THE CHANGING TREND OF WOMEN EMPLOYMENT
Syllabus:
- GS-3- Issue of Unemployment ,Women empowerment and related issues
Focus :
- The India Employment Report for 2024 was recently released by the Institute for Human Development and the International Labour Organization.
- The report highlights improvements in key labor market indicators in recent years, particularly in the context of economic distress and the COVID-19 pandemic.
Source- ILO
Trends in Labor Market Indicators:
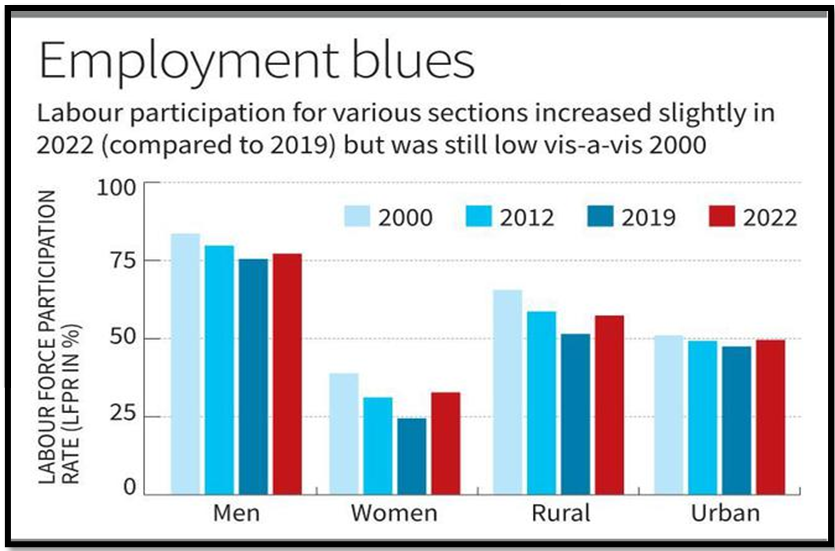
- The Labor Force Participation Rate (LFPR), Workforce Participation Rate (WPR), and Unemployment Rate (UR) experienced a long-term deterioration between 2000 and 2019.
- However, these indicators showed improvement thereafter, except for two peak pandemic quarters.
About ILO:
|
Women’s Participation in the Labor Force:
- Female LFPR remains significantly lower compared to males, with the male LFPR at 78.5 and the female LFPR at 37 in 2023.
- Despite a modest increase in recent years, female LFPR had been steadily declining since 2000, reaching 24.5 in 2019.
- Most of the increase in labor force participation among women occurred in rural areas and in self-employment, often characterized by unpaid work.
| Related Terms :
LFPR-LFPR is the percentage of the working-age population (aged 15 years and above) that is either employed or unemployed, but willing and looking for employment. |
Factors Contributing to Women’s Low Participation:
- Women face various barriers in accessing employment opportunities, including caregiving responsibilities, low wages, patriarchal mindsets, and safety concerns.
- The decline in women’s LFPR can be attributed to both supply and demand-side factors, including limited job opportunities, social norms restricting women’s mobility, and concerns over safety and transportation.
Insights from Economic Research:
- Research by Claudia Goldin, the 2023 Economics Nobel Laureate, emphasizes the influence of factors such as family responsibilities, education decisions, technical innovations, laws, and norms on female labor supply and demand.
- Goldin’s findings highlight the persistent challenge of balancing paid work with family responsibilities, limiting women’s choices in the labor market.
Policy Interventions for Change:
- Economists advocate for interventions addressing both demand and supply-side factors in the labor market.
- Policies promoting labor-intensive sectors, public investment in safety and transportation infrastructure, and affordable childcare and elderly care services are crucial to enabling women to participate more actively in the workforce.
Conclusion:
- The India Employment Report underscores the need for targeted interventions to address the persistent challenges hindering women’s participation in the labor force.
- By tackling both supply and demand-side barriers, policymakers can create a more conducive environment for women to access employment opportunities and contribute effectively to the economy.
Source:THE HINDU
Mains Practice Question :
GS-3
“Discuss the findings of the India Employment Report 2024, released by the Institute for Human Development and the International Labour Organization, focusing on the trends in key labor market indicators and the challenges and barriers faced by women in accessing employment.”(250 words)