Stock Market Crash: Causes, Investor Impact, and Future Outlook
Why in the News?
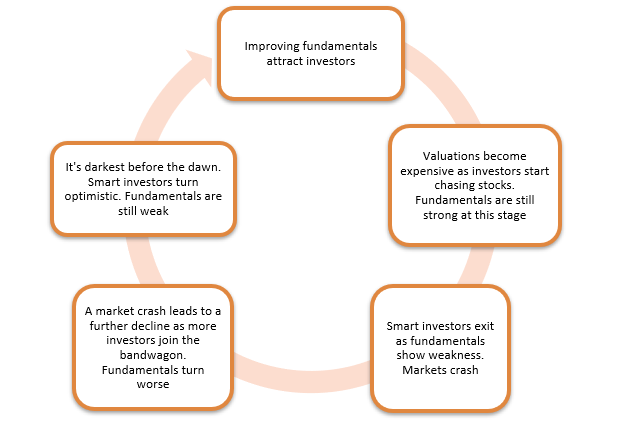
The BSE Sensex fell 1.9%, reaching an 8-month low, driven by foreign investor exits, high valuations, and weak corporate earnings. Experts suggest domestic slowdown is the key factor, while investment strategies focus on large-cap and multi-asset funds.
Causes of the Market Crash:
- Sensex Decline: The BSE Sensex fell 9%, hitting an 8-month low.
- Key Factors:
- Earnings disappointments and high valuations led to foreign investor exits.
- Global factors: Strengthening USD, better returns on US bonds, and investment shifts.
- Domestic slowdown: Weaker corporate results and reduced investor confidence.
Impact and Investor Reactions:
- Market Correction: The Nifty has dropped below its historical average.
- Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) continue selling, while Domestic Institutional Investors (DIIs) are buying.
- Retail Investors remain stable, whereas high-net-worth individuals (HNIs) show concern.
Future Outlook & Investment Strategy:
- Will the Market Decline Further?
- As long as FPIs sell, markets will remain volatile.
- Fundamentals remain strong, and once selling stabilizes, recovery is expected.
- Investment Approach:
- Avoid panic selling unless holding momentum stocks.
- Large-cap stocks and mutual funds are safer investment choices.
- Multi-asset allocation funds offer balanced exposure.
- Economic Resilience:
- No macro instability; demand-side issues can be addressed with monetary and fiscal policies.
- Budget income tax cuts may boost consumption and investments.
- Housing sector recovery is crucial for sustained economic momentum.
About the Regulation of Stock Markets in India:
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
- Regulates stock markets, ensuring transparency and investor protection.
- Oversees market intermediaries like stock brokers, stock exchanges, and mutual funds.
- Established as a statutory body under the SEBI Act, 1992.
- Monitors insider trading and fraudulent practices.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- Regulates the Government Securities (G-Secs) market and monetary policies.
- Manages foreign exchange regulations and capital flows.
- Ensures financial stability by overseeing banking sector liquidity.