A $ 5 TRILLION ECONOMY ,BUT FOR WHOM?
Relevance:
GS 3: Indian Economy and issues relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources, Growth, Development and Employment.
Why in the News?
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the extension of the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Ann Yojna scheme (PMGKAY), providing 5 kg of food grains free every month to beneficiaries of the National Food Security Act, by five years till 2028.
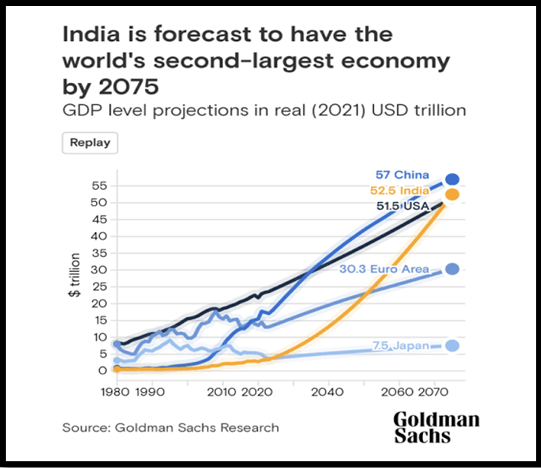
Source: Goldman Sachs
Imperative Behind the decision:
- This decision was taken to ensure that no citizen sleeps hungry as India becomes the third largest economy in the world with a GDP of $5 trillion in 2028.
Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Ann Yojna (PMGKAY) Extension
- Background and Initial Implementation
- Introduction during the Pandemic (2020):
- PMGKAY initiated in 2020 amid the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Aimed to provide 5kg free food grains to eligible ration card holders under NFSA 2013.
- Initial Expiry and Extension:
- Initially set to expire in December 2022.
- Extended till December 2023.
- Recently granted an additional extension for five more years.
- Government Allocation and Cost:
- 1,118 lakh metric tonnes of food grains allocated since inception.
- Allocated from the central procurement pool, incurring a cost of Rs 3.9 lakh crore.
- National Food Security Act, 2013 (NFSA)
- Paradigm Shift in Food Security:
- NFSA 2013 marks a shift from welfare to a rights-based approach to food security.
- Beneficiaries and Legal Entitlements:
- Legally entitles up to 75% rural and 50% urban population for subsidized food grains.
- Encompasses two categories: Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY) and Priority Households (PHH).
- Empowers women, mandating the eldest woman above 18 as the head for ration card issuance.
- Distribution Provisions:
- AAY households entitled to 35 kg of foodgrains. monthly, irrespective of family size.
- Priority Households receive 5 kg per member based on family size.
- Merger of PMGKAY and NFSA
- Integration in January 2023:
- PMGKAY merged with NFSA in January 2023.
- Resulted in providing rations to AAY and PHH families at no cost.
- Eliminated additional provisions introduced during the pandemic, incorporating PMGKAY’s free component into NFSA.
Japan’s Economic Journey
Drawing parallels with Japan, the third-largest economy globally, reveals socio-economic challenges despite economic success.
- Social Impact in Japan: Japan’s economic climb resulted in social issues, including
- high suicide rates,
- social withdrawal (hikikomori), and
- lonely deaths (kodokushi).
- Post-2008 Economic Crisis: After the 2008 financial crisis, Japan faced economic challenges, with reduced spending, shrinking exports, and a shift in the global economic order.
- Japan-China Relations(Ego-Free Diplomacy): Despite losing its second-largest economy status to China, Japan displayed diplomatic pragmatism, acknowledging China’s role in sustaining demand and fostering economic cooperation.
Indian Economic Growth and Citizens’ Reality
- $5 Trillion Economy Target:
As India aims for a $5 trillion economy by 2028, questions arise about its impact on citizens, especially the 80 crore still reliant on free rations.
- Capital Disparity:
Oxfam data reveals a significant wealth gap, with 1% owning 41% of the wealth, while 50% own only 3%.
- Resource-Rich Power Brokers:
The dash toward a $5 trillion economy appears controlled by resource-rich power brokers, with low-resource citizens funding the investment.
- Labour Contribution:
GST statistics indicate that 64% of the tax comes from the bottom 50% of the population, highlighting the contribution of low-resource citizens to economic growth.
Factors Influencing Economic Growth
- Educational and Skill Challenges:
- Labour, a key driver of growth, faces hurdles due to inadequate education, skill gaps, and limited digital literacy, hindering productivity.
- Government’s Tools for Growth:
- Key sectors and tools, includes, the digital economy, fintech, and climate change initiatives.
- However, the accessibility of these opportunities to marginalized citizens is questionable.
Concerns and Critique of Economic Target
- Per Capita Income Disparities:
India’s per capita income, ranking 149 among 194 countries, raises concerns about the well-being of its population compared to other nations.
- Distribution and Inequality Index:
The focus on achieving a $5 trillion GDP raises questions about the distribution of wealth and the potential deepening of the inequality index( by World Economics), currently at 21.9, below China and Japan.
Key challenges in becoming $5 trillion economy
- Economic Challenges
- High levels of poverty and inequality
Note: India secured the 107th position among 121 nations in the 2022 Global Hunger Index (GHI).
- Inadequate infrastructure
- Low levels of skill development
- Social Challenges
- Large and growing population
- Widespread illiteracy
Note: The Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) for higher education in India is recorded at 27.1 percent.
- Deep-rooted social divisions
- Political Challenges
- Corruption
Note: In the 2021 Corruption Perception Index by Transparency International, India held the 85th position out of 180 countries.
- Burdensome bureaucracy
- Regional tensions
- Other Challenges Includes:
- Digital Literacy Constraints
- Environmental Sustainability
- Technology Accessibility Gaps
Two Indias Amidst Economic Growth
- Economic Goals vs. Social Reality: While India pursues the ambitious $5 trillion economy goal, a significant portion of the population remains stuck in the slow lanes, highlighting the challenge of achieving inclusive growth.
Note: India’s per capita income projected at $2,400
- Inclusivity Concerns: The disparity in wealth distribution, education, and accessibility to growth sectors underscores the need for a more inclusive approach to ensure that economic prosperity benefits all citizens.
- Balancing Growth and Social Well-being: Achieving economic milestones should align with addressing social issues, emphasizing the importance of a balanced and equitable approach to development.
Key Initiatives towards achieving
$ 5 trillion economy target
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY): Financial inclusion initiative to provide access to banking services for all, promoting savings and investments.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST): Unified indirect tax system aimed at simplifying taxation, reducing corruption, and fostering a common market.
- Make in India: Campaign encouraging domestic manufacturing, job creation, and self-reliance in key sectors.
- Startup India: Promoting entrepreneurship by providing support, funding, and a conducive ecosystem for startups to flourish.
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY): Facilitating micro-enterprises by offering financial support and credit to small businesses.
- Digital India: Promoting digital literacy, e-governance, and technology-driven initiatives to boost efficiency across sectors.
- National Skill Development Mission: Enhancing the employability of the workforce through skill development programs aligned with industry needs.
- Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan: Self-reliance initiative focusing on economic resilience, local manufacturing, and reducing dependency on imports.
- National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP): Comprehensive plan for infrastructure development to support economic growth and create jobs.
- Swachh Bharat Abhiyan: Improving sanitation and cleanliness, contributing to a healthier population and promoting tourism.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY): Affordable housing scheme aimed at providing housing for all, boosting construction and related industries.
- Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY): Health insurance scheme to provide financial protection against medical expenses, ensuring better health outcomes.
- Saubhagya Yojana -Rural Electrification: to ensure electricity access in rural areas, promoting economic activities.
- PM Kisan Samman Nidhi: Direct income support to farmers, ensuring financial stability in the agriculture sector.
- National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS): Encouraging skill development through apprenticeships, bridging the gap between education and employment.
- One Nation, One Ration Card: Ensuring seamless access to food supplies for beneficiaries across states, promoting social welfare.
The pursuit of a $5 trillion economy raises critical questions about equitable distribution, societal well-being, and inclusivity. As India aims for economic heights, addressing disparities in wealth, education, and access to cutting-edge sectors becomes paramount for a truly prosperous and harmonious nation.
Source : https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/a-5-trillion-economy-but-for-whom/article67565388.ece
Mains Practice Question
Critically evaluate the implications of India’s goal of becoming a $5 trillion economy by 2028, considering the challenges as roadblocks.

 Source: Goldman Sachs
Source: Goldman Sachs

