THE ADVENT OF A HOLISTIC APPROACH TO ONE HEALTH
Syllabus:
GS-II:
Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Why in the news?
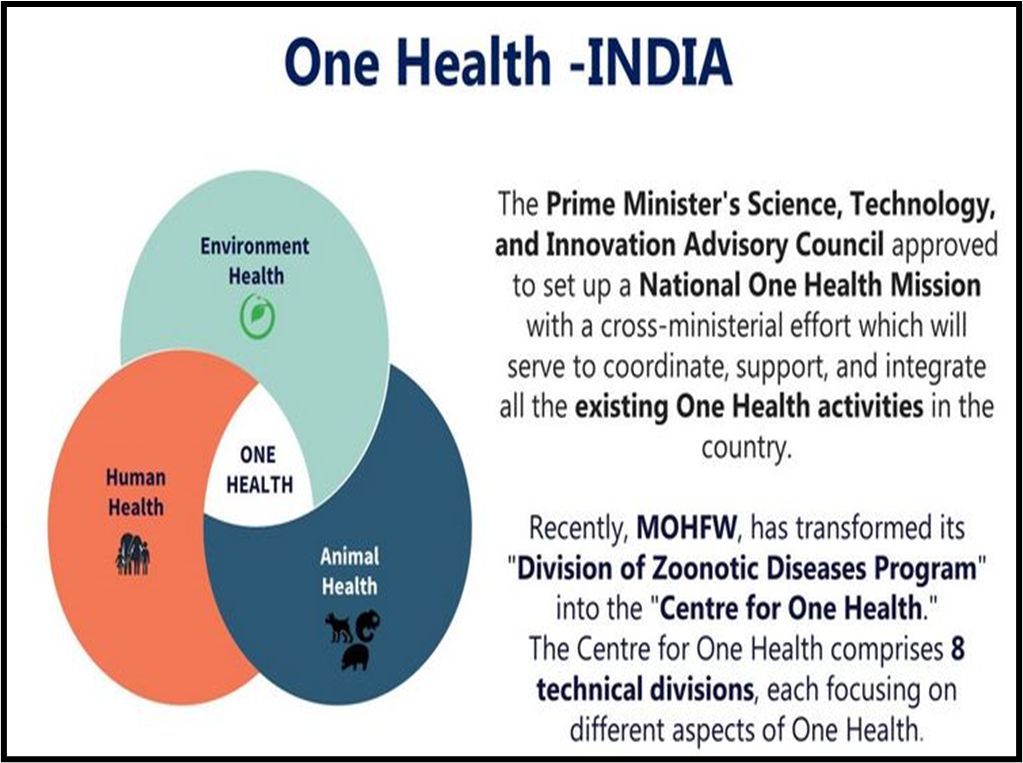
The “National One Health Mission” aims to address interdependence of humans, animals, and environment for pandemic preparedness.
Source:scrib
About Embracing a Holistic Approach to One Health:
- The interconnectedness of humans, animals, and the environment is increasingly evident, particularly with the rise of pandemics like COVID-19.
- The impact of pandemics extends beyond humans to include livestock, as seen with outbreaks such as lumpy skin disease.
- The decision on the ‘National One Health Mission’ by the cabinet represents a significant milestone, emphasising a holistic approach to pandemic preparedness.
What is One Health Concept ?
One Health issues encompass various interconnected concerns:
What is One Health Joint Plan of Action?
The One Health Joint Plan of Action focuses on:
What are Zoonotic diseases?
|
About the Importance of the One Health Concept :
- Human Expansion: As human populations grow and expand into new areas, close contact with animals and their environments increases, providing more opportunities for diseases to pass between animals and humans.
- Zoonotic Diseases: Over 65% of contagious diseases affecting humans originate from animals, highlighting the importance of understanding and addressing zoonotic diseases.
- Environmental Disruptions: Disruptions in environmental conditions and habitats can create new opportunities for diseases to spread among animals, further emphasising the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health.
- International Travel & Trade: The movement of people, animals, and animal products through international travel and trade has accelerated, leading to the rapid spread of diseases across borders and globally.
- Viruses in Wildlife: Scientists have identified millions of viruses circulating in wildlife, many of which have the potential to infect humans. Timely detection and response are crucial to prevent the emergence of new pandemics.
Understanding the National One Health Mission:
- Endorsement:
- PM-STIAC endorsement in July 2022.
- Collaboration: Involvement of 13 Ministries and Departments.
- Institute Establishment: Plans for National Institute for One Health in Nagpur.
- Goals of the Mission
- Integrated Surveillance: Develop strategies for integrated disease surveillance.
- Information Sharing: Ensure seamless information sharing for disease control.
- Animal Health Focus: Highlight the importance of diseases affecting animals.
- Importance of R&D
- Emerging Diseases: Emphasis on R&D for vaccines, therapeutics, diagnostics.
- Collaborative Efforts: Collaboration among government, academia, private sector.
- Coordination: Recognizes the importance of central-state coordination.
- Network of Laboratories
- Laboratory Creation: Establish a national network of high-risk pathogen laboratories.
- Integration: Integration of laboratories for better resource utilisation.
- Enhanced Capabilities: Focus on augmenting epidemiology and data analytics with AI and machine learning.
Global Collaboration:
- ‘One Health’ is a global topic highlighted during India’s presidency of the G-20, endorsed by all members for collaborative action.
- Focus extends beyond diseases to encompass antimicrobial resistance, food safety, plant diseases, and the impact of climate change.
- Emphasises the need for engagement from governmental agencies, non-governmental organisations, academia, the private sector, and citizens.
Way Forward for One Health Implementation:
- Learnings from COVID-19: Recognize the significance of One Health principles in managing infectious diseases, particularly zoonotic ones.
- Scaling Up: India should expand the One Health model nationwide and establish robust research collaborations globally.
- Guideline Development: Develop best-practice guidelines for informal markets and slaughterhouses to ensure effective disease control measures.
- Operationalization: Implement One Health strategies at all levels, including villages, through practical mechanisms and interventions.
- Awareness and Investment: Increase awareness about One Health principles and secure higher investments to achieve One Health targets effectively.
Conclusion:
India’s adoption of the One Health approach signifies its dedication to holistic well-being. By acknowledging the interconnectedness of humans, animals, plants, and the environment, India is establishing a foundation for comprehensive health strategies. Through ongoing initiatives and a vision to integrate resources and expertise seamlessly, India seeks to revolutionise its health landscape. This endeavour aims to enhance resilience against emerging challenges through a unified and holistic approach.
Source:
Mains Practice Question:
“Discuss the significance of the ‘National One Health Mission’ in India’s healthcare management and pandemic preparedness, emphasising its holistic approach and the collaborative efforts involved.”