FDI POLICY FOR SPACE SECTOR
Syllabus:
- GS 3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nano-technology, bio-technology and issues relating to intellectual property rights.
Focus:
- Recently, the Union Cabinet approved amendments in the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy pertaining to the space industry.
Source: Economics Time
Alignment with Indian Space Policy 2023:
- The Indian Space Policy 2023 aims to unlock the nation’s potential in the space domain through increased private participation.
- The policy supports the involvement of non-government entities (NGEs) in space-based activities.
Recent Amendments in FDI Policy for the Space Sector:
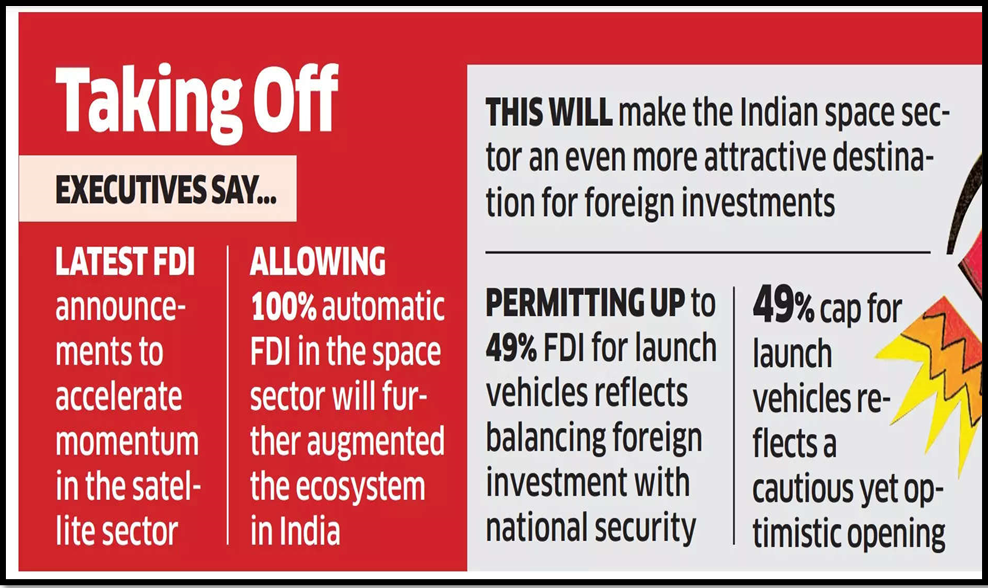
- 100% FDI Allowed: The policy permits 100% FDI in the space sector, attracting potential investors to Indian space companies.
- Liberalized Entry Routes:
-
- Up to 74% under Automatic Route: Applies to activities such as satellites manufacturing & operation, satellite data products, and ground and user segments. Beyond 74%, the government route applies.
-
- Up to 49% under Automatic Route: Applies to activities related to launch vehicles, associated systems or subsystems, and creation of spaceports. Beyond 49%, the government route applies.
-
- Up to 100% under Automatic Route: Allowed for the manufacturing of components and systems/sub-systems for satellites, ground segments, and user segments.
Major Developments in the Space Sector in India:
|
Key Features of Indian Space Policy 2023:
- Transition of ISRO’s Role: ISRO shifts focus from manufacturing operational space systems to R&D in advanced technologies.
- Encouraging Private Participation:
-
- NGEs can offer national and international space-based communication services through self-owned, procured, or leased satellite systems.
-
- NGEs encouraged to manufacture and operate space transportation systems, including launch vehicles, shuttles, and develop reusable and reconfigurable technologies and systems.
-
- NGEs allowed to engage in the commercial recovery of asteroid resources or space resources and sell them as per laws.
- Industry Collaboration and Commercialization:
-
- Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) promotes, guides, and authorizes space activities autonomously.
-
- NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) is responsible for commercializing space technologies, platforms, and servicing space-based needs on commercial principles.
Understanding Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):
- Definition: FDI involves investment by a foreign entity into a business or corporation in another country, including equity instruments or a controlling ownership stake in a business.
- FDI in India:
-
- Total FDI inflows in India for FY 22-23 amounted to USD 70.97 billion.
-
- The United States was the largest source of FDI in India in 2022-23, followed by Mauritius, the UK, and Singapore.
-
- Market value of FDI in India increased by 6.9% in rupee terms in 2022-23, mainly due to the rise in FDI in unlisted companies.
- FDI Routes in India:
-
- Automatic Route: Non-resident investors or Indian companies do not need government approval for investment.
-
- Government Route: Approval from the Government of India is required before investment.
- FDI Prohibited Sectors in India:
-
- Includes gambling and betting, chit funds, real estate business, manufacturing of tobacco products, and trading in transferable development rights (TDR).
-
- Some sectors, such as atomic energy and railway operations, remain closed to private sector investment except for specific permitted activities under the Consolidated FDI policy
Implications of Eased FDI for the Space Sector
- Enhancing Technological Capabilities: Discuss how increased FDI can lead to advancements in technology through partnerships and collaborations with foreign entities.
- Boost to Private Sector and Startups: Highlight how the policy change is likely to stimulate the private sector, including startups in the space industry.
- Infrastructure Development: Explain the potential impacts on infrastructure development within the space sector, such as the construction of new facilities and development of existing ones.
Economic Impact
- Investment Inflow: Discuss the potential increase in investment inflows and its impact on the overall economic health of the country.
- Job Creation: Highlight how fostering the space sector through FDI can lead to job creation and skill development.
- Contribution to Global Space Economy: Analyze India’s potential contribution to the global space economy with these new changes.
Challenges and Considerations
- Regulatory Challenges: Delve into the regulatory challenges that might arise with an increase in FDI, including concerns about national security and technology transfer.
- Market Competition: Discuss the competitive pressures that Indian companies might face from established foreign players and how it could affect the market.
- Sustainability Concerns: Touch on the environmental and sustainability concerns related to expanding space activities and how they could be mitigated.
Case Studies and Examples
- International Comparisons: Provide examples from other countries with liberal FDI policies in their space sectors, and the outcomes of such policies.
- Successful Foreign Investments in India: Cite successful examples of foreign investments in other sectors that could serve as a model for space sector investments.
Offer insights into the long-term impacts of the eased FDI policy on India’s stature as a space-faring nation. Suggest further policy improvements or initiatives that could support the sustainable growth of India’s space sector.
Source:The Hindu
Mains Practice Question:
“Discuss the recent amendments in the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy for the space sector in India. Analyze how these changes align with the Indian Space Policy 2023 and the potential impact on the growth and development of the country’s space industry. Evaluate the role of private participation and FDI in the advancements of the space sector in India.”
Associated Articles:
https://universalinstitutions.com/govt-approves-100-fdi-in-space-sector/