Plants and Processing
- Real-time Air Quality Monitoring
- Development of an Electronic Knowledge Sharing Platform
- Technical Expertise for Small and Medium Enterprises in Sustainability (Eco-Innovate) Accelerator
- Plastic Bio-fuel and Bio-diesel Research
- Software Development for Graduate Programs Linking Industry with Academia
- Blockchain and FinTech Solutions
- Training Programs – Big Data, Coding & Testing
- STEM Teaching
- Additional areas of S&T cooperation added by mutual consent.
Significance of Oman :
- Strategic Location:
- Oman’s strategic location at the mouth of the Persian Gulf and proximity to key trade routes make it a vital gateway for India’s access to the West Asia region.
- Oman holds a crucial position at the gateway of the Strait of Hormuz, a vital route for India’s one-fifth of oil imports.
- Regional Stability: Oman’s long history of neutrality and its ability to navigate complex regional dynamics make it a valuable partner for India in promoting peace and stability in West Asia.
- Shared Values: Both India and Oman are recognized as ambassadors of peace, advocating for dialogue and understanding across cultures and ideologies.
- International Cooperation: Oman actively participates in the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS), strengthening regional maritime cooperation.
- Countering China :India strategically secures access to the Port of Duqm in Oman for military and logistical support, countering Chinese influence in the Indian Ocean region.
Way Forward:
- India, facing insufficient energy resources for current and future needs, necessitates long-term energy partnerships, with Oman being a key collaborator.
- Duqm Port in Oman is strategically positioned in international shipping lanes between East and West Asia.
- India must proactively collaborate with Oman to capitalize on opportunities within the Duqm Port industrial city.
- Closer ties with Oman can enhance India’s strategic influence in the region, aligning with its Indo-Pacific vision in the Western and Southern Indian Ocean.
Sultan Haitham bin Tarik’s visit to India reaffirms the longstanding and multifaceted bond between the two nations. As India seeks to deepen its engagement in West Asia, Oman is well-positioned to remain its crucial partner and bridge to the region, fostering peace, prosperity, and cultural exchange in the years to come.
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the key areas of cooperation between India and Oman . Analyze the challenges and opportunities in further strengthening this strategic partnership, considering the evolving geopolitical landscape in West Asia.

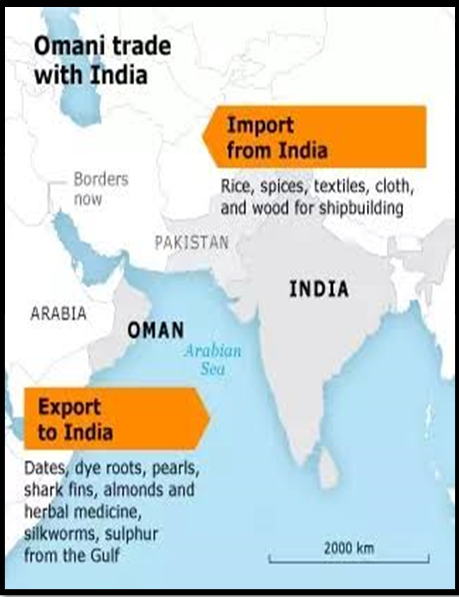 Source: Hindi Arise
Source: Hindi Arise Source: ET
Source: ET

