“NEPAL’S TRADITIONAL HONEY HARVESTING THREATENED BY CLIMATE CHANGE EFFECTS”
Why in the news?
- Rising temperatures attributed to climate change threaten the traditional honey-harvesting practices of Nepal’s Gurung community, impacting bee populations and honey collection.
- Experts cite climate change, deforestation, water diversion, and pesticide use as factors contributing to declining bee populations and honey yields, highlighting broader ecological disruptions.
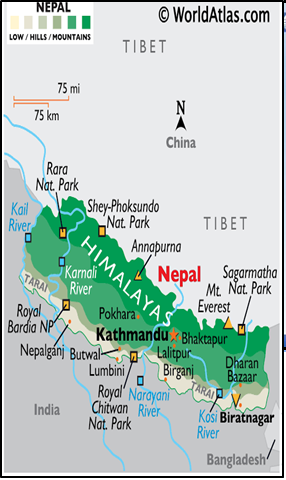
Key Facts :Nepal
- Location: Landlocked country in South Asia, bordered by China to the north and India to the south, east, and west.
- Capital: Kathmandu, the largest city.
- Ethnic Groups: Varied ethnic groups, including Khas Arya, Chhetri, Bahun, Magar, Tharu, Tamang, Kami, Musalman, Newar, Yadav, Rai, and others.
- International Relations:Member of the United Nations, SAARC, Non-Aligned Movement, and the Bay of Bengal Initiative.
- Armed Forces: Fifth-largest in South Asia, known for their Gurkha history and contributions to United Nations peacekeeping operations.
source:worldatlas
About Gurung Community:
|