DELIBERATIONS ON DATA PROTECTION RULES
Why in the news?
- “India’s Data Protection Rules Under Scrutiny: Challenges in Implementing Child Consent Framework”
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) seeks industry input on implementing parental consent standards under the upcoming Data Protection Act, 2023.
- Challenge lies in determining reliable methods for verifying parental consent and age verification for children under 18 using digital services.
source:wordpress
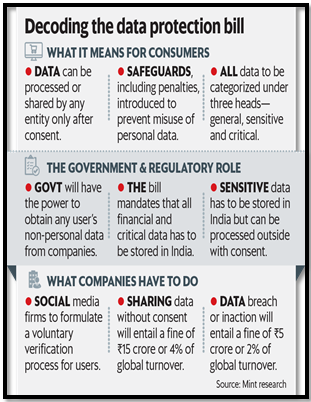
Key provisions of the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023:
- Legal Framework: Introduced to safeguard personal data, ensuring consent-based sharing and privacy protection in digital contexts.
- Applicability: Covers digital personal data processed within India and data processed abroad for Indian residents.
- Evolution: Based on recommendations from the Justice BN Srikrishna Committee, evolved from the 2019 Personal Data Protection Act.
- Citizen’s Rights: Includes rights to information, correction, erasure, grievance redressal, and representation after death or incapacity.
- Data Protection Board of India (DPBI): Independent body for adjudication and enforcement, appointed by the central government.
- Penalties: Monetary fines up to Rs. 250 crores for data fiduciaries; Rs. 10,000 for data principals; no criminal penalties.
- Conflict Resolution: DPDP provisions supplement existing laws; Act prevails in case of conflicts, with High Court handling breaches suo moto.
About Right to Privacy:
Associated Article: https://universalinstitutions.com/neither-the-right-to-privacy-nor-the-right-to-information/ |