A GLOBAL CALL TO EMBRACE SUSTAINABLE ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Syllabus:
GS 3:
- Science and Technology- Developments and their Applications and Effects in Everyday Life.
- Conservation, Environmental Pollution and Degradation, Environmental Impact Assessment.
Why in the News?
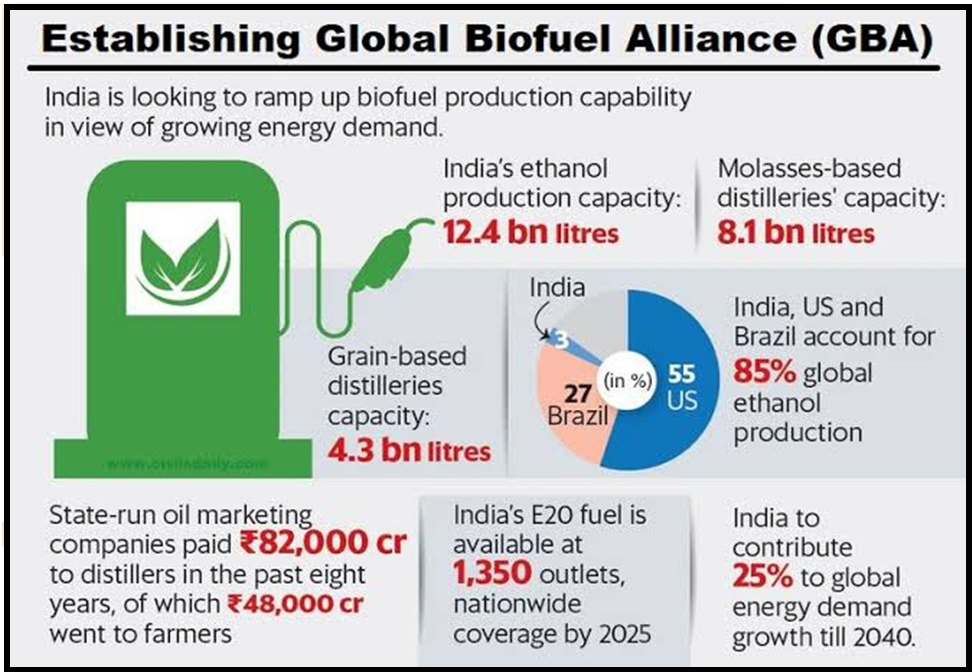
India’s recent launch of the Global Biofuels Alliance underscores its commitment to promoting sustainable energy solutions. This initiative, coupled with the push for increased ethanol blending under the Ethanol Blended Petrol Programme (EBP), highlights the nation’s strategic focus on reducing carbon emissions and enhancing energy security.
Source: UGI
Overview and Context:
- Biofuels Alignment: India’s emphasis on biofuels aligns with national campaigns like Swachh Bharat, Make in India, and AatmaNirbhar Bharat, reflecting its commitment to sustainable development.
- World Biofuel Day: Celebrated on August 10, this day highlights the transformative potential of biofuels as a renewable, low-carbon alternative, crucial for addressing global energy needs and environmental challenges.
- Renewable Energy Benefits: Biofuels, derived from organic materials, reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance energy security by decreasing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Global Contributions: World Biofuel Day recognizes the global efforts in promoting biofuels, encouraging their continued exploration and adoption as vital energy sources.
- India’s Vision: Indian Prime Minister Emphasizes that biofuels can significantly contribute to India’s growth, benefiting both urban and rural areas.
What are Biofuels?
Types:
|
Transforming Biomass into Liquid Energy
- Biofuel Categories: Biofuels, derived from biomass like plants and bio-waste, are categorized into first, second, and third generations, each representing different technological advancements.
- First-Generation Biofuels: Ethanol and biodiesel, the most common first-generation biofuels, are produced from food crops like corn, sugarcane, and vegetable oils, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
- Cost-Effective Alternative: Biofuels present a cost-effective, eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels by converting biomass directly into liquid energy.
- Environmental Impact: The use of biofuels reduces greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to global efforts in combating climate change and fostering a sustainable energy future.
- Technological Progress: Continued advancements in biofuel technology are essential for maximizing the potential of these renewable energy sources in addressing global energy challenges.
Ethanol: A Cornerstone of India’s Biofuel Strategy
- Significance of Ethanol: Ethanol, primarily produced from sugarcane and corn, is a key component of India’s biofuel policy, particularly in the transportation sector.
- E20 Target: India aims to achieve 20% ethanol blending with petrol by 2025 (E20), reducing its dependence on imported crude oil and enhancing energy security.
- Government Initiatives: The Indian government has implemented initiatives to boost ethanol production, including financial incentives for sugar mills and diversification of feedstock.
- Environmental Benefits: Ethanol blending reduces carbon emissions, alleviates air pollution, and supports India’s commitment to reducing its carbon footprint under the Paris Agreement.
- Economic Impact: Ethanol production supports farmers by providing an additional revenue stream, contributing to India’s agricultural and energy sectors simultaneously.
Global Biofuel Alliance: India’s Strategic Leadership in Biofuels
- Global Biofuels Alliance: India’s leadership in establishing the Global Biofuels Alliance underscores its commitment to sustainability, clean energy, and global collaboration in advancing biofuels.
- Promoting Collaboration: The alliance aims to foster international collaboration, bringing together countries, organizations, and stakeholders to promote biofuels as a key component of the global energy transition.
- National Policy Alignment: India’s proactive stance aligns with its broader energy strategy, including the National Policy on Biofuels 2018 and the Ethanol Blending Programme.
- Innovation and Best Practices: The alliance is expected to drive innovation, facilitate the sharing of best practices, and create a supportive global policy framework for accelerating biofuel adoption.
- Global Leadership: By spearheading this initiative, India positions itself as a global leader in the biofuels sector, contributing significantly to the global fight against climate change.
Challenges in Biofuel Implementation:
- Feedstock Availability: Limited availability of sustainable feedstock’s, such as non-food crops and agricultural waste, constrains biofuel production, affecting scalability.
- Technological Barriers: Inadequate technological advancements in converting biomass to biofuels, particularly second and third-generation biofuels, hinder efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Economic Viability: High production costs and limited financial incentives challenge the economic viability of biofuels, making them less competitive compared to fossil fuels.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Insufficient infrastructure for biofuel production, distribution, and storage hampers widespread adoption and integration into the existing energy system.
- Policy and Regulatory Issues: Inconsistent and fragmented policies, along with regulatory hurdles, create uncertainty for investors and slow down the development of the biofuel sector.
Way Forward/ What India Needs to do?
- Enhanced Feedstock Research: Invest in research to diversify and improve the availability of sustainable feedstock, focusing on non-food crops and agricultural residues.
- Technological Innovation: Promote R&D in advanced biofuel technologies, particularly for second and third-generation biofuels, to enhance efficiency and reduce production costs.
- Financial Incentives: Implement targeted subsidies, tax breaks, and financial support to make biofuel production economically viable and attract private investment.
- Infrastructure Development: Build robust infrastructure for biofuel production, distribution, and storage to ensure seamless integration into the energy supply chain.
- Clear Policy Framework: Establish a consistent, long-term policy and regulatory framework to provide stability and encourage investments in the biofuel sector.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Foster collaborations between government, industry, and academia to drive innovation and scale up biofuel production sustainably
Conclusion
The growing emphasis on biofuels marks a significant step towards achieving India’s energy sustainability goals. By advancing biofuel technology and infrastructure, and fostering global cooperation, India can lead the way in transitioning to a cleaner, greener energy future, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
Source:Indian Express
Mains Practice Question
Discuss the potential of biofuels in achieving energy security and environmental sustainability in India. What challenges hinder the large-scale adoption of biofuels, and how can these be addressed?”
Associated: