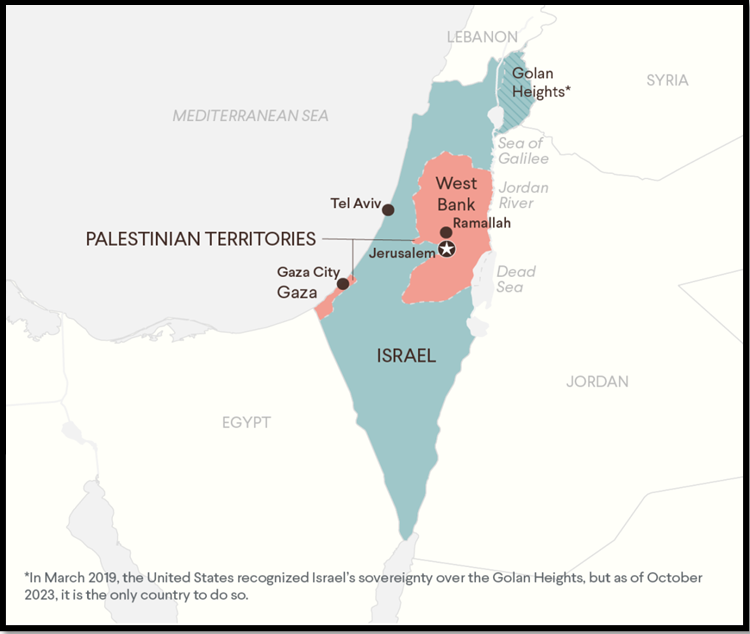
THE GAZA WAR NEEDS A SMART EXIT STRATEGY
Syllabus:
GS-1:
- World History -Gaza, Israel, Palestine issue
GS 2:
- Role of international agencies in resolving conflict , Humanitarian crisis , Superpower hegemony of US.
Focus :
- Gaza is an unwinnable conflict and Israel and Palestine, bound by geography and destiny, will need to search for major climb-downs.
Source- BBC
UNSC Resolution and Reactions
- On March 25, 2024, the UN Security Council (UNSC) passed a resolution urging an immediate ceasefire in Gaza during Ramadan and demanded the unconditional release of all hostages.
- This marked the UNSC’s first successful ceasefire resolution since the war in Gaza following Hamas’s terror attack in southern Israel last October.
- The U.S., which had previously vetoed four UNSC resolutions on this issue, chose to abstain this time, allowing the resolution to pass.
Mixed Reactions
- Israel’s Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu criticized the U.S., accusing it of abandoning its UN policy and undermining efforts to release Israeli hostages held by Hamas.
- Under Israeli pressure, the U.S. later declared the UN resolution as ‘non-binding’, permitting Israel to continue its actions in Gaza.
Hamas’s Stance
- Initially, Hamas welcomed the ceasefire resolution but later reiterated its demand for a permanent ceasefire and a complete withdrawal of Israeli forces from Gaza.
- The initial optimism for a swift ceasefire quickly dissipated, returning the situation to square one.
Current Situation and External Mediation
- With uncertainty surrounding the implementation of the ceasefire, attention has shifted back to the joint efforts of Egypt and Qatar, who have been negotiating independently for an early end to hostilities.
- Hezbollah increased missile strikes into Northern Israel, causing damage to key military assets and casualties.
- The conflict has resulted in over 32,000 deaths in Gaza, and tensions are further heightened by Israel’s strike on the Iranian Consulate in Syria.
Assessing War Objectives
- Israel’s stated objectives when launching its offensive were to flatten Gaza, eliminate Hamas, and secure the release of its hostages.
- Israel has significantly damaged Gaza, rendering parts of it uninhabitable for years. Additionally, a one-kilometer wide stretch along the Gaza border has been flattened to create a buffer zone.
- Estimates suggest that only 30% of Hamas fighters have been eliminated, and their fighting capability remains largely intact.
- Israel has failed to rescue its hostages, with around 32 reported deaths during the conflict, leading to public outcry against Netanyahu.
- Hamas aimed to remind the world of the Palestinian cause and expose the perceived invincibility of the Israeli military.
- While they might not have sought a military victory, they achieved their goals of making their voice heard.
The U.S. is turning into an enabler of Israel’s atrocities in Gaza
- S. Historical Tolerance: Historically, the U.S. has shown high tolerance levels towards Israel’s military actions, overlooking accusations of war crimes and ignoring UN report.
- Biden’s Policy: Joe Biden’s policy towards Israel’s recent war is criticized as a new low, with the U.S. abstaining from a UN Security Council resolution demanding a ceasefire.
- Lack of Enforcement: Despite the resolution, the U.S. took no action to enforce it, allowing Israel to continue military sales and potential invasions.
- Historical U.S. Pressure: Past U.S. presidents used hard pressure tactics to influence Israel’s decisions, such as threats to cut off aid or withhold military sales.
- Biden’s Support: Despite domestic and international criticism, Biden continues to support Israel, even amidst one of history’s worst massacres of Palestinians.
- Humanitarian Crisis: The UN warns of a famine in Gaza, with the Biden administration admitting to widespread hunger and ongoing violence causing casualties.
- Call for Action: Biden’s administration is urged to act as a statesman, calling for an immediate ceasefire, increased aid to Gaza, and halting arms supplies to Israel if the war persists.
Comparative Analysis
- Wars often end due to stalemates or international pressure rather than achieving clear military and political objectives.
- The S. wars in Afghanistan and Iraq serve as examples of prolonged conflicts without well-defined exit strategies.
Impact on Israel
- Israel faces military, economic, and political repercussions due to the prolonged conflict.
- The Israeli army has suffered losses, the economy is contracting, and Netanyahu’s position is becoming increasingly untenable both domestically and internationally.
- The U.S., traditionally a staunch ally, has indicated that Israel needs to exercise restraint and cannot expect unconditional support for its actions in Gaza.
| About GAZA STRIP :
· The Gaza Strip is surrounded by Israel to the north and east and Egypt to the southwest. · It is located in the eastern Mediterranean basin. The Mediterranean Sea borders it to the west. · With more than two million people residing in a small area, it is among the most densely populated places on Earth. · Scholars, activists, and journalists have all used the phrase “open air prison” to describe Gaza’s situation. HAMAS : · Founded in 1987, Hamas is an armed political organization based in Palestine. · This is a violent organization that started out as a movement of resistance against Israeli occupation. · Ideology: Hamas holds that no portion of Palestine’s territory should be given up or compromised.Any alternative to Palestine’s total freedom is rejected by Hamas. |
The Way Forward
- Israel needs to formulate a clear and achievable end goal, acknowledging that militarily defeating Gaza while eliminating Hamas entirely is improbable.
- An early ceasefire, withdrawal of forces, and the establishment of a surveillance buffer zone along the Gaza border could be viable options.
- A prisoner exchange agreement could be reached if Israel agrees to the above conditions.
- For a sustainable two-state solution, both Israel and Palestine must reconsider their positions and make significant compromises.
Conclusion
- The conflict in Gaza has reached an impasse, necessitating a strategic exit strategy that ensures a sustainable and peaceful future for both Israelis and Palestinians. It is imperative for all parties involved to negotiate a face-saving solution to this unwinnable war.
Source:The Hindu
Associated links :
- https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/the-gaza-war-needs-a-smart-exit-strategy/article68020974.ece
- https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/editorial/a-new-low-on-israels-gaza-war-and-the-us-response/article68020294.ece
Mains Practice Question :
GS-2
“Evaluate the role of the United States in the Israel-Palestine conflict, particularly in light of its commitment to human rights, and propose potential actions for the Biden administration to mitigate the ongoing violence.” (250 words)