Press Council of India (PCI): Ensuring Press Freedom and Ethics
Why in the news?
The Press Council of India focuses on maintaining press freedom, setting ethical standards, addressing complaints, and combating unethical practices like ‘paid news’ to preserve journalistic integrity.
Establishment and Composition:
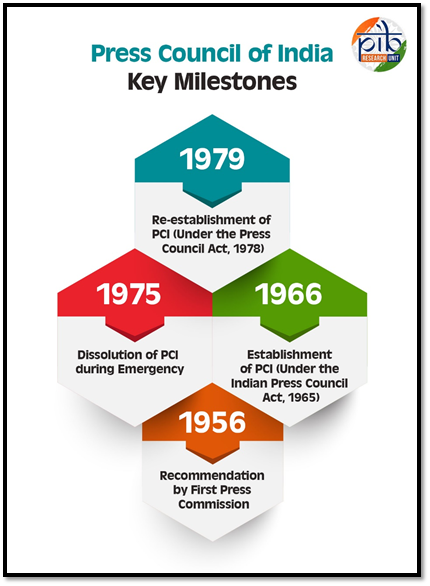
- The Press Council of India (PCI) was established in 1966 following the recommendations of the First Press Commission.
- It operates under the Press Council Act, 1978, as a statutory, quasi-judicial body.
- The PCI comprises 28 members, including a Chairman, traditionally a retired Supreme Court judge.
- The Chairman is nominated by a committee consisting of the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, Speaker of the Lok Sabha, and a council representative.
- All members, including the Chairman, serve a term of three years.
Key Functions of PCI:
- Safeguarding Press Freedom: The PCI ensures that the press remains free from external pressures and influences.
- Setting Ethical Standards: It establishes a code of conduct for journalists and media organisations to maintain high professional standards.
- Monitoring Developments: The council keeps track of policies or events that may limit the free flow of information.
- Addressing Complaints: PCI investigates complaints related to unethical practices or interference with press freedom.
Role in Upholding Journalistic Integrity:
- PCI’s recent advisory on ‘paid news’ highlights its role in ensuring transparency and accountability in the media.
- It emphasises maintaining journalistic integrity and combating practices that undermine the credibility of the press.
What is the World Press Freedom Index (WPFI)?
- Introduction: Compiled annually by Reporters Sans Frontiers (RSF) since 2002, assessing global press freedom.
- Objective: Measures journalists’ rights to report and access information, focusing on press freedom rather than journalism quality or human rights.
- Methodology: Press freedom is defined by journalists’ ability to operate independently, free from political, legal, economic, and social pressures, ensuring safety.
- Key Indicators:
- Political context
- Legal framework
- Economic context
- Socio-cultural environment
- Safety of journalists
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times