PAKISTAN REPORTS ASIA’S FIRST MPOX CASES; GLOBAL ALERT
Why in the news?
Pakistan’s detection of mpox cases is the first in Asia, prompting heightened airport screenings and a global health alert from WHO amid increasing international concerns.
source:tgov.org
About First Detection in Asia:
- Pakistan has reported its first cases of mpox, marking the initial detection in Asia.
- Three patients, all from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, were identified.
- Two patients had recently arrived from the UAE; the third case is under confirmation.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared mpox a global health emergency.
- The European Union’s health agency has urged member states to prepare for potential cases following Sweden’s detection of the virus.
Health Advisory and Global Impact:
- Pakistan’s Ministry of Health has issued an advisory to enhance airport and border screening.
- Federal hospitals have been instructed to implement precautionary measures.
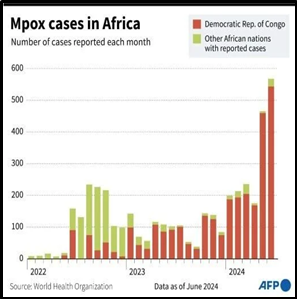
- Mpox, previously known as monkeypox, has caused significant concern due to its contagious nature and recent outbreaks.
- The disease, less severe than smallpox but still dangerous, has led to fatalities and is now spreading from person to person.
About Mpox (Monkeypox):
Symptoms:
Transmission:
Status:
Treatment and Vaccine:
|