“CLIMATE CRISIS IN ASIA: IMPACT, PREPAREDNESS, AND ADAPTATION CHALLENGES”
Syllabus:
- GS-3- Climate change and its impact on various stakeholders of society and nation
Focus :
- Highlights from the World Meteorological Organization’s 2023 report on climate in Asia.
- Emphasis on the region’s accelerated warming trend since 1960 and the alarming gap between climate projections and adaptation/mitigation efforts.
Toll of Extreme Heat in Asia
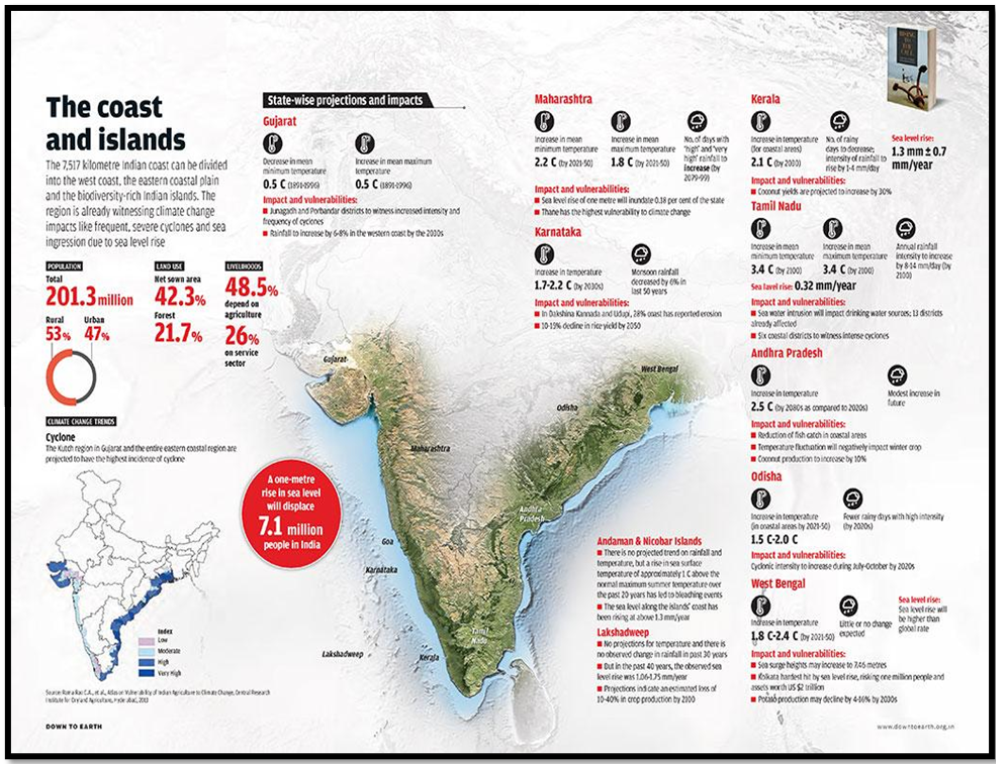
- Statistics on casualties and affected populations due to extreme heat events across Asia in 2023- More than 2,000 people were killed and more than nine million were affected by extreme climate events across Asia in 2023. More than 80% of these events were related to storms and floods
- Underreporting of heat-related mortality and specific cases in India.
Impact of Floods and Storms
- Effects of tropical cyclone Mocha in Myanmar and Bangladesh, and subsequent flooding, landslides, and lightning fatalities in India, Pakistan, and Nepal.
- Notable instances of flooding and landslides in India, particularly in Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
Early Warning Systems and Disaster Preparedness
- Definition and components of early-warning systems.
- An early-warning system is an integrated process that monitors, predicts, and forecasts hazards. It also includes activities related to risk-assessment, communications, and preparedness that allow individuals, communities, governments, businesses, etc. to take timely action to mitigate risks.
- Success stories of early-warning systems in Asia, such as Bangladesh’s response to cyclone Mocha- take anticipatory action in Cox’s Bazar, which allowed local communities to better survive its landfall.
- Analysis of the UN Office for Disaster Risk Reduction’s evaluation of early-warning systems in Asia and comparison with global averages.
Implications for India: Response and Challenges
- According to the UN Office for Disaster Risk Reduction, the average composite score for the availability of and access to multi-hazard early warning systems was 0.46 out of 1 in Asia; 0.58 for preparedness to respond; and 0.50 for observation and forecasting. To compare, the world scored 0.35, 0.78, and 0.33, respectively, on average on these counts.
- Commendation of India’s preparedness for cyclones but acknowledgment of challenges in managing lightning-related fatalities.
- Evaluation of India’s historical resilience and inadequacies in addressing new climate change challenges.
About CDRI :
|
Call for Urgent Action and Adaptation Strategies
- Perspective from Harjeet Singh, Global Engagement Director at the Fossil Fuel Treaty Initiative, on the need for strategic overhaul of policies and adaptation strategies.
- Importance of empowering communities to combat evolving climatic adversities.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question :
GS-3
“Discuss the impact of extreme climate events, such as heatwaves, floods, and storms, on Asia as highlighted in the World Meteorological Organization’s 2023 report. Evaluate the effectiveness of early-warning systems in mitigating disaster risks in the region” (250 words)