Israel’s Settlement Expansion in Disputed Golan Heights
Why in the news?
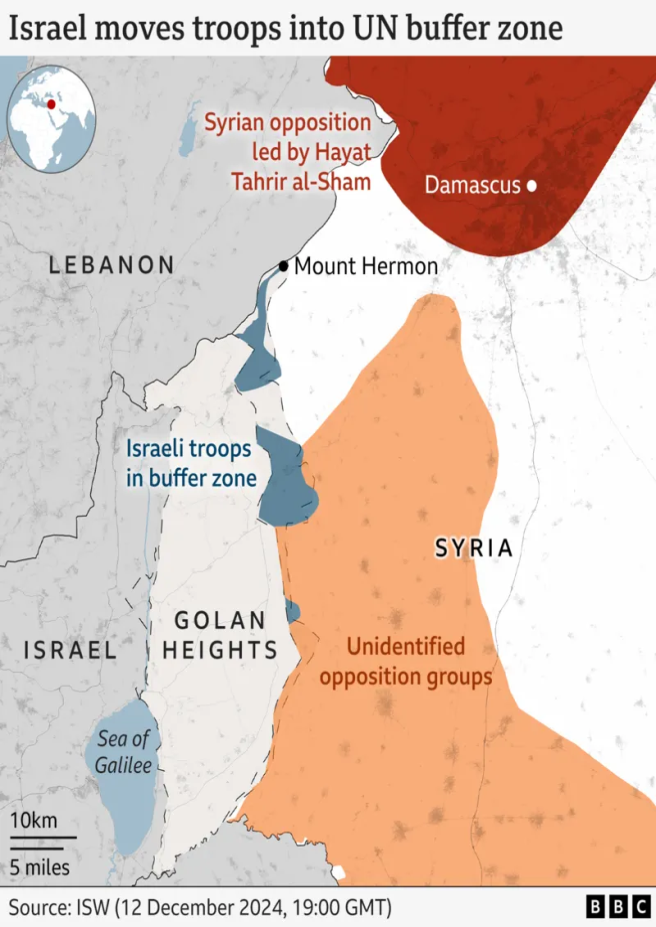
Israel’s recent decision to double its population in the Golan Heights highlights ongoing geopolitical tensions over the internationally recognized occupied Syrian territory.
Location, History, and Population of Golan Heights:
- Location: The Golan Heights is a hilly region overlooking the Jordan River Valley, bordered by:
- Jordan River and Sea of Galilee (west), Mount Hermon (north), Wadi Al-Ruqqād River (east), and Yarmūk River (south).
- Size: Covers 1,150 sq. km, stretching 71 km from north to south and 43 km from east to west.
- Historical Context:
- Originally part of southwestern Syria, Israel occupied the region during the 1967 Six-Day War.
- Syria’s attempt to reclaim it in the 1973 Middle East War failed.
- Israel annexed the Golan Heights in 1981, though the move remains unrecognized internationally.
- Population: Over 30 Israeli settlements house 20,000 settlers, while around 20,000 Druze Arabs of Syrian origin reside there.
Strategic Importance:
- Geopolitical Advantage:
- The Golan overlooks Syria’s capital, Damascus, northern Israel’s Galilee region, and the Sea of Galilee.
- It dominates strategic routes leading to Damascus.
- Border Security: The region shares borders with Jordan and Lebanon, making it critical for security.
- Water Resources: A significant water source for the region; rainwater from the Golan feeds into the Jordan River, supporting arid areas.
International Status and Recent Developments
- Recognized as occupied territory under international law and UN resolutions.
- Israeli settlements are considered illegal internationally, but Israel disputes this claim.
- Recent News: Israel’s plan to expand settlements in the Golan Heights has reignited geopolitical tensions surrounding this disputed region.
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times