India to assume chairmanship of Wassenaar Arrangement on January 1, 2023
Recently, on 26th annual plenary of the Wassenaar Arrangement in Vienna, Ireland handed over the chairmanship to India and India will officially assume the chairmanship from 1st January, 2023.
What is Wassenaar Arrangement?
- About:
- The Wassenaar Arrangement is a voluntary export control regime. The Arrangement, formally established in July 1996, has 42 members who exchange information on transfers of conventional weapons and dual-use goods and technologies.
- Dual-use refers to the ability of a good or technology to be used for multiple purposes – usually peaceful and military.
- Wassenaar Arrangement’s Secretariat is in Vienna, Austria.
- The Wassenaar Arrangement is a voluntary export control regime. The Arrangement, formally established in July 1996, has 42 members who exchange information on transfers of conventional weapons and dual-use goods and technologies.
- Members:
- It has 42 member states comprising mostly NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) and EU states.
- Participating States are required to report their arms transfers and transfers/denials of certain dual-use goods and technologies to destinations outside the Arrangement on a six-monthly basis.
- India became a member of the Arrangement in 2017.
- It has 42 member states comprising mostly NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) and EU states.
- Objectives:
- The group works by regularly exchanging information in respect of technology, both conventional and nuclear-capable, that is sold to, or denied to countries outside the grouping.
- This is done through maintenance and updating of detailed lists of chemicals, technologies, processes and products that are considered militarily significant.
- It aims at controlling the movement of technology, material or components to countries or entities which undermine international security and stability.
- Wassenaar Arrangement Plenary: It is the decision-making body of the Arrangement.
- It is composed of representatives of all Participating States and normally meets once a year, usually in December.
- The position of Plenary Chair is subject to annual rotation among Participating States.
- In 2018 the Plenary Chair was held by the United Kingdom, and in 2019 the Chair is held by Greece.
- All Plenary decisions are taken by consensus.
Why is the Chairmanship Significant for India?
- Can Bolster Anti-Terrorism Efforts:
- The timing of India’s WA chairmanship coincides with a recent increase in country’s anti-terrorism position in international bodies.
- India is also actively engaging global stakeholders in curbing terrorist financing.
- Indian home minister is presently the chair of the No Money for Terrorism (NMFT) ministerial initiative.
- Prevent Arms Diversion to Terrorists:
- As a chair of the plenary, India would be in a position to steer discussions of the group to further strengthen the export controls to prevent arms diversion to terrorists or to sovereign nations supporting terrorism.
- Strong Anti-Proliferation Framework:
- The worsening economic crisis in India’s western neighbour coupled with rapid radicalization of historically moderate sects in communities in the country poses a peculiar set of challenges to India.
- Strengthening the licensing and enforcement practices under the WA and adoption of new export controls in areas like flight technology, interception technology and digital investigation tools will pave the way for the creation of a strong anti-proliferation framework for South Asia.
- Democratization of space and Defense Technologies:
- India can play a significant role in democratising access to technologies and processes that can serve as crucial building blocks for the newly emerging defence and space manufacturing sectors in India.
- India is slowly emerging as a low-cost producer of several items in the WA’s control lists.
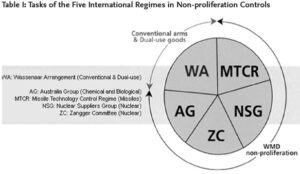
What are other Export Control Regimes?
- The Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG), for the control of nuclear related technology.
- The Australia Group (AG) for control of chemical and biological technology that could be weaponized.
- The Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) for the control of rockets and other aerial vehicles capable of delivering weapons of mass destruction.
Way Forward
- Membership to these not only allows greater technology and material access but enhances the credibility of a nation as a responsible member of the world order.
- India is poised to become a significant player in the world and thus requires a voice to further its claim as a rising power.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
- Recently, the USA decided to support India’s membership in multi-lateral export control regimes called the “Australia Group” and the “Wassenaar Arrangement”. What is the difference between them? (2011)
- The Australia Group is an informal arrangement which aims to allow exporting countries to minimize the risk of assisting chemical and biological weapons proliferation, whereas the Wassenaar Arrangement is a formal group under the OECD holding identical objectives.
- The Australia Group comprises predominantly of Asian, African and North American countries whereas the member countries of Wassenaar Arrangement are predominantly from the European Union and American Continents.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)