GROWING BILATERAL RELATIONS BETWEEN VIETNAM AND INDIA
Relevance: GS 2 – Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests; India and its neighborhood relations.
Why in the news?
- Recently, Vietnamese Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh visited India from July 30 to August 1 to strengthen bilateral strategic ties.
- India, the world’s biggest democracy, emphasizes Vietnam as a key pillar in its Act East policy.
- The relationship has evolved from historical solidarity to a comprehensive strategic partnership.
About Vietnam
- Vietnam, a vibrant Southeast Asian nation, is renowned for its breathtaking natural beauty, rich cultural heritage, and dynamic economic growth.
- The country is known for its resilient spirit, industrious populace, and a culture characterized by hospitality.
- Vietnam’s strategic location, the exemplary leadership of the Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV), and a young and skilled workforce contribute to its significance on the global stage.
- The government’s focus on economic reforms and global integration has propelled Vietnam to impressive economic growth.
- It is now recognized as one of the fastest-growing economies in the region.
Historical Background to Vietnam’s Remarkable Strides
- Under the CPV Leadership: The Communist Party of Vietnam (CPV), established on February 3, 1930, initiated transformative progress and development amidst patriotic uprisings.
- The Socialist Republic of Vietnam, a Southeast Asian Marxist-Leninist one-party state, has made remarkable strides under the CPV.
- Vietnam, under the CPV’s prudent leadership, achieved decisive victories in prolonged 20th-century warfare.
- 1945 August Revolution: Spearheaded by Ho Chi Minh, this revolution won Vietnam its independence, leading to the establishment of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam, Southeast Asia’s first workers’ and farmers’ state.
- Defeat of French Colonialism: Vietnam crushed French colonialist plans, with the epoch-making Dien Bien Phu victory in the Winter-Spring battle of 1953-1954 ending French attempts to reclaim power.
- 1975 Ho Chi Minh Campaign: The General Offensive and Uprising in 1975 liberated South Vietnam, leading to national reunification under CPV leadership.
- Doi Moi Policy (1986): The comprehensive national Doi Moi (Renewal) policy marked the shift from a centrally planned economy to a socialist-oriented market economy.
- This shift has resulted in significant economic growth, a rise in foreign direct investment, and improved living standards for Vietnamese citizens.
- Education and Healthcare: With improved literacy rates, expanded access to healthcare services, and enhanced quality of life, significant progress has been made.
- Socio-Economic Development: CPV’s policies lifted millions out of poverty, and transformed Vietnam into one of Southeast Asia’s fastest-growing economies.
Building Bridges Through Strategic Foreign Policy
- Principles of Foreign Policy: Vietnam’s foreign policy is centered on independence, self-reliance, and multilateralism.
- This approach stems from historical experiences of foreign invasions and the Vietnamese people’s desire to maintain sovereignty and peace while avoiding external dependencies.
- Post-Reunification Focus: Since reunification in 1975, and especially since the Doi Moi reforms, Vietnam’s diplomacy has aimed to create a peaceful and stable environment to support national industrialization and modernization.
- Bilateral Relations: Vietnam has established fruitful ties with major powers, politico-economic centers, and industrialized nations, prioritizing neighboring and regional countries.
- The policy is characterized by openness, diversification, and multilateralization of international relations.
- Vietnam actively engages in expanding international relations and developing mutually beneficial partnerships and cooperative ties with all countries, territories, and international organizations.
- Multilateral Diplomacy: Vietnam has strengthened its global standing and contributed to regional and global stability.
- By participating in multilateral diplomacy and joining international organizations such as the United Nations, ASEAN, ASEM, APEC, and the World Trade Organization
- Economic Diplomacy: Vietnam emphasizes economic diplomacy by attracting foreign investment, and enhancing trade relations.
- The country has signed multiple free trade agreements (FTAs) with key partners, opening new markets for Vietnamese goods and services and facilitating economic growth.
Vietnam and India Bilateral Relations
- Historical Solidarity: Vietnam and India share a history of solidarity rooted in their struggles for independence.
- Full diplomatic relations were established on January 7, 1972.
- Strategic and Comprehensive Partnerships:
- A ‘Strategic Partnership’ was formed in July 2007.
- This partnership was elevated to a ‘Comprehensive Strategic Partnership’ during Indian PM Modi’s visit to Vietnam in 2016.
- Strengthening Diplomatic Ties: Regular high-level visits, strategic dialogues, and cooperative efforts on regional and global platforms have strengthened diplomatic ties.
- Both nations are committed to fostering peace and security in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Trade Growth:
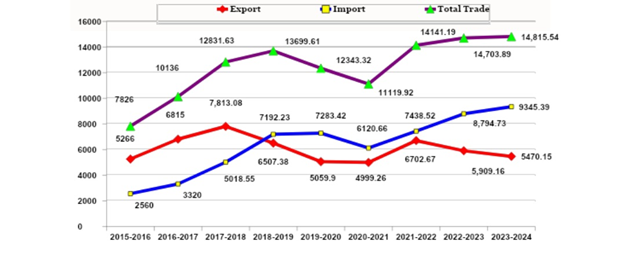
- Bilateral trade has grown significantly, from USD 200 million in 2000 to USD 14.36 billion in 2023.
- In FY 2023-2024, Vietnam was India’s 21st largest trading partner and 22nd largest export destination.
- India was Vietnam’s 7th largest trading partner, 7th biggest importer of Vietnam’s products, and 11th biggest import source.
- Economic Partnerships: Indian companies are exploring Vietnam as a manufacturing hub.
- Vietnamese enterprises view India’s vast consumer market as an expansion opportunity.
- Successful partnerships have been established in IT, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture sectors.
- Guided by a “Joint Vision for Peace, Prosperity and People” since December 2020, India-Vietnam relations encompass growing development cooperation alongside collaboration on defense and security matters.
- Educational and Cultural Exchanges:
- Regular educational exchanges and cultural programs have reinforced people-to-people connections.
- These exchanges foster mutual understanding and cooperation while enriching the cultural fabric of both nations.
Vietnam’s PM Pham Minh Chinh’s India Visit
- Significance: The visit underscored both nations’ steadfast commitment to deepening bilateral relations and exploring new avenues for collaboration.
- Comprehensive Strategic Partnership: The visit focused on strengthening traditional areas of cooperation and expanding into new sectors such as digital economy, telecommunications, information technology, infrastructure, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and renewable energy.
- Future Outlook: Driven by its dynamic economy, innovative strides, robust foreign policy, and strategic global partnerships, particularly with nations like India, Vietnam is poised for a promising future.
Way forward to India-Vietnam Relations
- Strengthen Maritime Security: Utilize the recently announced $300 million credit line to enhance Vietnam’s maritime security capabilities, focusing on joint naval exercises and intelligence sharing.
- Expand Trade and Investment: Aim to double bilateral trade and investment within five years by removing trade barriers and exploring new sectors such as renewable energy, agriculture, and technology.
- Enhance Defense Cooperation: Continue to develop defense ties through joint military training, counter-terrorism initiatives, and collaboration in defense technology.
- Promote Economic Partnerships: Encourage Indian companies to invest in Vietnam’s growing sectors like IT, agriculture, and infrastructure, while facilitating Vietnamese investments in India.
- Cultural and Educational Exchanges: Increase people-to-people connections through cultural programs and educational exchanges to foster mutual understanding.
- Joint Development Projects: Expand the number of Quick Impact Projects (QIPs) in Vietnam to enhance socio-economic infrastructure and support local communities.
- Focus on Digital Transformation: Collaborate on digital economy initiatives, including artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and cybersecurity, to modernize both economies.
- Leverage Multilateral Platforms: Work together in international forums like ASEAN and the United Nations to promote regional stability and a rules-based Indo-Pacific.
- Joint Research and Development: Establish partnerships in science and technology, particularly in agriculture and healthcare, to drive innovation and share best practices.
- Sustainable Development Goals: Align bilateral cooperation with global sustainability goals, focusing on climate action and green technology initiatives.
Alternative articles:
https://universalinstitutions.com/strong-and-growing-india-vietnam-bilateral-relations/
Source: Indian Express
Mains question
Examine the significance of India and Vietnam strengthening the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership while focusing on new areas of cooperation and regional stability. (250 words)