Alaknanda River: Vital Source and Environmental Challenges
Why in the news?
Researchers from IIT Roorkee identified the Alaknanda River as highly vulnerable to landslide-induced natural dams, emphasizing the need for sustainable development to protect this key Ganges tributary and its ecosystem in the Garhwal Himalayas.
Overview of the Alaknanda River:
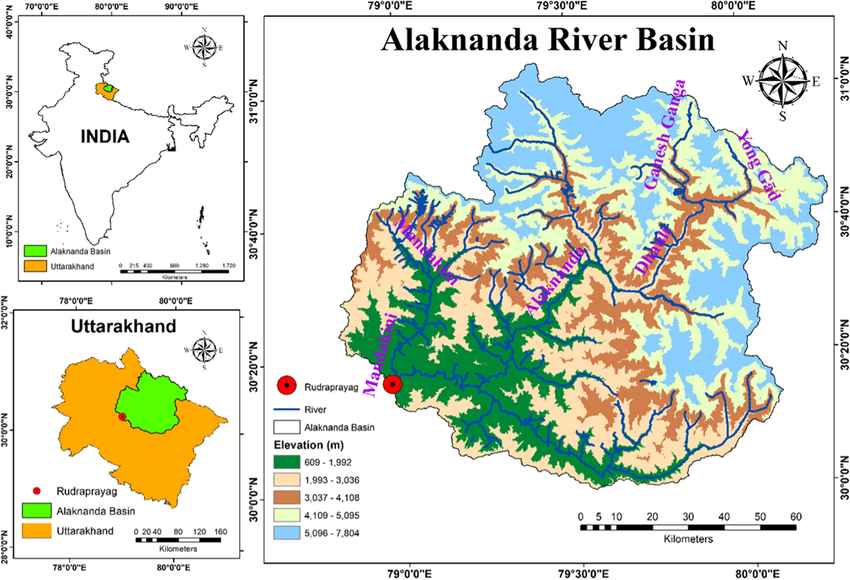
- The Alaknanda River, a significant headstream of the Ganges River, originates from the Satopanth and Bhagirath Kharak glaciers in Uttarakhand’s Garhwal Himalayas.
- It flows for approximately 190 kilometers before merging with the Bhagirathi River at Devprayag to form the Ganga.
Environmental Challenges and Conservation
- Research by IIT Roorkee identifies Alaknanda as highly vulnerable to landslide-induced natural dams, posing risks to nearby communities.
- Despite its religious and geographical importance, the region faces environmental challenges.
- There is a pressing need for sustainable development and conservation efforts to protect the river and its ecosystem.
Spiritual and Cultural Significance of river Ganga:
- The river is joined by five major tributaries at sacred confluences, known as Prayags:
- Vishnuprayag (Dhauliganga).
- Nandprayag (Nandakini).
- Karnaprayag (Pindar).
- Rudraprayag (Mandakini).
- Devprayag (Bhagirathi).
- These Prayags hold immense religious significance and are integral to the Char Dham Yatra, linking pilgrimage sites such as Badrinath, Hemkund Sahib, and Joshimath.
- Alaknanda contributes more to the Ganga’s flow than the Bhagirathi, highlighting its critical role in sustaining the holy river.
- Spiritual Purification: Bathing in the Ganga is believed to cleanse sins and purify the soul.
- Hindu Mythology: Associated with Lord Shiva, the river is considered divine and provides salvation.
- Religious Festivals: Hosts major gatherings like the Kumbh Mela, attracting millions of devotees.
- Sacred Cities: Varanasi and Haridwar are significant pilgrimage sites along its banks.
- Sacred Water Use: Ganga water is used in rituals, idol bathing, and consecration ceremonies.
- Healing Properties: Believed to have medicinal and purifying qualities.
- Economic and Ecological Role: Supports agriculture, livelihoods, and diverse ecosystems.
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times