A STRATEGIC WINDOW: SEIZING OPPORTUNITIES FOR INDIA
Syllabus:
GS 2:
- India and its Neighbourhood- Relations.
- Bilateral, Regional and Global Groupings and Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interest.
Focus:
The intersection of European and Asian geopolitics, highlighted by recent diplomatic moves and strategic debates involving major powers like Russia, China, and the United States, underscores the evolving global dynamics shaping regional security and economic interdependencies.
Source: German Marshal
The Growing Interdependence
- Russian visit: Russian President Vladimir Putin’s recent visits to North Korea and Taiwan highlight deepening interconnections between European and Asian security.
- Presidential debate: Recent debates between Joe Biden and Donald Trump underscore the strategic opportunities emerging for middle powers like India.
- Eurasian geopolitics: Four dimensions define the new Eurasian geopolitics amidst increasing interdependence between European and Asian theaters.
- Historical context: Asia’s role is no longer passive but actively shapes global narratives and balances of power, contrasting with its colonial-era status.
- Military contributions: India’s historical military contributions under British rule exemplify its pivotal role in shaping European and Asian geopolitics.
Asian Agency in Global Affairs
- Decision-making shift: Unlike colonial times, Asian states now influence global power dynamics, evidenced by Russia and Western Europe’s engagements with Asia.
- Ukraine peace efforts: Asia’s influence was evident during the Ukraine peace conference, where global South nations played significant roles.
- Arms supply: Asia has emerged as a major arms supplier in European conflicts, with Korea Peninsula dynamics influencing Ukraine’s military landscape.
- China’s role: China supports Russia indirectly in conflict, while South Korea and Japan engage in joint production and arms support for Ukraine.
- Impact of diplomacy: Conference diplomacy and Asian arms supply are crucial in shaping contemporary European conflicts and global dynamics.
Enhanced Asian Agency
- Putin’s diplomacy: Putin’s visits to North Korea and Vietnam reflect increased Asian agency, with Moscow seeking strategic balance.
- North Korea’s strategy: North Korea and Russia leverage mutual ties to challenge Western influence, impacting regional dynamics profoundly.
- US-South Korea alliance: The US strengthens alliances with South Korea amid regional tensions, balancing China’s influence in East Asia.
- Vietnam’s strategic balancing: Vietnam hosts key global leaders, enhancing its strategic importance in balancing China-US relations.
- Strategic maneuvering: Asian states’ maneuverability increases as Western dilemmas sharpen, particularly in balancing European and Asian priorities.
Western Dilemmas and Strategic Responses
- American debate: US foreign policy debates focus on balancing European and Asian priorities, particularly in light of China’s rise and European security concerns.
- Strategic challenges: Europe’s struggle to define its defense stance amidst Russian and Chinese pressures highlights transatlantic differences.
- US-China relations: US urges European allies to stand firm against China while navigating economic interdependencies with Beijing.
- Indo-Pacific security: US encourages Asian allies like India, Japan, and South Korea to contribute to European security amidst global strategic shifts.
- Middle power influence: Middle powers like India have a strategic opportunity to enhance national power through integrated deterrence and arms production.
Seizing the Strategic Window
Current opportunities: The interdependence of European and Asian theaters presents unprecedented strategic opportunities for India.
- Military modernization: India can enhance comprehensive national power by modernizing defense industrial capabilities and expanding arms production.
- Strategic autonomy: Self-sufficiency in arms production is crucial for India’s strategic autonomy and national security.
- Bureaucratic challenges: India needs agile bureaucratic responses to capitalize on current international dynamics and strengthen defense capabilities.
- Future prospects: The strategic window for India’s enhanced influence and security won’t last indefinitely, emphasizing the need for swift action and strategic foresight.
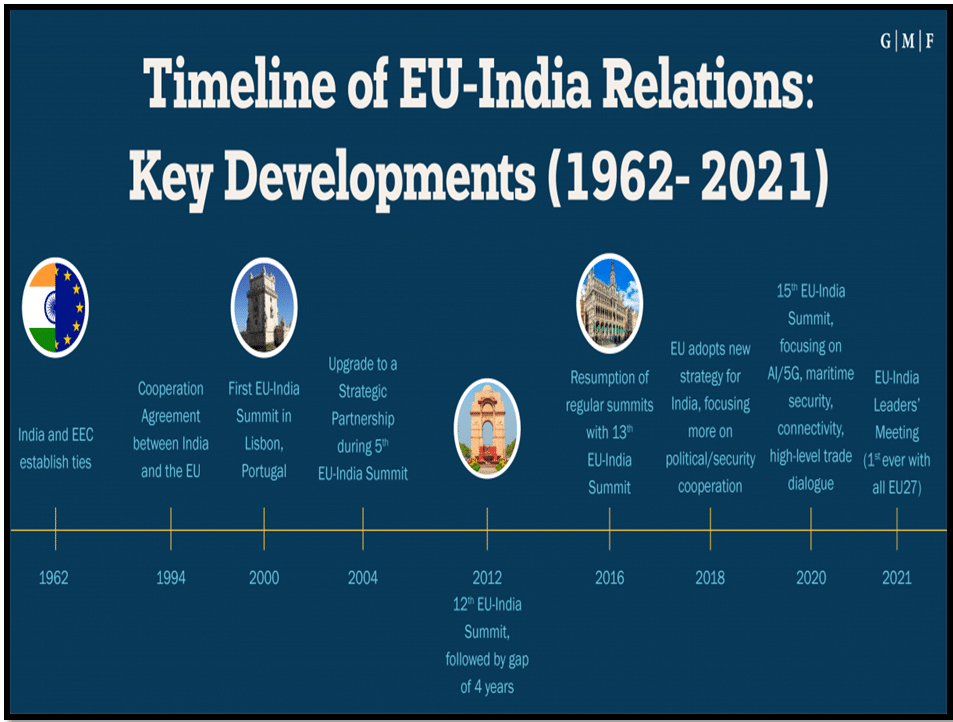
India’s initiatives to foster diplomatic ties globally:
|
Challenges
- Historical Legacies and Colonial Dependencies: Overcoming historical legacies where Asian nations were once subordinate to European powers, now asserting independent decision-making amidst global conflicts, remains a challenge.
- Complex Geopolitical Interdependence: Balancing European and Asian security interests poses a challenge as India navigates evolving global dynamics, influenced by Russia’s strategic moves and US-China tensions.
- Divergent Strategic Priorities: Asia’s increasing agency in global affairs contrasts with Europe’s nuanced responses to Russian and Chinese influences, posing dilemmas for transatlantic relations and India’s strategic alignments.
- Technological and Economic Integration: The deep economic ties between Europe and China complicate Western responses to Asian security issues, affecting global strategic stability and cooperation.
- Bilateral and Multilateral Diplomacy: Managing diverse diplomatic engagements, as seen in Vietnam’s hosting of global leaders, requires nuanced strategies to balance regional alliances and strategic autonomy.
Way Forward
- Promoting Strategic Autonomy: Prioritizing self-sufficiency in defense production to enhance India’s strategic autonomy and reduce dependency on global supply chains.
- Strengthening Regional Alliances: Enhancing partnerships with countries like Japan, South Korea, and Vietnam to bolster regional security and economic cooperation in both European and Asian contexts.
- Adapting to Global Shifts: Adapting swiftly to geopolitical shifts by leveraging diplomatic channels and military alliances to safeguard national interests and regional stability.
- Investing in Technological Innovation: Investing in cutting-edge technology and innovation to bolster defense capabilities and contribute effectively to global security architectures.
- Navigating Multilateral Forums: Active participation in multilateral forums to shape international narratives and policies, contributing to global peace and stability.
- Balancing Economic and Security Interests: Striking a balance between economic partnerships and security imperatives to ensure comprehensive national development and security resilience.
- Empowering Diplomatic Corps: Strengthening diplomatic corps’ capabilities to navigate complex international relations and advocate for India’s strategic interests effectively.
- Enhancing Military Modernization: Continuous modernization of military capabilities and strategic infrastructure to meet evolving security challenges and maintain regional stability.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of modern geopolitical interdependence requires strategic foresight and robust diplomatic engagement. India’s proactive stance in enhancing regional alliances, promoting technological innovation, and ensuring defense autonomy will be crucial in safeguarding its national interests amidst shifting global paradigms.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the strategic implications of India’s evolving role in balancing European and Asian geopolitics. How can India leverage its historical ties and current alliances to strengthen its position in the global arena?
Associated Article: