A REBOOT AT G7
SYLLABUS:
GS 2:
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora – their structure, mandate.
Focus:
- PM Modi’s first trip abroad in his third term, to the summit in Italy, is a chance to re-energise relations with the West
Source: G7
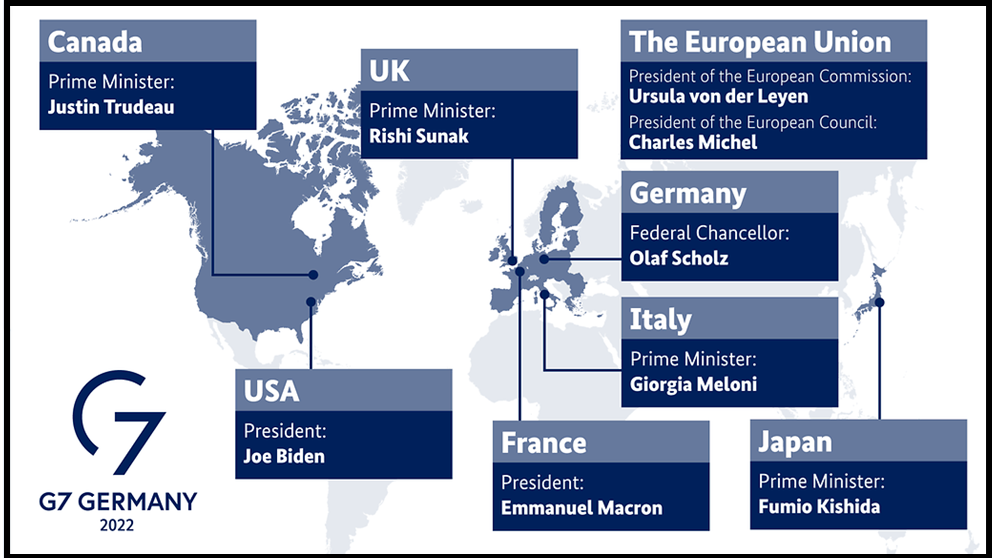
How G7 functions
- Informal Structure: The G7 functions as an informal intergovernmental organization without a formal charter or secretariat. It operates based on consensus rather than formal voting, and its decisions do not carry legal obligations.
- Membership: The G7 consists of seven member countries, with the European Union also participating fully as a “non-enumerated” member since 1981.
- Annual Presidency: The presidency of the G7 rotates annually among the member countries. The presiding country hosts the summit and sets the agenda for the year.
- Meetings: The G7 convenes annual meetings to discuss and coordinate on various global issues.
- Focus Areas: Key areas of focus for the G7 include economic growth and stability, climate change, international security, health, gender equality, and humanitarian assistance.
- Outreach Initiatives: The G7 engages in outreach programs to collaborate with non-member countries and organizations, such as the G7+ Dialogue on Women’s Empowerment and the G7 Partnership for Africa.
Overview of PM Modi’s Participation at the G7 Summit
Strategic Re-engagement
- Prime Minister’s First Trip Abroad in Third Term: Narendra Modi’s attendance at the G7 summit in Fasano, Italy, marks his first international visit in his third term.
- Renewing Western Ties: This visit provides Modi with an opportunity to strengthen and renew relationships with Western leaders, building on past improvements in relations with the US and Europe.
- G7’s 50th Anniversary: The event coincides with the 50th anniversary of the G7, adding significance to the meeting.
- Italy’s Political Welcome: Hosted by Italian Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni, the summit aims to further solidify the growing political rapport between Italy and India.
- Global Governance Engagement: Modi’s participation underscores India’s ongoing engagement with global governance structures led by the G7.
Diplomatic Challenges and Opportunities
- Sino-Russian Relations: The G7 summit highlights the increasing conflicts between the West and the Sino-Russian alliance, presenting both challenges and opportunities for Indian diplomacy.
- Balancing Diplomatic Relationships: Modi faces the challenge of managing India’s conflicts and cooperations—navigating tensions with China while maintaining ties with Russia and expanding relations with the West.
- Future Engagements: Following the G7, Modi plans to engage with key leaders like Xi Jinping and Vladimir Putin at the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation summit in Kazakhstan.
- Ukraine Conflict and Western Relations: The ongoing conflict in Ukraine and related military tensions in the Western Pacific will test India’s diplomatic strategies in balancing these complex relationships.
- Reaffirming Democratic Values: Modi’s reduced electoral mandate is viewed as a testament to India’s robust democratic mechanisms, which may counter criticisms of democratic backsliding in India.
Focus Areas and Key Discussions
- Artificial Intelligence: Pope Francis is expected to participate in discussions on artificial intelligence, aligning with the G7’s focus on global governance in this area.
- Food and Energy Security: Modi is set to participate in discussions on food and energy security, areas where India plays a critical role globally.
- Migration and Talent Flow: As a significant source of global migrants, India’s perspective on managing migration and facilitating talent flow is crucial.
- Economic and Political Shifts: The summit will also address broader economic challenges posed by nations like China, aligning with India’s strategic interests.
- Regional Engagements: Italy’s focus on enhancing G7’s relations with Africa and the Mediterranean aligns with India’s policy interests in these regions.
Prospects for Enhanced Global Roles
- Influence in Global Governance: The G7 summit serves as a platform for India to assert its role and perspectives in global governance frameworks.
- Engagement with Non-Western Leaders: Meloni’s invitation to leaders from the non-Western world provides Modi opportunities to establish and strengthen ties with a diverse array of global leaders.
- Meeting with Pope Francis: Modi’s scheduled meeting with Pope Francis during the G7 outreach sessions underscores the broader diplomatic and cultural engagement.
- Shaping Global Discourse: Modi’s participation in the G7 discussions on pressing global issues like AI regulation and energy security highlights India’s active role in shaping global policies.
- Navigating Great Power Conflicts: The evolving dynamics of great power conflicts present Modi with a strategic opportunity to position India as a key player in mitigating tensions and fostering cooperation.
Long-term Strategic Implications
- Strengthening Western Alliances: Modi’s engagements during the summit are likely to influence India’s long-term relationships with Western nations.
- Enhancing India’s Global Stature: Successful diplomacy at the G7 could elevate India’s stature on the world stage, influencing future international policy directions.
- Potential for Leadership in Global South: Italy’s emphasis on G7’s engagement with the Global South aligns with India’s priorities, potentially boosting Modi’s leadership role among these nations.
- Strategic Economic Collaborations: The discussions may lead to enhanced economic collaborations, particularly in technology and sustainable development sectors.
- Future Diplomatic Engagements: The outcomes of this summit could set the stage for India’s future diplomatic engagements, particularly in balancing relationships with both Western and Eastern powers.
| Key Points About the Group of Seven (G7)
Formation and Purpose
Annual Summits
Member Countries
Relationship with G20
Operational Structure
|
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Question: Analyze the significance of the Group of Seven (G7) in shaping global economic policies. Discuss how India’s engagement with the G7 nations could influence its strategic positioning on the global stage. (250 words)
Associated Articles: