India’s Accelerated Fight Against Tuberculosis: A Unified Approach
Syllabus:
GS-2:
Health , Government Policies & Interventions , Important International Institutions
Why in the news?
India has launched a transformative 100-day campaign across 347 high-burden districts to eliminate tuberculosis (TB). This initiative aims to accelerate early diagnosis, treatment, and nutritional support, reflecting the country’s commitment to achieving the 2025 TB elimination target under Prime Minister Modi’s leadership.
Progress in India’s TB Elimination Journey:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s leadership has brought innovative approaches in TB care, prevention, and treatment.
- WHO’s Global TB Report 2024 acknowledged a 7% decline in TB incidence in India from 2015 to 2023—double the global average decline.
- Treatment coverage increased significantly, from 59% in 2015 to 85% in
- Over 1 lakh TB patients were diagnosed in 2023, reflecting India’s enhanced detection capabilities.
The 100-Day Campaign: A Focus on High-Burden Districts
- Objective: Accelerate TB response in 347 high-burden districts across India.
- Key Strategies:
- Early identification of TB patients.
- Proactive outreach to vulnerable populations with timely, quality treatment.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Elected representatives, health practitioners, civil society, corporations, and communities to collaborate under the spirit of Jan Bhagidari (community participation).
- Vision: Mobilize collective efforts to make the campaign a national success and strengthen TB elimination strategies.
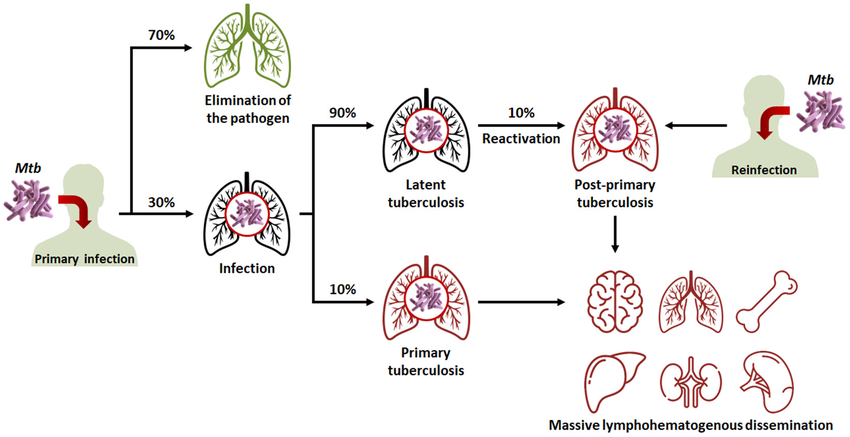
About Tuberculosis (TB):
- Cause: Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria from the Mycobacteriaceae family.
- Types:
- Pulmonary TB: Affects lungs.
- Extra-pulmonary TB: Affects other organs.
- History: Documented as early as 3000 BC in Egypt; treatable and curable disease.
Infection Prevalence
- Global Impact: 10 million people fall ill yearly; 1.5 million deaths, making TB the leading infectious killer.
- Vulnerable Groups: Major cause of death among HIV patients; contributes to antimicrobial resistance.
- High-Burden Nations: Includes India, China, Indonesia, and others.
Treatment
- Standard Care: 6-month course of 4 antimicrobial drugs with patient support.
- Drug Resistance:
- MDR-TB: Resistant to isoniazid and rifampicin; treatable with second-line drugs like Bedaquiline.
- XDR-TB: Resistant to second-line drugs, often limiting treatment options.
Global Initiatives to Combat TB:
- WHO Initiatives:
- “Find. Treat. All. #EndTB” campaign with Global Fund and Stop TB Partnership.
- Global Tuberculosis Report.
India’s Efforts:
- Schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan.
- National Strategic Plan for TB Elimination (2017-2025).
- TB Harega Desh Jeetega Campaign.
- NTEP: Central to India’s TB eradication efforts.
- TB-Free India Campaign: Promotes awareness and action.
- Nikshay Poshan Yojana: Provides nutritional support to TB patients.
- Active Case Finding (ACF): Detects hidden TB cases.
- Universal Drug Susceptibility Testing (UDST): Ensures effective treatment.
International Best Practices:
- BPaL/M Regimen: WHO-recommended shorter, effective treatment for drug-resistant TB.
- AI and Portable X-rays: Innovative tools for TB detection.
- Rapid Molecular Tests (GeneXpert): Quick, accurate TB diagnosis.
- Community-Based Models: Localized care for diagnosis, treatment, and follow-ups.
- Targeted Screening: Focus on high-risk groups like HIV patients, prisoners, and migrants
Nutritional and Social Support: Nikshay Poshan Yojana
- Launched in 2018, the scheme provides Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) for nutritional support to TB patients.
- Over ₹3,295 crore disbursed to 16 crore beneficiaries.
- Monthly support doubled from ₹500 to ₹1,000 in November 2024.
- Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (PMTBMBA):
- Tackles nutritional challenges and enhances community mobilization.
- Over 75 lakh Nikshay Mitras provided 21 lakh food baskets to patients.
- Encourages awareness, psychological support, and vocational assistance for TB patients.
Advancing Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnostic Innovations:
- Introduction of indigenous molecular diagnostic tools reduced costs and time for testing.
- Diagnostic machines increased from a few hundred in 2014-15 to 8,293 across all districts by
- Endorsed by WHO, showcasing India’s leadership in TB diagnostics.
- Treatment Advancements:
- Introduction of newer drugs like Bedaquiline and Delamanid to improve treatment success rates.
- Shorter 6-month BPaLM regimen approved for drug-resistant TB, alongside the conventional 9-20-month treatments.
- ICMR Leadership: Consistently ranked among top global public funders of TB research, driving innovations in diagnostics and treatment.
A Holistic Approach: India as a Global Leader
- India’s Make in India initiative contributed to cost-effective, high-quality molecular tests, positioning the nation as a leader in global TB response.
- Universal social support provisions combined with advanced tools ensure equitable access to care.
- The upcoming 100-day campaign represents another milestone in India’s collective commitment to eliminate TB.
Community Participation: The Power of Jan Bhagidari
- The TB elimination drive emphasizes the importance of community involvement.
- Grassroots initiatives like Nikshay Mitras showcase how collective efforts can support TB patients with nutritional, psychological, and social assistance.
- Collaboration between government, civil society, corporations, and individuals strengthens the fight against TB.
- Community-driven campaigns have raised awareness, reduced stigma, and fostered a sense of shared responsibility.
Global Recognition and India’s Pioneering Role
- WHO acknowledges India’s significant progress in reducing TB incidence, far outpacing global trends.
- Indigenous innovations in diagnostics and treatments endorsed by WHO have set benchmarks for cost-efficiency and accessibility.
- India’s leadership in TB research, exemplified by ICMR’s global contributions, underscores its pioneering role.
- Through initiatives like Make in India and PMTBMBA, India is establishing itself as a global leader in TB elimination efforts.
Challenges in India’s TB Elimination Efforts:
- High TB Burden: India still accounts for a significant proportion of global TB cases despite progress.
- Drug-Resistant TB: The emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) and extensively drug-resistant (XDR) TB strains complicates treatment.
- Delayed Detection: Limited awareness and stigma lead to delayed diagnosis, particularly in rural areas.
- Healthcare Infrastructure Gaps: Although diagnostic facilities have expanded, accessibility and efficiency in remote areas remain concerns.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Malnutrition among TB patients hinders recovery, highlighting the importance of sustained nutritional support.
- Social Stigma: TB patients face discrimination, impacting their mental health and willingness to seek treatment.
- Funding Challenges: Adequate and consistent funding is crucial for diagnostics, treatment, and community outreach initiatives.
Way Forward for TB Elimination in India:
- Strengthen Early Detection: Expand molecular diagnostic tools and awareness campaigns for proactive identification of TB cases.
- Enhance Treatment Access: Provide shorter, more effective regimens like BPaLM universally to improve adherence and outcomes.
- Focus on Nutrition: Scale up initiatives like Nikshay Poshan Yojana to ensure comprehensive nutritional support.
- Community Engagement: Strengthen Jan Bhagidari by mobilizing more stakeholders to reduce stigma and improve outreach.
- Invest in Innovation: Increase funding for TB research to develop advanced diagnostic tools and effective treatments.
- Policy Support: Integrate TB elimination into broader public health strategies for sustainable progress.
- Global Collaboration: Share India’s innovations and learn from international best practices to refine strategies.
Conclusion:
India’s fight against TB showcases significant progress through innovative diagnostics, enhanced treatment regimens, and community-driven campaigns like the 100-day initiative. Sustained efforts, global collaboration, and robust participation from all sectors will be crucial in achieving the vision of a TB-free India, ensuring better health outcomes for all.
Source: The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss India’s progress in tuberculosis (TB) elimination, focusing on innovative strategies like the Nikshay Poshan Yojana and BPaLM regimens. Highlight challenges in achieving the 2025 target and suggest measures to ensure a comprehensive and sustainable approach to eradicating TB.
Associated Article:
https://universalinstitutions.com/eliminating-tuberculosis/