A DEMAND THAT COULD HAMPER GENDER EQUALITY
Relevance:
- GS 1 – Role of women and women’s organization
- GS 2 – Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes
Why in the News?
- Recently, the Union Women and Child Development Minister opposes paid menstrual leave, stating menstruation is not a “handicap.”
- She argues that implementing menstrual leave could potentially lead to discrimination against women in the workforce.
- She emphasises the importance of not proposing measures that could deny women equal opportunities based on viewpoints regarding menstruation.
- Critique of Paid Menstrual Leave
- Demanding paid leave for menstruation undermines the struggle against discrimination.
- It risks trivializing the women empowerment movement by collectively labeling all women as needing special accommodations.
- Such demands fail to consider individual experiences and may perpetuate stereotypes about women’s capabilities.
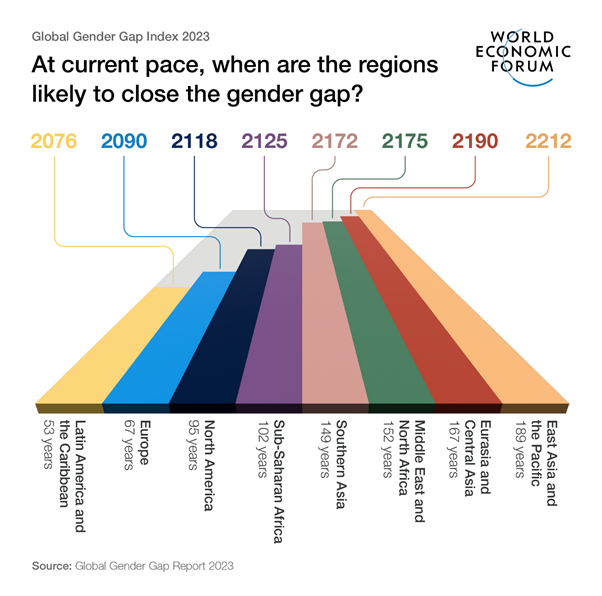
Global Gender Gap Widening
- The World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Report 2023 reveals a widening gender gap instead of progress.
- It estimates 149 years to achieve gender equality in Southern Asia at the current pace.
- Women earn 84 cents for every dollar earned by men, reflecting disparities in workforce compensation.
Low Female Workforce Participation
- Women’s participation in the labor force lags behind men’s.
- Fewer women occupy leadership positions compared to men.
- These disparities contribute to the gender gap in economic opportunities and decision-making roles.
Impact of Mandatory Paid Menstrual Leave on Employment
- It could discourage companies from hiring women.
- It adds to existing barriers faced by women in accessing employment opportunities.
- Such policies may inadvertently perpetuate gender inequality in the workforce.
- Well-intentioned measures could inadvertently widen the gender gap by reinforcing stereotypes
- Government endorsement of ‘special status’ for menstruating women could reinforce social stigma.
- It may intensify period shaming in cultures where menstruation is considered impure.
- Validating such beliefs contradicts efforts to combat menstrual taboos and promote gender equality..
- Effective strategies for gender equality should address root causes while avoiding unintended consequences.
Challenges Faced by Women in Menstrual Health
- The National Family Health Survey (NFHS) indicates widespread reliance on cloth for menstrual protection among young women in India.
- Reusing cloth poses health risks due to infections, driven by insufficient awareness and societal taboos.
- Menstruation-related challenges, including lack of access to menstrual hygiene products and stigma, contribute to girls’ school dropout rates and social exclusion.
| Menstrual Leave Policies in Japan
● Japan provides unpaid menstrual leave, but it’s largely unused due to reluctance among women. ● Fear of sexual harassment deters women from availing this leave and disclosing their menstrual status. ● Data shows only 0.9% of women in Japan’s workforce utilize menstrual leave, despite the policy existing for over seven decades. Gender Inequality in Japan’s Workforce ● Japan ranks poorly in gender equality, slipping from 121st to 125th in the World Economic Forum’s rankings. ● Despite higher education levels among young women, disparities emerge in the workforce. ● Women face lower employment rates and unequal pay compared to men, even with equivalent qualifications. |
Implementation Challenges of Paid Menstrual Leave
- Potential Misuse: Implementing paid leave for menstruation raises questions about rightful usage and potential misuse.
- Balancing the rights of employees with the objectives of such policies is crucial to avoid instances of abuse or discrimination.
- Logistical Challenge: Determining when such leave is justified and preventing abuse poses logistical challenges.
- Employers may struggle to enforce policies without infringing on employees’ rights or dignity.
- Inappropriate enforcement methods:
- In 2020, 66 girl students in Bhuj, Gujarat, were subjected to strip searches to check for menstruation.
- Similar incidents occurred in 2017 in Muzzaffarnagar, where 70 girls were forced to undress by school staff.
Acknowledgment of Menstrual Challenges
- Menstrual cycles can be physically and emotionally challenging for some individuals.
- Symptoms may range from discomfort to debilitating effects, impacting daily functioning.
- Addressing menstrual challenges requires a nuanced approach that
| Sabrimala Temple Issue
● The exclusion of menstruating women from the Sabrimala temple sparked widespread debate. ○ It challenged the notion of menstrual taboo and highlighted discrimination based on menstruation. ● Advocates emphasized menstruation as a natural phenomenon, not a condition warranting exclusion. Women’s Push for Inclusion in Combat Roles: ● Women have advocated for inclusion on the front lines of war, prompting the Supreme Court of India to push for equal evaluation and testing standards. ● The government’s argument against women in ground combat roles highlights ongoing debates about gender and suitability for certain positions. Gender Pay Equity in Corporate Organizations: ● Women in corporate settings are fighting for pay equal to their male counterparts, highlighting persistent disparities in compensation. ● The struggle for gender pay equity underscores broader issues of gender discrimination in the workplace. |
- balances individual needs with broader gender equality goals.
- Rather than blanket policies, solutions should be inclusive and considerate of diverse experiences.
- Empowerment lies in acknowledging and accommodating individual realities while striving for systemic change.
- Acknowledging period pain and symptoms is important, but labeling them as a blanket biological disadvantage may not fully capture the diverse nature of menstrual experiences.
- Recognizing individual needs and tailoring support on a case-by-case basis promotes inclusivity and addresses the unique challenges faced by individuals during menstruation.
- Promoting Inclusivity Through Individualized Support:
- Promotes inclusivity while addressing the diverse needs of individuals.
- Providing accommodations on a case-by-case basis ensures that women are not disadvantaged due to their menstrual cycles.
Mains Question
What are the implications of opposition to paid menstrual leave, citing menstruation as a natural aspect of women’s lives, on workplace equality and discrimination? Analyse.