“GOVERNMENT INCREASES STANDARD DEDUCTION, ADJUSTS NEW TAX SLABS”
Why in the news?
- The standard deduction under the New Tax Regime (NTR) increased from Rs 50,000 to Rs 75,000.
- Taxpayers with a taxable income of Rs 15 lakh or more will save Rs 17,500 annually under the NTR due to higher standard deduction and rate rationalisation.
- Tax slabs adjusted: 5% rate for Rs 3-7 lakh, 10% for Rs 7-10 lakh, and 15% for Rs 10-12 lakh income brackets.
source:midsquare
Key Features of New Tax Regime:
- Default Option: Becomes the norm if not chosen otherwise.
- Lower Tax Rates: Offers reduced rates compared to the old regime.
- No Deductions: Most deductions and exemptions under sections like 80C, 80D, 24(b) are not claimable.
- Simplified Structure: Aims to simplify and make the tax system user-friendly.
- Few Allowed Deductions: Some deductions are permitted.
About Old Tax Regime Deductions and Exemptions:
What is Tax?
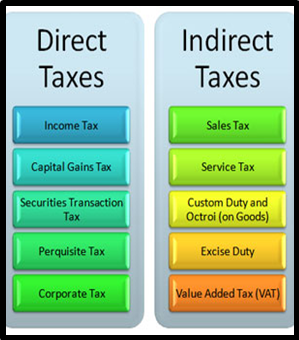
Types of Taxes in India
Associated Article: |