Gender Barriers in TB Treatment: Challenges and Solutions
Syllabus:
GS-2:
Health , Government Policies & Interventions, Important International Institutions
Focus:
Despite India’s commitment to eliminate TB by 2025, women face unique challenges in diagnosis and treatment due to stigma, financial constraints, and social isolation. Reports highlight underdiagnosis, treatment dropouts, and discrimination, necessitating gender-sensitive policies and stronger support systems to ensure equitable healthcare access for women suffering from tuberculosis (TB).
Gender Disparities in TB Diagnosis and Treatment:
The Impact of Social Norms
- Women face stigma, discrimination, and isolation due to TB.
- Many are advised to hide their illness to avoid societal backlash.
- Stigmatization leads to delayed diagnosis and incomplete treatment, worsening health outcomes.
Underdiagnosis and Access to Healthcare
- The India TB Report 2023 highlights that men are more affected by TB due to factors such as smoking and occupational exposure.
- However, women face underdiagnosis due to lack of health-seeking behavior and prioritization of family needs over personal health.
- Poverty and financial constraints make accessing TB care difficult for women, especially those in low-income families.
Psychological and Social Impact on Women
- Women who recover from TB face mental health challenges due to changes in appearance, physical weakness, and social exclusion.
- Many experience job loss and family abandonment, worsening their financial instability.
About TB Tuberculosis (TB):
- Cause: TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a bacterium from the Mycobacteriaceae family.
- Types:
- Pulmonary TB: Affects the lungs.
- Extra-pulmonary TB: Affects other organs.
- History: TB dates back to 3000 BC in Egypt.
- Impact: Despite being treatable and curable, TB remains a global health challenge.
Infection Prevalence
- Global Burden: 10 million people contract TB annually.
- Mortality: 1.5 million deaths per year, making it the world’s deadliest infectious disease.
- HIV & TB: TB is the leading cause of death among HIV-positive individuals.
- Geographical Distribution: 50% of cases are in Bangladesh, China, India, Indonesia, Nigeria, Pakistan, Philippines, and South Africa.
Treatment & Drug Resistance
- Standard Treatment:
- 6-month course of 4 antimicrobial drugs under supervision.
- Drug Resistance:
- Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB): Resistant to isoniazid & rifampicin.
- Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB): Resistant to second-line drugs like Bedaquiline.
Strategies to Mitigate TB Crisis:
- A. Patient-Centric Approach
- Prioritizing Patient Needs: Focus on holistic TB care, including social and economic support.
- Advocacy & Community Involvement: TB survivors push for better healthcare policies.
- B. Strengthening Healthcare Infrastructure
- Bridging Policy & Ground Realities: Expand TB testing, free treatment, and quality drugs.
- Molecular Testing: Gold standard, but less than 25% of patients get it as their first test.
- C. Improving TB Care Accessibility
- Community-Based TB Care: Train frontline workers for comprehensive patient support.
- Mental Health Support: Address stigma, discrimination, and psychological stress.
- D. Multi-Sectoral Approach
- Addressing Socio-Economic Factors: Poverty alleviation, nutrition, ventilation, and air quality improvements.
- E. Technology-Driven Solutions
- AI & Digital Health: For diagnosis, treatment adherence, and surveillance.
- Portable X-ray Technology: AI-driven X-ray interpretation for early detection.
- 8-Point Agenda for TB Elimination:
- Early Detection:
- Mandatory screening of contacts & families of TB patients.
- Treatment Categorization:
- Identify drug resistance early for personalized regimens.
- Treatment Adherence:
- Ensure sustained medication despite migration or symptom relief.
- Zero Mortality Goal:
- Prevent TB deaths through efficient healthcare intervention.
- Ensuring Drug Availability:
- Address procurement issues of MDR-TB medicines.
- Health System Integration:
- Strengthen referral networks to prevent treatment gaps.
- Robust Notification System:
- Improve Ni-Kshay for real-time TB data tracking.
- Treatment Portability:
- Allow seamless access to TB treatment across states & regions.
Key Initiatives to Combat TB:
- A. Global Efforts
- WHO’s ‘Find. Treat. All. #EndTB’ initiative.
- Global Tuberculosis Report by WHO.
- B. India’s Efforts
- Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan.
- National Strategic Plan (2017-2025) for TB Elimination.
- TB Harega Desh Jeetega Campaign.
- Nikshay Poshan Yojana: ₹1000/month nutritional support for TB patients.
- India aims to eliminate TB by 2025, focusing on early detection, effective treatment, community support, and policy interventions.
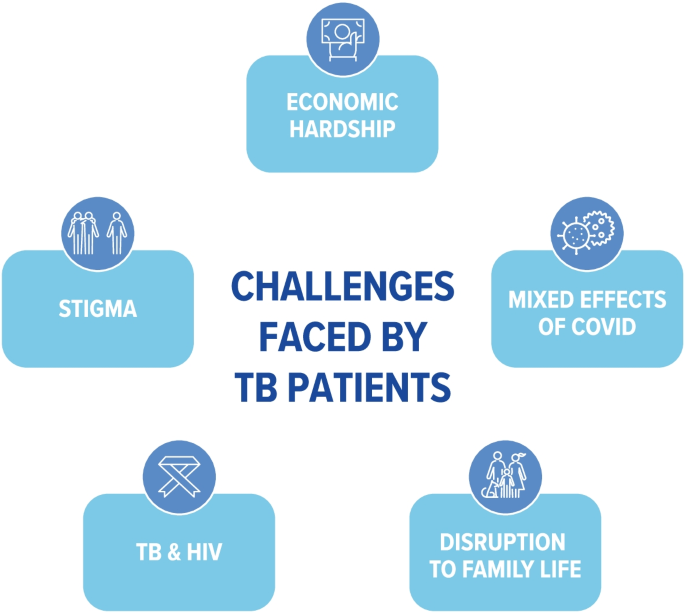
Barriers Faced by Women in TB Treatment:
Financial and Nutritional Challenges
- High cost of TB treatment forces many women to either delay or discontinue medication.
- Nutritional needs during TB treatment are often neglected, leading to poor recovery.
Social Isolation and Family Neglect
- Lack of family support discourages women from seeking medical care.
- Women diagnosed with TB are often abandoned by their families, leading to economic hardship.
- Many are hesitant to disclose their illness due to fear of losing income or facing discrimination.
Midway Treatment Dropouts
- Many women stop taking medication prematurely once symptoms reduce, leading to drug resistance and worsening health.
- Fear of stigma prevents them from seeking follow-up treatment.
India’s TB Elimination Goals and Government Initiatives:
National Targets for TB Elimination
- India aims to eliminate TB by 2025, ahead of the global 2030 target.
- In 2022, 331,000 TB-related deaths were recorded, with India contributing 27% of the global TB burden.
- 5% of new cases and 13% of previously treated cases are drug-resistant.
- 2% of TB patients in India are also HIV-positive, increasing treatment complexity.
Key Government Programs
- National TB Elimination Program (NTEP): Previously called Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP), renamed in 2020.
- Nikshay Poshan Yojana: Provides ₹1,000 per month to TB patients during treatment.
- Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan: Community-driven initiative for additional nutritional support.
Government Strategies for Effective Implementation
- Strengthening early detection, effective treatment, and prevention measures.
- Improving direct benefit transfer mechanisms to ensure patients receive financial aid.
- Enhancing public-private partnerships to engage private healthcare providers.
- Promoting awareness campaigns to reduce TB stigma and encourage treatment adherence.
The Role of NGOs and Community Support:
Need for Grassroots-Level Interventions
- Women at the grassroots level face multi-layered problems in accessing TB care.
- Many are abandoned after diagnosis, left without financial or emotional support.
- NGOs play a crucial role in bridging gaps in healthcare access and social support.
Policy Recommendations
- Strengthening outreach programs to identify and support women with TB.
- Ensuring free and accessible TB treatment to remove financial barriers.
- Providing employment security for TB-affected women to reduce income loss.
- Expanding nutritional support programs to improve recovery outcomes.
The Way Forward: Addressing Gender Inequalities in TB Care
Addressing Stigma and Raising Awareness
- Community education programs to reduce discrimination and encourage early TB diagnosis.
- Media campaigns to normalize TB treatment and recovery.
Enhancing Healthcare Accessibility
- Free TB testing and treatment centers to be expanded, especially in rural areas.
- Mobile healthcare units for TB screening in remote and marginalized communities.
Strengthening Economic and Social Support
- Incentives for employers to retain TB-affected women in the workforce.
- Government should introduce rehabilitation programs for abandoned women TB patients.
- Improved mental health support to address post-treatment psychological distress.
Focused Research and Policy Reforms
- More research on gender-specific TB challenges.
- Integrating gender-sensitive approaches into TB elimination policies.
- Stronger legal frameworks to protect TB-affected women from workplace discrimination.
Conclusion:
- Women face unique challenges in TB diagnosis, treatment, and recovery.
- Stigma, financial barriers, and lack of family support hinder effective TB care for women.
- Holistic government policies, community support, and public awareness are crucial to eliminating TB by 2025.
- Gender-sensitive approaches must be integrated into India’s TB elimination strategies to ensure no woman is left behind in the fight against TB.
Source: TH
Mains Practice Question :
Discuss the gender-specific challenges faced by women in tuberculosis (TB) diagnosis and treatment in India. How do social stigma, financial dependency, and family neglect impact their healthcare access? Suggest policy measures to ensure equitable TB care for women and accelerate India’s goal of TB elimination by 2025.