THE SPECTRE OF NEO-FASCISM THAT IS HAUNTING EUROPE
Syllabus:
GS 2:
- Policies and Politics of Developed and Developing Countries.
- Fascist Aggression & Response of Western Democracies.
Why in the News?
Kylian Mbappé’s comments on France’s political climate ahead of UEFA Euro 2024 have spotlighted the rising influence of neo-fascist ideologies in Europe. The resurgence of ultra-right parties, particularly Marine Le Pen’s National Rally, underscores the growing threat to democratic values across the continent.
Source: IAhub
Introduction to Neo-Fascism
- Player Comments: Kylian Mbappé and Marcus Thuram voiced concerns about France’s political climate, highlighting the rise of extremism and urging action against Marine Le Pen’s National Rally.
- Election Influence: The rise of the ultra-right in Europe is likened to the haunting spectre of neo-fascism, reminiscent of historical dangers.
- Political Climate: Europe is experiencing a significant shift as the ultra-right gains ground in EU elections, with Paris being a central point of concern.
- Macron’s Gamble: French President Emmanuel Macron’s snap election call is seen as a risky move to counter the ultra-right’s momentum.
- Voter Dynamics: The political landscape in France is evolving, with strategic voting and alliances influencing election outcomes.
Inflection Point in Europe
- Historical Context: The resurgence of the ultra-right echoes the historical spectres of nationalism and fascism, challenging Europe’s post-war values.
- Macron’s Defeat: Emmanuel Macron faced significant defeat by Marine Le Pen in EU elections, prompting drastic political decisions.
- Strategic Elections: Macron’s snap election aims to mobilize moderate voters against the ultra-right, although it risks further empowering extremist factions.
- Election Results: The RN party’s increased vote share and the rise of left-wing alliances indicate shifting political allegiances in France.
- Uncertain Future: France may face unprecedented political scenarios, with the far-right potentially becoming a dominant force.
Growth of the Far-Right
- Immigration Backlash: The far-right’s influence grows amid resistance to immigrants, a legacy issue gaining recent momentum.
- Literary Reflection: Michel Houellebecq’s novels, depicting hypothetical far-right victories, mirror real societal anxieties in France.
- Temporary Quelling: Macron’s centrist politics temporarily subdued the far-right, but its resurgence poses ongoing challenges.
- Political Fiction: Houellebecq’s latest work foresees a near future where the far-right is dangerously close to presidential power.
- European Trend: The far-right’s popularity is not limited to France; similar movements gain traction across Europe, from Italy to Sweden.
Immigration and Integration
- Sports Icons: French football stars of African, Arab, or Antillean descent symbolize the complexities of immigration and integration.
- Identity Issues: Karim Benzema’s remark underscores the dual identity and societal perception challenges faced by immigrant communities.
- Election Impact: The outcomes of the French elections could significantly influence both national and European politics, especially regarding immigration policies.
- Neo-Fascist Threat: A far-right victory could herald the rise of neo-fascism across Europe, altering political and social landscapes.
- Long-Term Effects: Although political waves may normalize, the impact of the ultra-right’s rise will leave lasting effects on European societies.
Future Implications
- Historical Lessons: History suggests that political storms eventually calm, but the current ultra-right wave will have enduring consequences.
- Political Strategies: Future strategies will need to address the underlying causes of the far-right’s rise, focusing on social integration and economic stability.
- European Unity: The challenge for Europe is to maintain unity and uphold democratic values amid rising nationalist sentiments.
- Moderate Mobilization: Mobilizing moderate and progressive forces will be crucial to counteract the influence of extremist factions.
- Sociopolitical Balance: Achieving a balance between addressing legitimate concerns and preventing the normalization of extreme ideologies is essential for Europe’s future stability.
| Understanding Fascism
Origins and Spread:
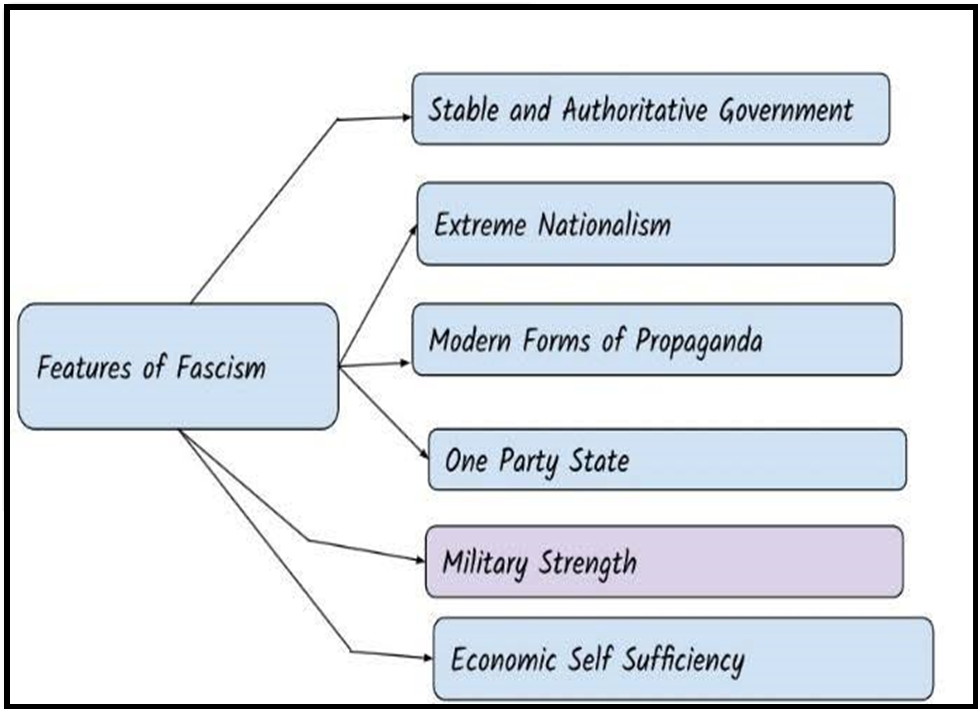
Core Concept (Stanley G. Payne): Fascism is an Anti-liberalism, anti-communism, and anti-conservatism ideology that aims to regulate the economy and structure social relations to transform a nation into an empire. It Utilizes romantic symbolism, mass mobilization, positive view of violence, and authoritarian leadership. Features of Fascism:
|
Challenges Related to Neo-Fascism
- Political Polarization: Neo-fascism exacerbates divisions within society, leading to heightened political tensions and instability.
- Erosion of Democracy: The rise of ultra-right parties can undermine democratic institutions and principles, threatening the rule of law.
- Social Fragmentation: Neo-fascist ideologies often promote exclusionary policies, deepening societal divides and marginalizing minority groups.
- Human Rights Violations: The ultra-right’s stance on immigration and civil liberties can lead to policies that infringe on human rights.
- Economic Disruption: Protectionist and nationalist economic policies may disrupt trade relations and economic stability.
- Cultural Intolerance: Neo-fascism fosters xenophobia and racism, undermining multiculturalism and social cohesion.
- Media Manipulation: Ultra-right groups often use propaganda to spread misinformation, influencing public opinion and undermining trust in the media.
- Violence and Extremism: The rise of neo-fascism can embolden extremist groups, leading to increased violence and hate crimes.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Democracy: Reinforce democratic institutions and processes to ensure resilience against extremist influences.
- Promoting Inclusivity: Foster inclusive policies that address the needs and rights of all societal groups, countering exclusionary ideologies.
- Enhancing Education: Implement educational programs that promote critical thinking, tolerance, and understanding of democratic values.
- Economic Reforms: Address economic disparities through policies that promote equitable growth and reduce socio-economic inequalities.
- Protecting Human Rights: Ensure robust mechanisms to protect human rights and hold violators accountable.
- Supporting Civil Society: Empower civil society organizations to advocate for democratic principles and human rights.
- Regulating Media: Combat misinformation and propaganda through media literacy initiatives and stricter regulations on media outlets.
- International Cooperation: Collaborate with international partners to address the transnational nature of neo-fascism and promote global democratic norms.
Conclusion
The rise of neo-fascism in Europe poses significant challenges to democracy, social cohesion, and human rights. Addressing these threats requires strengthening democratic institutions, promoting inclusivity, and fostering international cooperation. Collective action is crucial to counteract the spread of extremist ideologies and safeguard democratic principles.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the rise of neo-fascism in Europe and its implications for democratic governance. What steps can be taken to counteract this trend and protect democratic values?