CURES, CARE, COMPETITION
Syllabus:
GS-II:
Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Why in the news?
Amended Indian patent rules raise concerns over drug affordability, accessibility, and competition, impacting healthcare accessibility and pricing.
source:mapsofindia
About the Impact of Amended Patent Rules on Drug Availability:
- Access to affordable medicines is integral to a robust healthcare system.
- High medication costs, often a result of stringent patent laws, pose challenges.
- The recent amendments to Indian patent rules have raised concerns about accessibility and pricing of drugs.
- With medication costs constituting nearly 50% of healthcare expenses, patenting plays a pivotal role in determining drug accessibility and affordability.
- The recent amendments to Indian patent rules have sparked concerns regarding their implications on healthcare, competition, and patient welfare.
| Understanding TRIPS: Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights:
● TRIPS: Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights. ● Part of the World Trade Organization (WTO) framework. ● Establishes standardised rules for global intellectual property rights. ● Covers patents, copyrights, trademarks, and trade secrets. ● Aims to balance innovation promotion with accessibility to essential goods and services. ● Sets minimum standards for IP protection and enforcement. ● Requires member countries to implement these standards in their legal sy Understanding Intellectual Property Rights (IPR): ● Definition: Protection of intangible creations and innovations. ● Legal entitlement granted to creators and inventors. ● Importance of safeguarding intellectual property. Types of Intellectual Property Rights (IPR): ➢ Copyright ○ Protects literary, artistic, and creative works. ○ Grants exclusive rights to reproduce, distribute, display, and adapt. ➢ Patents ○ Protects inventions for a specified period (usually 20 years). ○ Exclusive rights to make, use, and sell the invention ➢ Trademarks ○ Identifies goods or services of a particular business. ○ Prevents confusion among consumers. ➢ Trade Secrets ○ Safeguards valuable and confidential business information. ○ Includes formulas, processes, and technical know-how. ➢ Industrial Designs ○ Protects the visual ornamental aspects of products. ○ Covers shape, colour, texture, and aesthetics. ➢ Geographical Indications (GI) ○ Ensures product quality linked to specific geographical origin. ○ Prevents misrepresentation and protects traditional knowledge. ➢ Plant Varieties ○ Grants exclusive rights to breeders over new plant varieties. ○ Encourages innovation in agriculture and horticulture. ➢ Sui Generis Systems ○ Unique systems protecting traditional knowledge and genetic resources. ○ Specifically designed to address indigenous and local community concerns. |
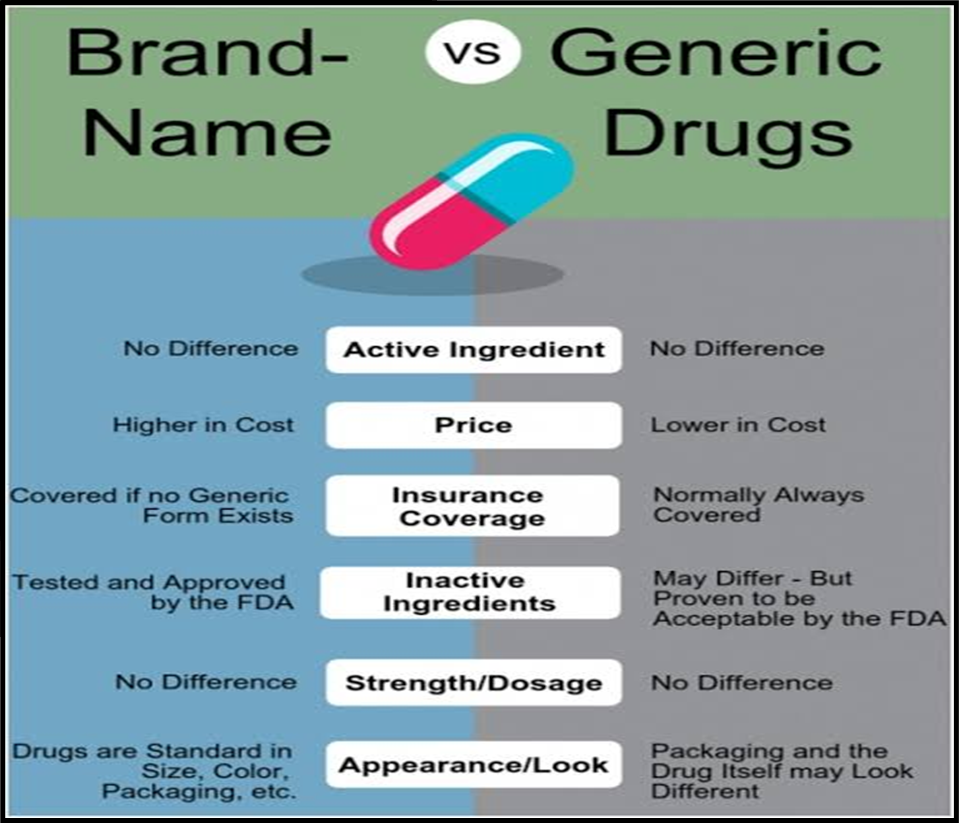
Understanding the Importance of Generic Pharmaceuticals:
- Generic drugs, provided by Indian companies, offer quality medications at affordable prices globally.
- Competition from generic pharmaceuticals has historically kept drug prices in check.
- The amended patent rules may disrupt this ecosystem, leading to increased prices and reduced accessibility.
- Role of Competition in Lowering Drug Prices:
- Competition, particularly from generic pharmaceutical companies, plays a crucial role in driving down drug prices.
- The Indian generic industry has been instrumental in providing quality medicines at affordable rates globally.
- Impact on Pre-grant Opposition:
- The recent amendments alter the dynamics of pre-grant opposition, potentially limiting the ability to challenge frivolous patents.
- While patient groups and civil society organisations have historically been active in opposing such patents, increased procedural complexities and financial burdens may discourage their participation.
- Implications for Healthcare Access:
- The amended rules could prolong the life of frivolous patents, leading to increased drug prices and reduced affordability.
- Limited competition resulting from patent monopolies can exacerbate healthcare disparities, particularly for vulnerable populations with limited financial resources.
- Historical Context:
- India’s Patent Act underwent significant changes in the early 1970s, allowing the country to emerge as a leading manufacturer and exporter of generic drugs.
- Flexibilities in patent laws allowed India to become a leading manufacturer and exporter of drugs.
- The TRIPS Agreement of 1995 mandated the reintroduction of product patents, posing challenges to India’s generic drug industry.
- These changes, which focused on process patents rather than product patents, spurred the growth of the generic industry, enabling India to supply affordable medicines globally.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Financial Burden on Patients:
- Patients and civil society organisations now face financial barriers to filing pre-grant oppositions due to imposed fees.
- This discourages opposition to unjust patents, compromising patient rights and welfare.
- Lack of Transparency:
- Changes in reporting requirements hinder transparency in patent working, affecting the issuance of compulsory licences.
- Limited access to data impedes public scrutiny of patent holders’ compliance with licensing obligations.
- Diminished Competition:
- Reduced generic competition limits market dynamics, allowing patent holders to dictate drug prices.
- This undermines efforts to ensure equitable access to essential medicines, particularly for marginalised communities.
- Concerns Regarding Frivolous Patents:
- Frivolous patents, particularly for “me-too” drugs with minimal therapeutic benefits, contribute to rising healthcare costs without significant clinical advancements.
- Opposition to such patents, facilitated by pre-grant opposition mechanisms, helps prevent monopolies and fosters competition, ultimately benefiting patients.
- Concerns Regarding Compulsory Licensing:
- Compulsory licensing, a mechanism to ensure access to essential medicines, may face challenges due to limited transparency resulting from the amended rules.
- Non-working of patents is a key criterion for issuing compulsory licences, and reduced access to patent data could impede this process.
- Challenges Posed by Amendments:
- Amendments aim to repeal Section 3(d), a crucial provision preventing frivolous patenting.
- Pre-grant oppositions, often filed by patient groups, play a vital role in challenging dubious patents.
- New rules impose financial burdens on opponents, discouraging them from contesting patents, and potentially allowing undeserving patents to pass through.
Way Forward:
- Restore Pre-Grant Oppositions:
- Reinstate provisions facilitating pre-grant oppositions to prevent the proliferation of frivolous patents.
- Ensure equitable access to patent information for all stakeholders, fostering transparency and accountability.
- Promote Generic Competition:
- Encourage a competitive market environment by supporting generic pharmaceutical companies.
- Implement measures to expedite generic drug approvals, enhancing accessibility and affordability for patients.
- Enhance Patient Advocacy:
- Provide financial assistance and legal support to patients and civil society organisations for challenging unjust patents.
Conclusion:
Amended patent rules threaten to prolong drug monopolies, increase prices, and hinder patient access to essential medications.
Upholding the principles of affordable healthcare requires a balance between patent protection and promoting generic competition.Policymakers must ensure that patent laws prioritise public health interests and foster a competitive pharmaceutical market.The recent amendments to Indian patent rules raise concerns regarding their potential impact on drug accessibility, affordability, and competition. It is imperative to strike a balance between patent protection and public health interests to ensure equitable access to essential medicines for all.
Source: Indian Express
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the implications of the recent amendments to Indian patent rules on healthcare accessibility, affordability, and competition. Evaluate the potential challenges posed by these amendments and suggest measures to ensure equitable access to essential medicines in India.