ESG: A Lighthouse and a Compass For Corporation
Why in the News?
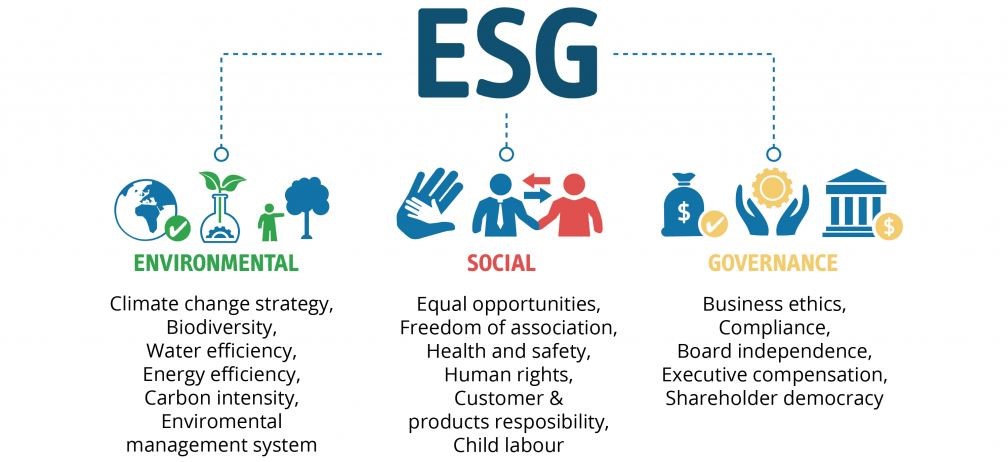
- Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) serves as both a moral and strategic compass for aligning corporate actions with societal and environmental goals.
- Helps companies set clear, measurable goals:
- Reducing emissions
- Fostering diversity
- Improving governance practices
- Adapts to evolving scenarios, allowing businesses to remain flexible while pursuing sustainable and ethical objectives.
ESG: A Guiding Force for Corporations
Lighthouse and Compass Analogy:
- ESG practices function as both a lighthouse and a compass for companies.
- Lighthouse: Provides situational awareness and immediate guidance.
- Compass: Offers directional stability for long-term navigation.
Moral and Strategic Compass:
- Aligns corporate actions with societal and environmental goals.
- Supports commitments like India’s net zero targets and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Navigating Modern Challenges:
- Helps businesses tackle complex regulations, market pressures, and stakeholder expectations.
- Offers a directional framework for addressing these challenges systematically.
Clear, Measurable Goals:
- Facilitates goal setting such as: Reducing emissions, Fostering diversity, and Improving governance practices
- Ensures companies stay adaptable while pursuing these goals amidst evolving scenarios.
Roundtable Meeting on Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) Framework (Early 2021)
Purpose of the Meeting:
- Convened by the then SEBI Chairman, the meeting involved CEOs, Managing Directors, Chief Financial Officers, and representatives from industry bodies (CII, FICCI, Assocham).
- The main focus was to discuss the proposed BRSR framework for top listed companies.
Objective of the BRSR Framework:
- Designed to enhance transparency by requiring the disclosure of material ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) information.
- The goal was to provide relevant data to all stakeholders, including investors.
Stakeholder Feedback and Discussions:
- SEBI sought feedback from stakeholders on their preparedness for ESG disclosures before finalising the BRSR formats.
- Participants recognized the increasing significance of ESG issues in the corporate world and welcomed SEBI’s initiative as critical and timely.
- The discussions centred on improving key ESG disclosures to help market participants better assess sustainability-related risks and opportunities.
SEBI’s Commitment to Sustainability:
- The BRSR framework reflected SEBI’s commitment to aligning corporate reporting with global sustainability standards.
- This initiative aimed to promote sustainable investments and contribute to a sustainable economy.
Implementation and Impact:
- The BRSR framework was formally introduced in May 2021, initially making it mandatory for the top 1,000 listed entities by market capitalisation.
- This marked a significant step in integrating ESG factors into corporate governance in India.
Current ESG Reporting Landscape:
- While many large companies had established strong ESG practices for years, the information was often not structured, consistent, or measurable across companies.
- Global ESG rating agencies like MSCI ESG Research, Sustainalytics, and S&P Global were already evaluating Indian companies, but the ratings were not always reflective of the actual progress made.
Standardisation and Transparency:
- SEBI’s regulatory framework aimed to standardise ESG ratings within India.
- This would ensure greater transparency and reliability for rating agencies, investors, and other stakeholders.
Introduction of ESG Rating Provider Framework (Mid-2023)
SEBI’s Regulation for ESG Rating Providers:
- In mid-2023, SEBI introduced a framework for regulating and accrediting ESG rating providers in India.
- This led to some global ESG rating agencies adjusting their operations to comply with these regulations, further contributing to the standardisation of ESG ratings.
Strategic Importance of ESG:
- ESG practices are increasingly viewed as critical pillars for sustainable and responsible business operations.
- Indian businesses are recognizing the strategic importance of ESG in driving long-term success, resilience, and societal impact.
Corporate Initiatives:
- In mid-2021, Ashok Leyland formed a board-led ESG committee, headed by an Independent Director, highlighting a growing trend among businesses.
- Bharat Forge also took similar steps, and other companies expanded their existing Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) committees to specifically address ESG issues.
- Over half of FTSE 100 companies have already instituted board-level ESG committees, reflecting a global shift toward more comprehensive ESG governance.
The Transformative Potential of ESG in India
- India’s distinct socio-economic challenges, regulatory environment, and increasing investor awareness position ESG not just as a trend but as a transformative force for businesses in the country.
- The growing adoption of ESG principles has the potential to drive significant change and create long-term value in the Indian corporate landscape.
Why ESG is Good for Business
Enhanced Brand Reputation, Customer, and Employee Loyalty:
- Customers and employees, particularly from Gen Y and Z, prefer brands that demonstrate a strong commitment to good governance, sustainability, and social responsibility.
- Companies that align with these values build stronger loyalty, especially as these generations are driven by a sense of purpose.
Building Stakeholder Trust:
- Strong governance processes lead to transparent decision-making and effective communication.
- Proactive disclosures, audits, and stakeholder engagement help businesses respond effectively to crises such as financial downturns or supply chain disruptions.
- The Tata Group is a prime example of a company that has built strong stakeholder trust through consistent adherence to governance and transparency.
Improved Financial Outcomes and Heightened Investor Engagement:
- Energy-efficient technologies, waste reduction, and optimized resource usage not only lower carbon footprints but also bring financial rewards.
- As global and domestic funds increasingly integrate ESG into their investment decisions, companies benefit from higher valuations and improved access to finance.
Effective Risk Management in a Dynamic Business Landscape:
- ESG practices ensure transparency and accountability across the supply chain, particularly regarding labour practices, environmental violations, and risks from extreme weather events.
- This proactive approach reduces reputational damage and operational disruptions.
Fostering Innovation:
- The shift toward sustainability promotes investment in technologies like renewable energy, electric vehicles, and waste management systems, creating new revenue streams.
- Start-ups in the clean tech space serve as a key example of how sustainability drives innovation.
Smoother Entry into International Markets:
- Businesses with established ESG frameworks are better positioned to compete in markets with stringent sustainability standards, such as the EU.
- This positions them for greater success and acceptance in global markets.
Way forward
- ESG is not just a moral obligation or regulatory requirement; it is a strategic imperative for businesses.
- Just as lighthouses guide ships safely and compasses provide direction in stormy seas, businesses integrating ESG principles into their core strategies can gain respect, public goodwill, and grow profitably.
- By doing so, they contribute to building a sustainable and inclusive “Viksit Bharat” for India at 100.
Source: The Hindu Businessline
Mains question
Discuss the strategic importance of integrating ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) principles into governance for businesses in India, highlighting its impact on sustainability and global competitiveness. (250 words)