Navigating growth challenges in Sri Lanka
Syllabus:
GS 2 : India and its neighbourhood
Why in the News?
Recently, Sri Lanka’s new NPP government, led by Anura Kumara Dissanayake, inherited a stabilizing economy but faces critical challenges, including brain drain, fiscal sustainability, and fostering sustainable tourism growth.
Introduction
- Sri Lanka’s economy is at a crucial juncture following its severe economic crisis in 2022-2023.
- The newly elected National Peoples Power (NPP) government, under President Anura Kumara Dissanayake, faces the challenge of balancing growth with debt sustainability.
- While economic recovery signs are emerging, the government must address internal challenges, including brain drain and fiscal sustainability, while strengthening foreign ties.
Sri Lanka’s Economic Outlook Under the NPP Government
- Sri Lanka’s new National Peoples Power (NPP) government, led by President Anura Kumara Dissanayake, assumed office at a critical time.
- The country is recovering from its worst economic crisis in post-independence history.
Economic Stabilization
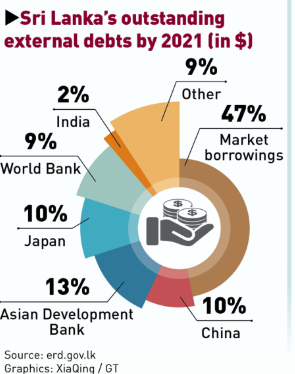
- Debt Crisis and Recovery: After defaulting on external debt in April 2022, Sri Lanka faced its worst economic downturn. However, recent efforts have stabilized the economy.
- IMF and Indian Aid: The prudent policies of the Central Bank of Sri Lanka, a $3 billion IMF program, and $4 billion of aid from India have stabilized the economy.
- Debt Restructuring: Sri Lanka agreed to a $17.5 billion debt restructuring deal with private bondholders and China, providing much-needed relief to the country.
- Tourism Revival: With the revival of the tourism sector, foreign exchange reserves have started to recover, supporting the country’s financial stability.
- Growth Projections:
In the context of the World Bank, Sri Lanka’s growth is forecast to slow down to 4.4% in 2024 and down to 3.5% in 2025. - This reflects challenges that are ongoing despite stabilization efforts.
Challenges Sri Lanka’s New NPP Government facing
- Despite the inheritance of a stabilizing economy, the ruling National Peoples Power (NPP) government, headed by President Anura Kumara Dissanayake, is presently battling several internal issues.
- It is crucial to address these issues for long-term growth and sustainability.
Brain Drain
- Mass Emigration: In 2024 alone, 3,00,000 professionals, including IT, banking, marketing, and healthcare experts, migrated out of Sri Lanka in the pursuit of better opportunities abroad.
Impact on Governance and Business
- This talent outflow has brought a gap to the skilled force, which makes it difficult for economic prosperity and good governance.
- Government has to introduce poli-cies that retain talent locally, create more opportunities, and enhance the livelihood of professionals as well as their family.
Inexperienced Parliamentarians
- New Legislators: Out of 225 legislators in the Parliament, 150 are first-time legislators belonging to the NPP, and people are skeptical about their ability to bring change.
Good Governance
- The government must train the legislators in the functioning of the parliament, economic policy, and public administration.
Capacity Building
- The establishment of a high-quality public policy school will train civil servants and legislators and will be able to upgrade the legislative and governance framework.
Tourism Development
- Tourism Growth: Over 2 million tourists visited Sri Lanka in 2024, a 38% rise from 2023.
- This growth offers immense potential for boosting foreign exchange reserves.
- Sustainable Tourism: Efforts should be made to develop less-visited areas like the north and east and promote Sri Lanka as a multicultural destination.
- Promotion of Smallscale Enterprises: Tourism would encourage local small enterprises connected to tourism. This would ensure larger developments in other regions
- Reducing the Problem of Gang-Related Crime will also increase the security and attractiveness of the country.
Fiscal Sustainability
- Expensive government expenditure still persists as the state performs a large percentage of economic functions even if revenue is increasing.
- Reforming state-owned enterprises (SOEs): Although the government has put privatization out of the question, loss-making SOEs like SriLankan Airlines and the Ceylon Petroleum Corporation must be turned around.
- Some restructuring or privatization of SOEs could alleviate some of the pressure on public funds.
- Balancing Expenditure: Rationalizing expenditure combined with improved management efficiency in SOEs will provide for fiscal stability.
External Challenges and Opportunities for Sri Lanka
- Sri Lanka’s foreign policy will be critical in its economic recovery and growth.
- The shifting geopolitics and the country’s economic dependencies require a balanced approach to external relations and fiscal challenges.
Building Ties with India
- India has emerged as a strategic partner in Sri Lanka’s economic recovery, providing immense aid and investment opportunities
Cooperation Sectors
- Bilateral relations are enhanced through business-to-business (B-B) relations, cross-border energy initiatives, and the in-implementation process of the digital identity program.
- Deeper bilateral trade arrangement is currently in discussion as well.
No Meddling into Security Issues
- Sri Lanka must oblige to security needs of India that includes forbidding visits from spy ships coming from China if there is cooperation.
Indo-Pacific Dynamics: Re-election of Donald Trump as U.S.
- It sets off the wave of change in the Indo-Pacific geopolitics, and Sri Lanka has to gear up its foreign policy with the new changing global order.
Debt and Fiscal Risks
- Sri Lanka has critical external debt repayment due from mid-2027.
- In the absence of growth through trade, there is a high chance of default.
- Support from Partners: Collaboration with IMF, World Bank, and India is essential to control fiscal challenges to avoid another crisis.
Conclusion
Sri Lanka’s Road to recovery requires visionary leadership, pragmatic reforms, and sustainable growth strategies in order to strike a balance between the pressing economic issues and long-term opportunities for inclusive and resilient development.
Source: The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Analyze the importance of Sri Lanka’s foreign policy in its economic recovery, focusing on India-Sri Lanka relations and the geopolitical dynamics of the Indo-Pacific region.