🌏NISAR: India and NASA’s Eye in the Sky – A Game-Changer for Earth Observation! 🚀
The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) mission is set to make history as the world’s first dual-frequency radar imaging satellite, scheduled for launch in March 2025. This joint venture between NASA (USA) and ISRO (India) aims to provide unparalleled insights into Earth’s dynamic processes, from climate change to natural disasters. Here’s a detailed look at NISAR, packed with crucial facts for aspirants preparing for competitive exams like IAS, UPSC, and other government exams.
🚀 What is NISAR?
NISAR stands for NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar. It’s an advanced Earth observation satellite designed to track changes on the planet’s surface with unmatched precision.
The satellite uses dual-frequency radar technology:
- L-band (provided by NASA) – Penetrates through forests and vegetation to track ground movements.
- S-band (provided by ISRO) – Focuses on surface-level changes like agriculture and coastal dynamics.
- This dual capability makes NISAR a game-changer in global environmental monitoring.
🌏 Why is NISAR Important?
The Earth is constantly changing, and understanding these changes is crucial for managing natural resources and preparing for disasters. NISAR’s data will help scientists track:
- Land Deformation:
- Detects minute movements of the Earth’s crust, which are crucial for predicting earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
- Glacier and Ice Sheet Movements:
- Monitors ice loss in polar regions, providing key data on rising sea levels due to climate change.
- Natural Disasters:
- Helps in early detection and response to floods, landslides, and earthquakes.
- Agricultural Monitoring:
- Assists in tracking crop patterns, soil moisture, and yield predictions, aiding farmers and policymakers.
- Urban Expansion:
- Tracks infrastructure growth, helping urban planners manage resources efficiently.
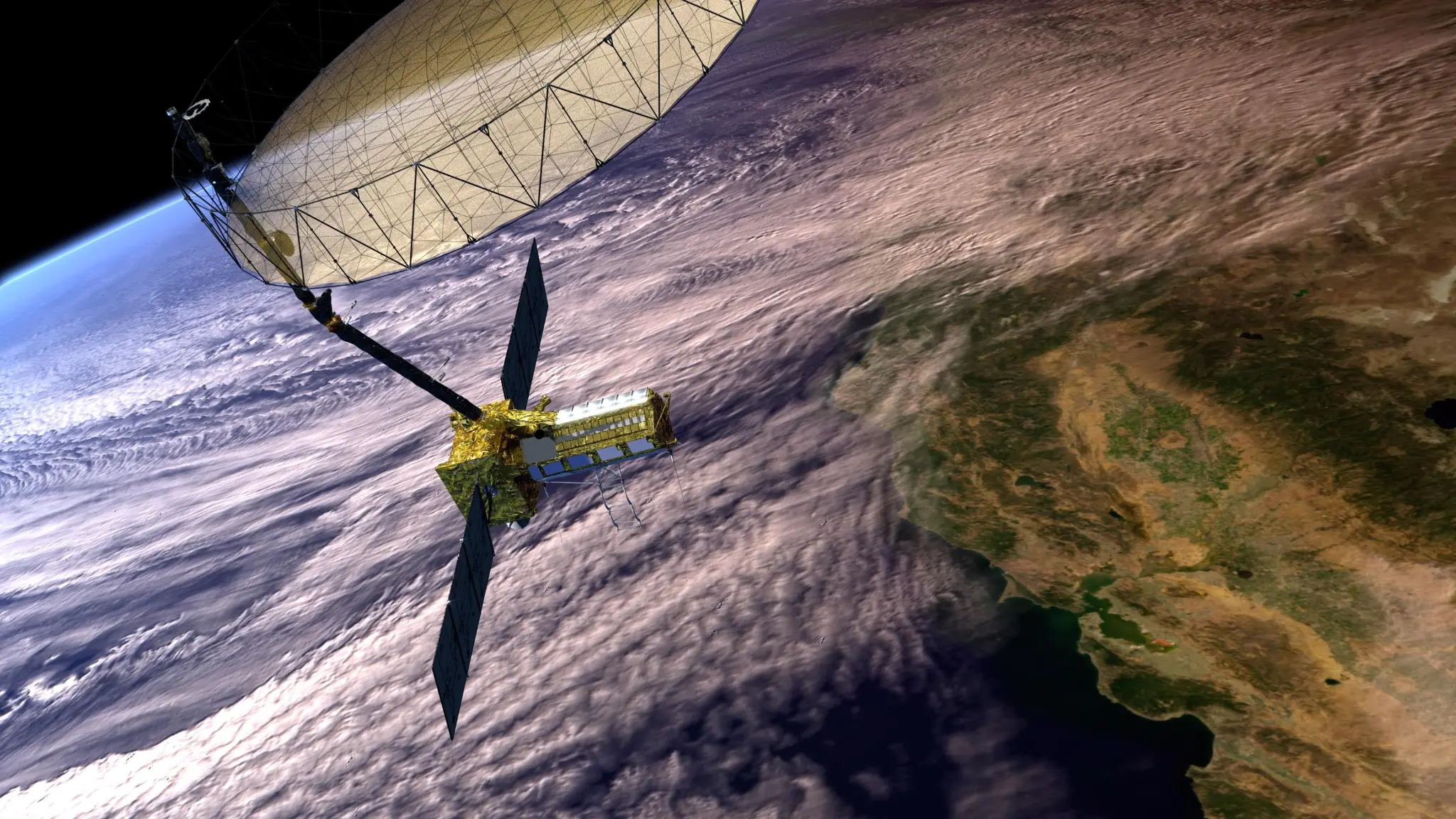
🛰️ How Does NISAR Work?
NISAR will scan the Earth’s land and ice surfaces twice every 12 days. Its Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) can see through clouds, smoke, and darkness, ensuring uninterrupted monitoring.
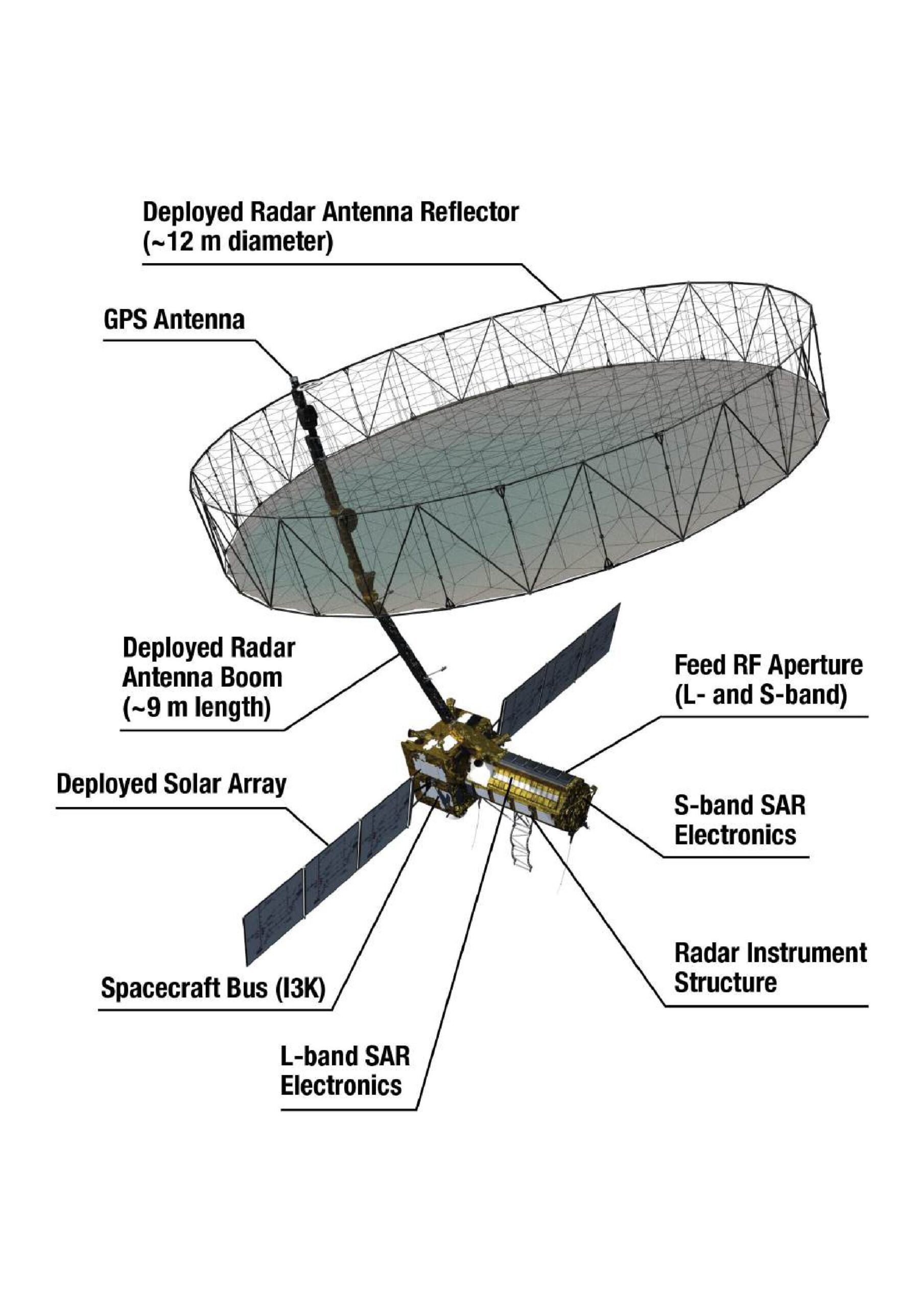
Key Components:
- Large Unfurlable Antenna (12 meters in diameter) – The radar’s eye in space.
- SAR Instrument Payload – Captures high-resolution images of Earth’s surface changes.
Operational Orbit: - Sun-synchronous polar orbit at about 747 km altitude.
Scanning Area: - Covers the entire Earth with high precision and frequency.
🌿 Significance for India
Disaster Management: India, being highly prone to natural disasters like floods, cyclones, and landslides, will benefit immensely from NISAR’s real-time data.
Agricultural Insights: With agriculture being a backbone of the Indian economy, NISAR will support precision farming and resource optimization.
Climate Change Studies: The satellite will help Indian researchers understand climate patterns and their impact on monsoons and biodiversity.
Global Prestige: This collaboration showcases India’s growing prowess in space technology on the international stage.
🔍 NISAR and Competitive Exams: Key Points to Remember
Key Points to Remember
| Feature | Details |
| Launch Date | March 2025 |
| Collaborating Agencies | NASA (USA) & ISRO (India) |
| Radar Bands | L-band (NASA) & S-band (ISRO) |
| Orbit | Sun-synchronous polar orbit (747 km altitude) |
| Frequency of Observation | Twice every 12 days |
| Primary Applications | Land deformation, ice-sheet monitoring, disaster management, agriculture monitoring |
🌐 Why Should Aspirants Care?
Science & Tech Section (UPSC/SSC): NISAR is a key development in India’s space journey.
Environment & Geography: Its applications in climate change and resource management are vital for geography-related topics.
Disaster Management: India’s NDMA can use NISAR data for better disaster preparedness and response.
International Relations: This joint mission exemplifies strong Indo-US collaboration in space research.
🚀 Conclusion
The NISAR mission is more than just another satellite; it’s a technological marvel that will revolutionize Earth observation. For competitive exam aspirants, understanding NISAR’s significance offers insights into India’s space capabilities, climate change efforts, and international collaborations.
As we move closer to the March 2025 launch, NISAR is set to make history while providing a treasure trove of data to safeguard our planet’s future.
Watch on Youtube : https://www.youtube.com/shorts/VkeZs5Fkof0