Sustainable development is a commonly known phrase with regard to environment. Briefly explain what do you mean by it. Also explain the steps to be taken in different levels to achieve this goal.
Introduction:
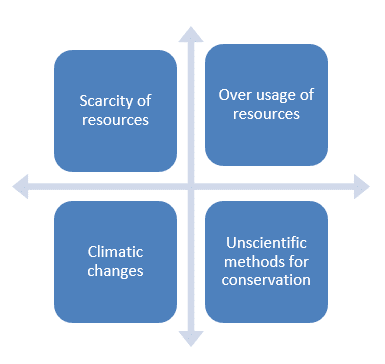
The resources we use can be broadly classified as renewable and non-renewable. Sustainable development refers to utilizing these non-renewable resources in optimum manner, so that it meets the demands of this generation without compromising the needs and deamnds of upcoming generations.
Body:
Need for sustainable development:
Elements of Sustainable development:
1) Environmental aspects:-
• Minimizing the usage of exhaustible resources.
• Includes step such as rain water harvesting, construction of sustainable buildings, environmental conservation,etc
2) Social aspects:-
• Developing communities & culture
• Providing education & creating awareness
• Fairly distributed quality of life
3) Economic aspects:-
• Equity in distribution of resources
• Not mongering for power
International efforts for achieving Sustainable Development:
United Nations has launched the 2030 agenda for sustainable development. There are 17 goals and 169 targets in this agenda.
The other major initiatives are:
• Ramsar convention, 1971
• Vienna convention, 1985
• Montreal Protocol, 1987
• Kyoto Protocol, 1997
• Environment action plan adopted by South Asian Association for Regional Co-operation, in 1997.
• Community initiatives like Wetlands International
• Co-operative movements such as AMUL India.
Conclusion:
Although there are many efforts in this regard, most of them are not legally bound. Hence, many nations have not met their goals. There is a clear divide between the developed, developing and under developed countries. Under developed and Developing countries are still struggling to provide basic needs whereas most developed countries tend to not take measures for sustainable development. A unified effort is needed from all the countries of the world to make sustainable development a reality and protect our planet from environment degradation.