A MANDATE FOR A NEW ECONOMIC APPROACH
Syllabus:
GS 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources, Growth, Development and Employment.
- Inclusive Growth and issues arising from it.
Focus:
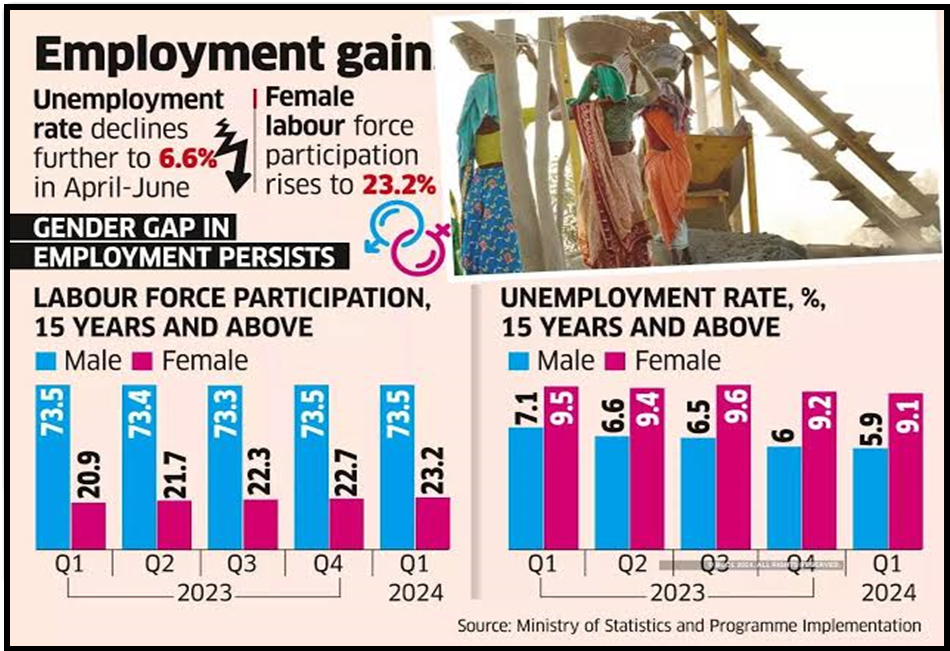
- The mandate for a new economic approach has become pressing following recent electoral outcomes signalling discontent with economic conditions, particularly unemployment and inflation.
- These challenges underscore the need for strategic reforms and targeted interventions to address public concerns and foster inclusive growth.
Source: TH
Discontent, its Sources
- Election signals: The recent general election results, particularly in Uttar Pradesh, reflect discontent with economic conditions.
- Governance dissatisfaction: High unemployment and persistent inflation have fueled dissatisfaction with governance.
- Food price inflation: Food price inflation, especially for cereals and pulses, has remained elevated, impacting household expenditures significantly.
- Historical context: Past high food inflation has influenced electoral outcomes, such as the end of the NDA government led by Vajpayee in 2004.
- Unemployment challenge: Since 2014, the unemployment rate has mostly been high, affecting both regular employees and the self-employed.
Spirit of Democracy
- Honouring the mandate: Prime Minister Narendra Modi must honour the mandate given by addressing the sources of economic discontent.
- Call for change: A shift from the economic approach of the past decade is necessary to meet the people’s expectations.
- Lack of indications: There is no clear indication yet that the government plans to change its economic strategy.
- Reform promises: Vague promises of ‘reforms’ have been made by the Finance Minister, emphasizing their essential role in economic growth.
- Growth outcomes: Despite praised reforms, average growth rates have not significantly increased since 2014, highlighting policy inefficacy.
The Current Economic Landscape
- Growth disparities: Recent economic growth has not met public aspirations, particularly in addressing food inflation and inequality.
- Infrastructure needs: Indians aspire for improved physical and social infrastructure, including healthcare and education.
- Policy focus: Economic policies have emphasized foreign investment, digital payments, manufacturing subsidies, and infrastructure development.
- Welfare measures: While welfare transfers have been implemented, they have not secured a majority mandate for the BJP.
- Macro-stability: Despite efforts towards fiscal consolidation, macroeconomic stability alone does not guarantee economic growth or meet citizen expectations.
Addressing Economic Deficits
- Specific interventions: Rather than generic reforms, targeted interventions are needed to alleviate economic pressure points.
- Food price control: Rising food prices, especially staples, indicate an underdeveloped agricultural sector needing urgent attention.
- Infrastructure gaps: Issues in the Indian Railways and urban water supply demand immediate governmental focus.
- Public sector role: The public sector’s capacity is crucial for addressing infrastructure deficits that hinder economic activity.
- Long-term vision: Moving beyond short-term fixes, long-term infrastructure investments are essential for sustainable growth and development.
Public Sector Leadership
- Critical deficits: Infrastructure deficiencies hinder economic productivity and employment growth across sectors.
- Sectoral needs: From transportation to sanitation, essential services must be prioritized to stimulate economic activity.
- Public sector capacity: Only the public sector can provide infrastructure at the necessary scale and pace.
- Private sector limitations: Relying solely on the private sector has not bridged infrastructure gaps over the past decade.
- Policy adjustment: Instead of continued liberalizing reforms, immediate action on critical infrastructure gaps is imperative for sustainable development.
Challenges
- Economic Discontent: Persistent unemployment and inflation have created widespread dissatisfaction among the populace.
- Political Mandate: Recent electoral outcomes reflect a voter mandate for addressing economic grievances and improving living standards.
- Food Price Inflation: High and sustained inflation in essential food items, particularly cereals and pulses, burdens low-income households.
- Infrastructure Deficits: Critical gaps in physical and social infrastructure, such as healthcare and education, hinder economic progress and social development.
- Public Sector Capacity: The public sector’s ability to deliver essential services like transportation, sanitation, and healthcare remains insufficient.
- Private Sector Limitations: Reliance on the private sector alone has not adequately addressed long-standing infrastructure needs and economic disparities.
- Policy Efficacy: Previous economic policies have not effectively translated into tangible improvements in quality of life and economic opportunities for the majority.
| Government initiatives to improve economic conditions in India:
1. Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan: Launched to promote self-reliance across sectors through incentives for domestic manufacturing and reducing dependency on imports. 2. National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP): Aims to invest ₹111 lakh crore in infrastructure projects over 5 years to boost economic growth, create jobs, and improve connectivity. 3. Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY): Ensures financial inclusion by providing bank accounts to the unbanked population, facilitating direct benefit transfers and access to credit. 4. Make in India: Initiative to encourage manufacturing in India by easing regulations, enhancing infrastructure, and promoting skill development. 5. Digital India: Promotes digital literacy, e-governance, and digital infrastructure development to enable inclusive growth and enhance efficiency. 6. Skill India Mission: Aims to train and skill youth for better employability, fostering entrepreneurship and reducing unemployment. |
Way Forward
- Targeted Economic Reforms: Implement specific reforms aimed at reducing unemployment, controlling inflation, and fostering inclusive growth.
- Infrastructure Investment: Prioritize substantial investments in physical and social infrastructure to support economic activities and enhance living standards.
- Agricultural Sector Focus: Address agricultural productivity and food security by promoting sustainable farming practices and ensuring fair food pricing.
- Public Sector Strengthening: Enhance the capacity of the public sector to deliver essential services efficiently and at scale, focusing on healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
- Social Welfare Enhancements: Expand and improve welfare programs to provide adequate support to vulnerable populations and mitigate economic disparities.
- Long-term Development Vision: Develop and implement a comprehensive long-term economic development plan that addresses both immediate challenges and future growth needs.
- Strengthening Governance: Ensure effective governance and accountability in policy implementation to build public trust and confidence in economic management.
Conclusion
Addressing the economic discontent mandates a shift towards targeted reforms, substantial infrastructure investments, and enhanced public sector capacity. This approach not only meets immediate challenges of unemployment and inflation but also sets a sustainable course for inclusive economic development, aligning with the aspirations of the electorate.
Source:Indian Express
Mains Practice Question:
Critically analyze the economic challenges highlighted by recent electoral outcomes in India. Discuss the strategic reforms and policy measures needed to address these challenges and foster inclusive growth.
Associated Article:
https://universalinstitutions.com/economic-growth-and-development/