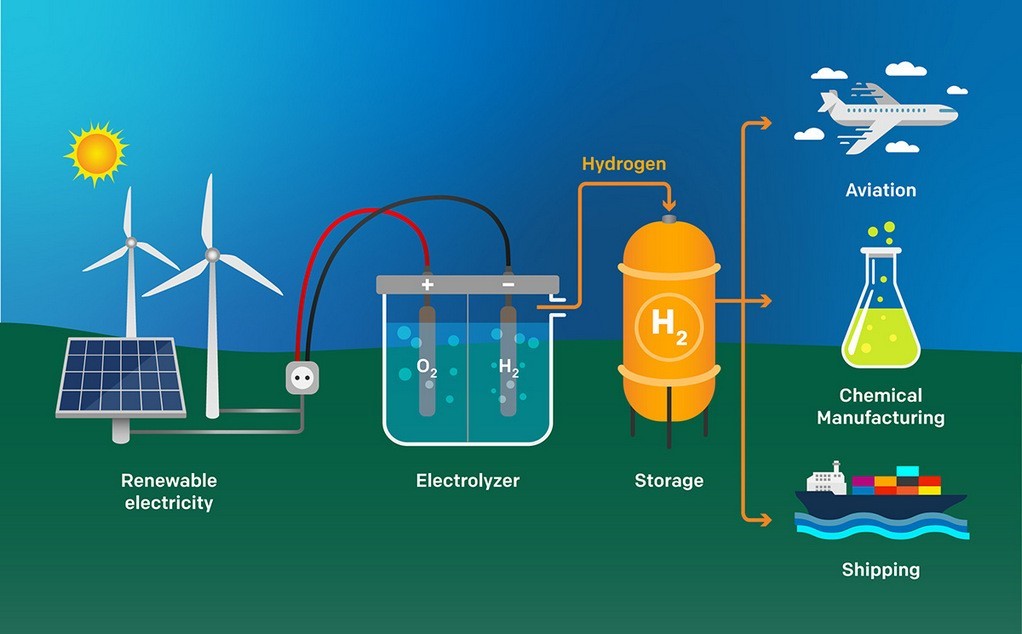
Hydrogen for Clean Energy
Hydrogen for Clean Energy
Why in the News ?
India’s preliminary assessment of natural hydrogen reserves, including findings in the Andaman Islands, has sparked interest in tapping these resources to meet growing hydrogen demand and achieve net-zero emissions by 2070, reducing dependence on hydrogen manufacturing.
India’s Natural Hydrogen Potential:
- India’s hydrogen demand is projected to rise from 6 Mt/year (2020) to 50 Mt/year by 2070.
- A preliminary study estimates India may have 3,475 million tonnes of natural hydrogen.
- If tapped, this resource could eliminate the need for costly hydrogen production and accelerate decarbonisation.
- Recent discovery in the Andamans calls for targeted geological surveys.
- Key assessment factors include rock quality, reservoir accessibility, seals, and accumulation viability.
Key Challenges in Hydrogen Exploration
- Unlike oil and gas, exploration techniques for natural hydrogen are still nascent.
- Extraction technology must adapt to hydrogen’s high diffusivity and small molecular size.
- Safety concerns are significant due to hydrogen’s reactivity—mitigation includes resistant coatings, additives, and durable materials.
- Cost-effectiveness will depend on finding large reserves and reducing infrastructure costs.
Policy and Technological Roadmap
- India can replicate the SRRA model used for solar mapping to assess hydrogen sites.
- The S. ARPA-E is exploring techniques to generate hydrogen in-situ using iron-rich rocks and CO₂ injection.
- India’s oil and gas industry, under DGH, can lead exploration with grants and loans.
- Modified pipelines and underground storage are key to a viable hydrogen ecosystem.
- Clear regulations and public-private partnerships are essential to attract investment.
What is Natural Hydrogen?●Definition: Naturally occurring molecular hydrogen (H₂) formed via geological processes like serpentinisation and radiolysis. |