UNDERSTANDING YOUTH SUICIDE IN INDIA:
A COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS
Syllabus:
- GS 1 : Population and Associated Issues
- GS 2 : Government Policies and interventions
Why in News?
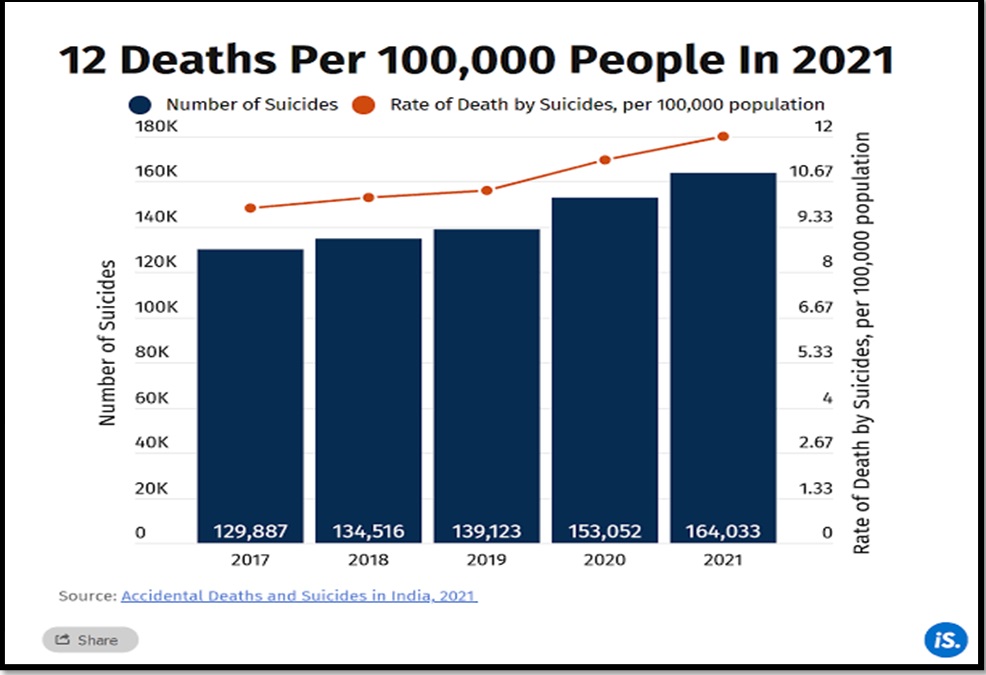
- The article highlights the alarming rise in suicide rates in India, with the country recording the highest number of suicides globally.
- The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) reported a staggering 1.71 lakh suicides in 2022, marking an all-time high.
Source: Scroll
Alarming Suicide Rates
- Disturbing Statistics: India is confronted with the distressing reality of having the highest suicide rates globally.
- Record High: The NCRB’s 2022 data highlights a concerning figure of 1.71 lakh suicides, marking an all-time high.
- Critical Crisis: The suicide rate has surged to 12.4 per 1,00,000 individuals, signaling a critical public health crisis.
- Youth Impact: Young individuals below 30 years constitute a significant portion, accounting for 41% of all suicide cases.
- Women Affected: Suicide stands as the primary cause of mortality among young Indian women.
- Urgent Concern: Shockingly, every eight minutes, a young Indian succumbs to suicide, emphasizing the urgency of addressing this issue.
About National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB)
Key Initiatives and Responsibilities:
Additional Functions:
|
Suicide Determinants:
- Multifaceted Issue: Suicide is a multifaceted issue influenced by various factors, including biological, psychological, familial, and societal aspects.
- Mental Health: Mental health challenges are prevalent risk factors among Indian adolescents, with 54% citing them as a reason for suicidal tendencies.
- Family Conflicts: Family conflicts and negative familial experiences contribute to 36% of youth suicides.
- Academic Pressures: Academic pressures, stemming from a competitive education system, are responsible for 23% of suicides.
- Social Challenges: Social challenges, including violence and discrimination, impact 20% of young individuals.
- Economic & Relationship Issues: Economic distress and relationship issues also play a role, accounting for 9.1% and 9% of youth suicides respectively.
Impacts of Technology and Media
- Technological Influence: The rise of technology and media has significantly impacted the mental well-being of the youth.
- Internet Addiction: A meta-analysis from 19 Indian states revealed that nearly 20% of college students are addicted to the internet.
- Cyberbullying: Cyberbullying is rampant, affecting one-third of young individuals, with a third of this subset exhibiting suicidal tendencies.
- Social Media Usage: Excessive social media usage, over two hours daily, correlates with increased suicidal ideation among teens.
- Media Sensationalism: Sensationalized media coverage, especially of celebrity suicides, has been linked to spikes in suicidal behaviors.
- Search Surges: Following a prominent actor’s suicide, there was a notable surge in online searches related to “how to commit suicide.”
Charting a Path Forward: Solutions and Strategies
- Prevention Potential: Despite prevalent beliefs, suicides can be prevented through proactive measures and interventions.
- Youth Skills: Equipping youth with problem-solving, impulse control, and emotional regulation skills is crucial.
- Early Detection: Early detection of mental health issues and provision of youth-friendly support services can be life-saving.
- Holistic Wellness: Adopting a holistic wellness approach, including physical activity, balanced nutrition, and digital well-being, promotes mental health.
- Systemic Challenges: Addressing systemic challenges like domestic violence, economic disparities, and discrimination is vital for sustainable prevention.
- Educational Reforms: Educational reforms emphasizing reduced academic stress and mental health education are essential.
The National Suicide Prevention Strategy: A Unified Approach
- Task Force Initiative: The establishment of a task force in 2019 marked a significant stride towards a cohesive national strategy.
- 2030 Objective: The strategy aims to reduce suicide rates by 10% by 2030, emphasizing collaboration across various ministries.
- Role of Institutions: Educational institutions and youth organizations are pivotal in promoting mental health and reducing addictive behaviours.
- Implementation Steps: Immediate actions include the widespread dissemination of the strategy, ensuring adequate budgetary allocations, and grassroots-level implementation.
- Community Engagement: Leveraging community engagement and inter-ministerial collaboration are central to the strategy’s success.
- Grassroots Implementation: Implementation of the strategy at the state, district, and community levels is crucial for effective suicide prevention.
Conclusion
Addressing the youth suicide epidemic in India requires a comprehensive, multi-pronged approach involving various stakeholders. By fostering resilience, promoting mental well-being, and addressing systemic challenges, India can mitigate the youth suicide crisis and pave the way for a brighter future.
Source:
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the factors contributing to the rising suicide rates among youth in India. Examine the strategies proposed to address this critical public health issue, highlighting the role of multi-sectoral collaboration and community engagement in suicide prevention.
Associated Articles: