THE PRESIDENT OF INDIA PAYS A CALL FOR PROPER JUDICIAL EFFICIENCY REFORMS.
Why in the news?
This was said by President Droupadi Murmu while inaugurating the National Conference of District Judiciary held in New Delhi on 30th August when she spoke on judicial process reforms, clearance of backlogs and efficient delivery of justice at the grassroots.
source:slideshare
Analysis about the news:
- Event: The President of India Droupadi Murmu delivered a speech on the occasion of valedictory session of the 18th National Conference of District Judiciary held at New Delhi.
- Judicial Reforms: On that she stressed that there is need for radical change in the district judiciary, where measures should be taken to reduce case backlog and enhance judicial facilities.
- Culture of Adjournment: The President pointed at the tendency to adjourn as something that should be considered in the attempts to deliver justice on time.
- Local-Level Justice: They say that the justice should be taken to grassroots like Panchayats & Municipalities for the easy access of justice by the poorer section of society.
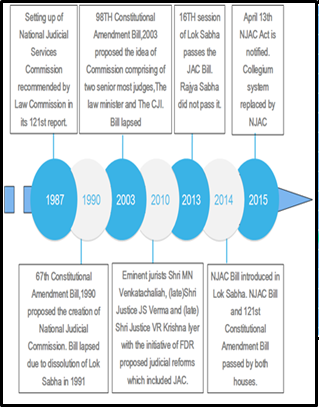
| About Judicial Appointment in India:
Collegium System:
National Judicial Appointments Commission (NJAC):
Judicial Reforms and Accountability in India:
Associated Article: |