India Rises as Third-Largest Ethanol Producer
Why in the news?
- India has become the world’s third-largest producer and consumer of ethanol.
- Food and Public Distribution Minister Pralhad Joshi highlighted this achievement while inaugurating the India Sugar and Bio-Energy conference in New Delhi.
- The government is committed to creating a robust and sustainable sugar industry that supports India’s renewable energy goals.
Growth in Sugarcane Cultivation and Production
- In the past decade, sugarcane cultivation in India has increased by 18%, while sugarcane production has surged by 40%.
- The government’s introduction of a Minimum Support Price (MSP) has eliminated the issue of farmer dues.
- Farmers are now playing a vital role in renewable energy, transitioning from “Anna Dattas” (food providers) to “Urja Dattas” (energy providers).
Government Initiatives for Green Hydrogen
- The national Green Hydrogen Mission was launched last year with an outlay of ₹19,744 crores.
- This initiative aims to make India a global hub for the production, usage, and export of green hydrogen.
- The government continues to prioritise the sugar industry’s integration into the renewable energy sector.
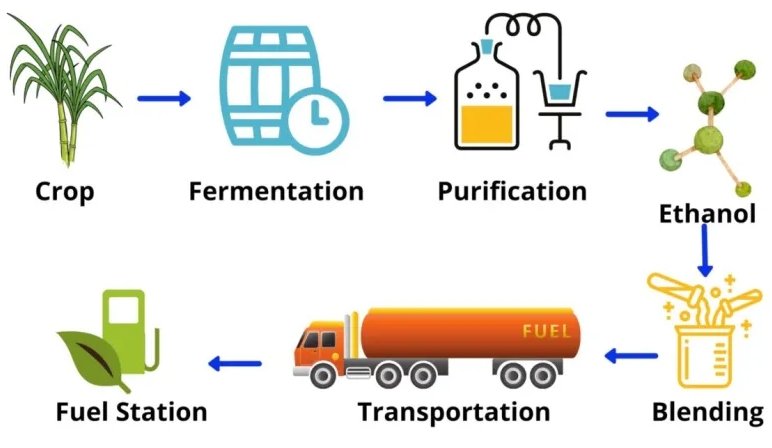
About the Ethanol Blending Programme:
- Launched in January 2003, aims to blend ethanol with petrol to reduce pollution, conserve foreign exchange, and support the sugar industry.
- Targets: 10% ethanol blending (E10) by 2021-22, 20% blending (E20) by 2025-26.
- Blending rate increased from6% (2013-14) to 11.8% (2022-23).
Sources of Bioethanol:
- Sugarcane (juice, syrup, B-heavy, and C-heavy molasses).
- Maize usage is increasing for ethanol.
- Surplus rice and damaged grains allowed for ethanol production.
What is Green Hydrogen?
- Produced using renewable energy sources (wind, solar) with no GHG emissions.
- Compared to grey hydrogen (from fossil fuels) and blue hydrogen (from fossil fuels + carbon capture).
Applications
- Used in refining, fertiliser, and steel industries.
- Future uses: transportation, power generation, and grids.
India’s Green Hydrogen Standard:
- Defines green hydrogen as <2 kg CO2 per kg H2.
- BEE monitors and certifies production projects.
- The National Green Hydrogen Mission targets 5 MMT by 2030.
Sources Referred:
PIB, The Hindu, Indian Express, Hindustan Times