California Wildfires Rage Amid Santa Ana Winds
Why in the news?
Wildfires in Southern California have killed 10 people, fueled by strong Santa Ana winds and extreme heat. Climate change is intensifying fire seasons, with unprecedented dry conditions contributing to the destruction and increased fire risks.
About the Wildfires and Destruction:
- At least 10 fatalities have occurred due to the wildfires in Southern California.
- The fires, fueled by Santa Ana winds gusting at 112 km/h, have destroyed thousands of acres and buildings, displacing over 200,000 residents.
- By Friday, five major fires were still active, notably the Palisades fire (17,000 acres burned) and the Eaton fire (10,000 acres burned).
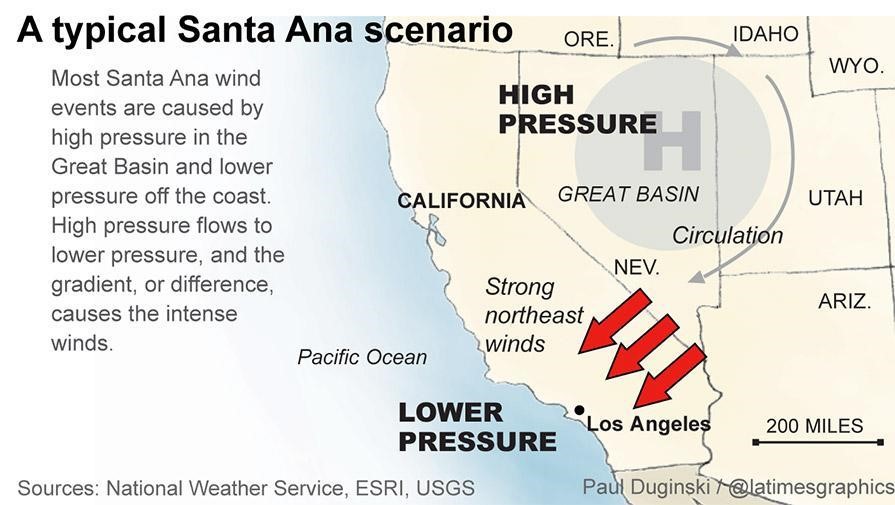
The Role of Santa Ana Winds
- Santa Ana winds are seasonal winds that occur when high pressure builds over the Great Basin, creating strong winds from the desert areas to Southern California.
- These winds heat up and dry out the vegetation, making it highly susceptible to wildfires.
- The winds typically blow from October to January, increasing the risk of wildfires during the dry season.
Climate Change and Fire Intensity
- California faced its hottest June, July, and October in recorded history in 2024, exacerbating wildfire conditions.
- Drought conditions, with little rainfall since July, have left forests extremely dry, contributing to the intensity of the fires.
- Climate change has led to longer fire seasons, with twice as many fire weather days as in the 1970s, and more intense fires.
- A study reports that global warming accounts for 66-90% of the increased fire weather days, with more frequent and extreme wildfire growth in the region.
Key Facts about Santa Ana winds:
- Origin: Santa Ana winds occur due to high pressure over the Great Basin and low pressure along California’s coast.
- Wind Movement: Winds blow from inland deserts towards the Pacific Ocean.
- Effect: As winds descend from mountains, they compress, heat up, and lower humidity.
- Impact: Extremely dry air reduces vegetation moisture to 10%, increasing fire risk.
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times