INDONESIA TO START WORKING FROM NEW CAPITAL IN JULY 2024
Why in the news?
- Indonesian President Joko “Jokowi” Widodo announced plans to begin working from the new capital city, Nusantara, starting next month.
- The announcement follows concerns about the project’s future after senior executives overseeing development resigned.
source:worldmap
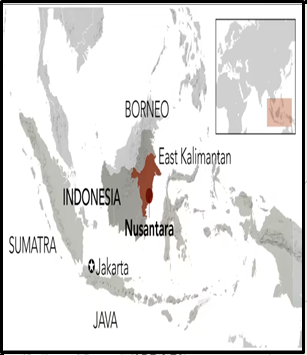
About Nusantara, New Capital of Indonesia
- In April 2019, President Joko Widodo cited rising sea levels and severe congestion on Java as reasons for the move.
- Jakarta is located on Java’s northwest coast.
- Indonesian parliament approved relocating the capital from Jakarta to Kalimantan, Borneo Island.
- New capital named ‘Nusantara,’ a Javanese term for the Indonesian archipelago.
- Move aims to address Jakarta’s congestion, floods, and air pollution issues.
- Indonesia’s largest islands: Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan (Borneo), Sulawesi, and Papua (New Guinea).
- Jakarta’s Issues:
- Serious infrastructure problems, flooding worsened by climate change; potential for one-third underwater by 2050.
- Overcrowded and extremely polluted, housing over 30 million in the metro area.
- Overpopulation and relentless construction in Jakarta hinder water absorption, causing run-off.
| About Kalimantan, Borneo Island:
Kalimantan
Borneo Island
About Sea Level Rise (SLR):
|