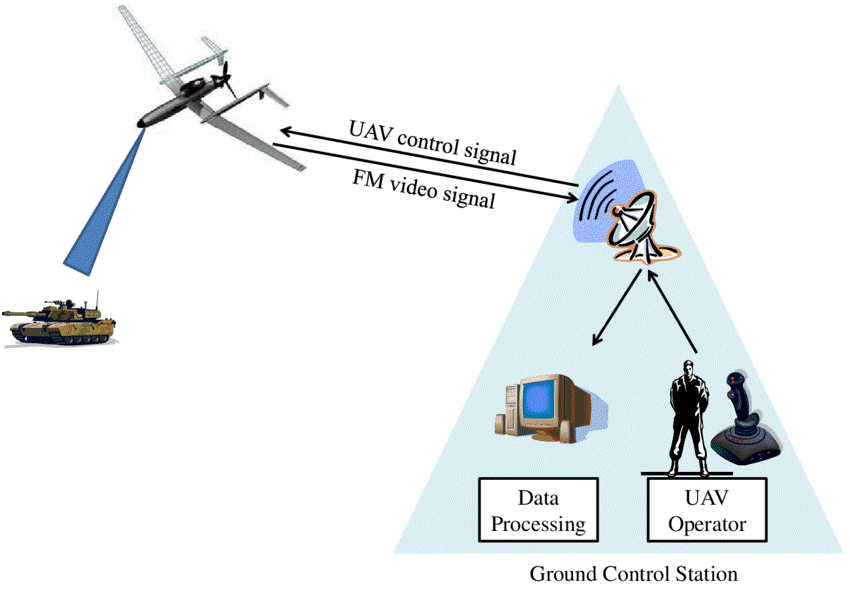
Evolving Role of UAVs in Modern Military Operations
Why in the News?
Recent sightings of Chinese UAVs near Okinawa raised concerns but did not trigger strong military responses, highlighting how drones are perceived as less threatening than fighter jets. This underscores the growing role of UAVs in global military strategies.
Advantages of UAVs :
- UAVs provide surveillance, reconnaissance, and precision strikes without risking human lives.
- They are cost-effective compared to piloted fighter jets, reducing financial loss if downed.
- UAVs can operate in hazardous environments, ensuring intelligence gathering with minimal risk.
- Their ability to loiter for extended periods enhances real-time monitoring of threats.
- Countries can use UAVs for covert operations, minimizing diplomatic fallout.
Why UAVs Are Perceived as Less Threatening ?
- Most UAVs are unarmed and primarily used for intelligence gathering.
- Even armed UAVs are generally less capable than fighter jets.
- The absence of human pilots makes UAV operations seem less aggressive.
- Lower diplomatic stakes—losing a UAV does not escalate tensions as much as losing a manned jet.
- Recent incidents, like Iran downing a S. drone (2019) and Russia intercepting an MQ-9 Reaper (2023), resulted in limited military responses.
India’s Strategy for Evolving UAV Warfare
- Enhance indigenous UAV development to reduce reliance on foreign technology.
- Integrate UAVs for border surveillance, counter-terrorism, and maritime security.
- Develop anti-drone measures to counter potential threats.
- Expand AI-driven autonomous UAVs for improved battlefield efficiency.
- Strengthen policy frameworks for ethical and strategic UAV deployment.
- Collaborate with allies to develop next-generation drone warfare capabilities.
About Drones and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs):
What Are UAVs?
- Remotely operated or autonomous aircraft with no onboard pilot.
- Used in military, commercial, and industrial applications.
- Equipped with sensors, cameras, and navigation systems for various tasks.
Types of UAVs:
- Fixed-Wing UAVs – Long-range surveillance & mapping.
- Rotary-Wing UAVs – VTOL, search & rescue, photography.
- Hybrid UAVs – Combines fixed & rotary-wing benefits.
- Combat Drones – Military strikes, intelligence gathering.
- Power Source:Battery, fuel, hybrid, hydrogen, solar—UAVs use diverse energy sources.
- Commercial & Delivery Drones – Logistics, photography, agriculture.
Applications
- Defense – Reconnaissance, surveillance, strikes.
- Agriculture – Crop monitoring, pesticide spraying.
- Disaster Management – Search & rescue, relief aid.
- Infrastructure & Surveying – Inspection, mapping, land surveys.
- Environmental Monitoring – Wildlife tracking, deforestation analysis.