A FIVE-YEAR ROADMAP
Syllabus:
GS 3:
- Government
- Taxation in India
Why in the News?
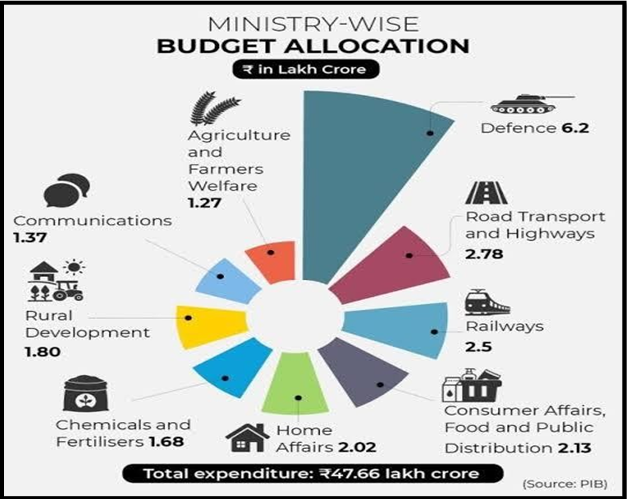
The 2024 Budget is crucial as it aims to address significant economic challenges such as unemployment and inequality. It introduces a medium-term economic framework focusing on fiscal consolidation, infrastructure improvement, and tax reforms to create a sustainable and inclusive growth path.
Source: PIB
Introduction
- Fiscal Consolidation Focus: The Budget 2024 aims to provide a clear fiscal consolidation roadmap, addressing both the reduction of the fiscal deficit and medium-term economic
- Fiscal Deficit Target: The Finance Minister has set a fiscal deficit target of 4.9% of GDP for 2024-25, progressing towards the goal of 45% by the next fiscal
- Debt Reduction: Central government debt is projected to decrease from 58.2% to 56.8% of GDP, reflecting progress in fiscal discipline and financial
- Uncertainty in Targets: While the Budget lacks specific post-2025-26 fiscal deficit targets, it commits to maintaining a declining debt-to- GDP ratio, allowing flexible policy
- Predictability Issues: The absence of firm long-term fiscal targets introduces some unpredictability, which could impact economic planning and investor confidence.
- Employment and Infrastructure: Initiatives aimed at improving employability and infrastructure have been proposed, reflecting the government’s commitment to addressing these issues.
Proposed Economic Policy Framework
- Medium-Term Initiatives: The Budget outlines a five-year economic policy framework, including measures for employment generation, infrastructure development, and GST rationalization.
- Green Deal Elements: The framework suggests a structured approach to addressing employment, infrastructure needs, and the rationalization of indirect taxes, ensuring consistent policy implementation.
- GST Rationalization: The Budget signals potential changes in GST rates and customs duties, aiming to enhance the stability and predictability of the tax
- Customs Duties Adjustments: The recalibration of customs duties is proposed to balance economic concerns, with a need for a framework to ensure stability and predictability in this area.
- Direct Tax Reforms: A review of the Income Tax Act is proposed to simplify and clarify tax regulations, with efforts to reduce disputes and litigation in tax matters.
Augmenting Expenditures and Fiscal Space
- Increased Expenditures: Recent fiscal space, created by buoyant tax revenues, has been utilized to enhance various spending programs, balancing consolidation with expenditure needs.
- Fiscal Consolidation Sources: The surplus funds from the Reserve Bank of India have contributed to fiscal consolidation, demonstrating a strategic use of available resources.
- Spending Trends: The Budget shows some increase in expenditure and minor tax revenue compression compared to the interim Budget, highlighting ongoing fiscal adjustments.
- Economic Survey Insights: The Economic Survey 2023-24 has identified key challenges such as youth employability and infrastructure, guiding the Budget’s focus on these critical areas.
- Medium-Term Initiatives: The Budget outlines a five-year economic policy framework, including measures for employment generation, infrastructure development, and GST rationalization.
- Green Deal Elements: The framework suggests a structured approach to addressing employment, infrastructure needs, and the rationalization of indirect taxes, ensuring consistent policy implementation.
- GST Rationalization: The Budget signals potential changes in GST rates and customs duties, aiming to enhance the stability and predictability of the tax regime.
- Customs Duties Adjustments: The recalibration of customs duties is proposed to balance economic concerns, with a need for a framework to ensure stability and predictability in this area.
- Direct Tax Reforms: A review of the Income Tax Act is proposed to simplify and clarify tax regulations, with efforts to reduce disputes and litigation in tax matters.
Addressing Taxation and Inequality
- Direct Tax Review: The Budget proposes a review of the Income Tax Act to improve clarity and reduce litigation, focusing on simplifying tax regulations for better compliance.
- Vivad se Vishwas Scheme: The introduction of the “Vivad se Vishwas, 2024” scheme aims to resolve tax disputes and reduce revenue lock-up due to litigation.
- Tax Dispute Resolution: Augmenting manpower to handle first appeal cases and limiting appeals in smaller liability cases are proposed to streamline tax dispute resolution.
- Capital Gains Tax: To address concerns of inequality, the Budget raises taxes on both short-term and long-term capital gains while offering some relief to retail investors.
- Securities Transaction Tax: Enhanced securities transaction tax on futures and options transactions aims to moderate market exuberance and stabilize the capital markets in the medium term.
What Needs to Be Done
- Clear Long-Term Fiscal Targets: Establish specific long-term fiscal deficit and debt-to-GDP ratio targets to enhance economic predictability and guide consistent policymaking.
- Sustainable Employment Policies: Develop and implement comprehensive employment strategies, including enhanced skilling programs and financial incentives for job creation, to address youth unemployment.
- Infrastructure Investment: Allocate significant resources to infrastructure development, focusing on projects that improve connectivity, boost productivity, and support long-term economic growth.
- GST Rationalization: Introduce a clear roadmap for GST rate adjustments and structural reforms to streamline the tax regime, reduce compliance burdens, and improve revenue efficiency.
- Customs Duty Framework: Create a stable and predictable customs duty framework that balances the need for economic protection with promoting fair competition and trade.
- Direct Tax Simplification: Undertake a thorough review and simplification of the Income Tax Act to reduce disputes, enhance clarity, and streamline tax administration processes.
- Enhanced Tax Dispute Resolution: Implement measures to expedite the resolution of tax disputes, including increasing resources for handling cases and limiting appeals on minor issues.
- Equitable Taxation Measures: Adjust tax policies to address income inequality, including higher taxes on capital gains and increased securities transaction tax, while providing relief to small investors.
Conclusion
The 2024 Budget sets a foundation for a stable economic future by addressing key issues like fiscal discipline, employment generation, and tax reforms. While it offers a roadmap for medium-term policies, continuous efforts are needed to ensure these initiatives translate into tangible benefits for the broader economy.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the key features of the 2024 Budget. How do the proposed measures aim to address the issues of unemployment and inequality? Critically evaluate the potential impact of the budget on India’s economic growth and stability in the medium term.
Associated Article: